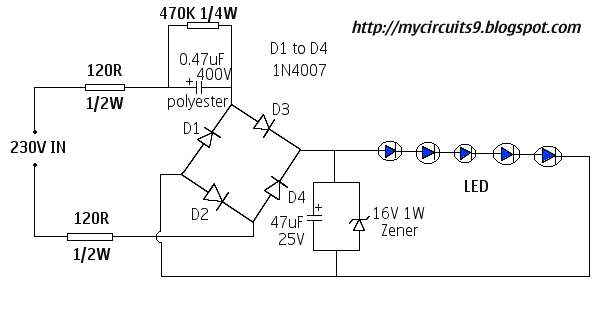
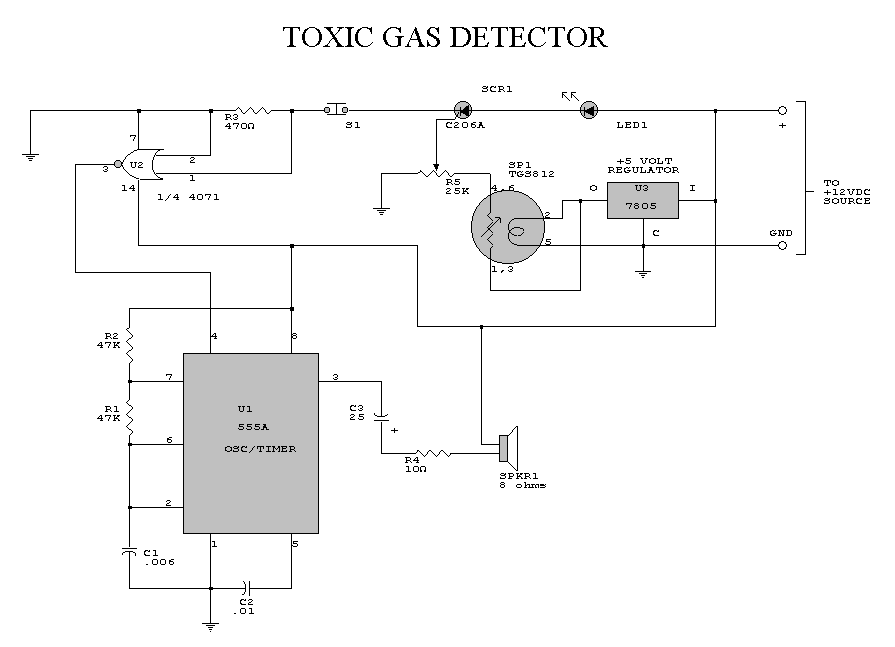
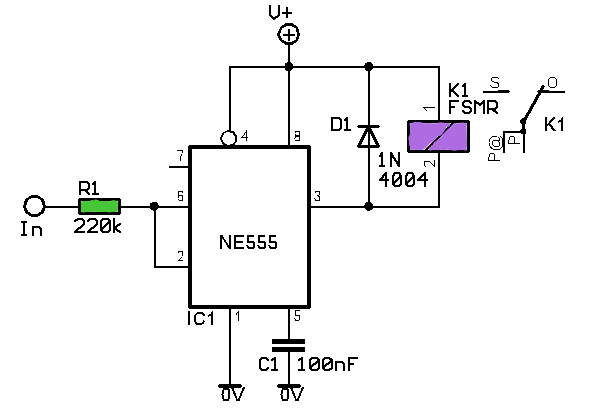
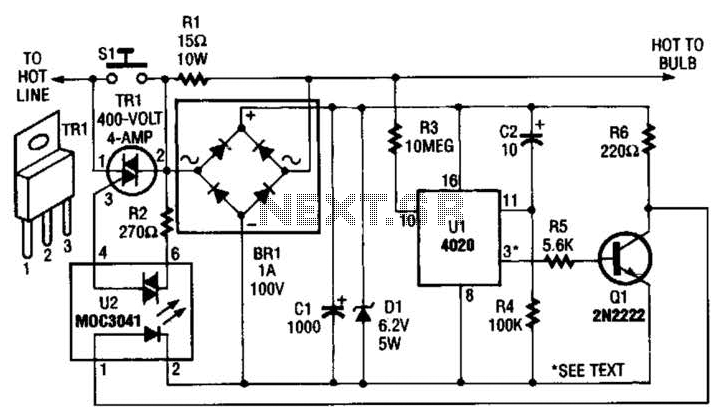
Voltage controlled gain amplifier circuit diagram
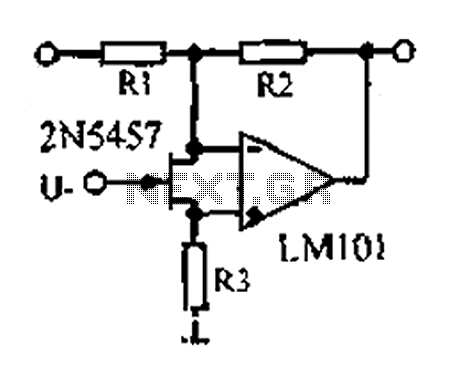
A 1.53 voltage-controlled gain amplifier (VGA) utilizes a FET connected between the two inputs of the operational amplifier (op-amp) as a voltage-controlled resistance. The resistance changes linearly with voltage and varies from several dozen square ohms, exhibiting excellent control characteristics. Each resistance value is dependent on the op-amp used in the circuit.
The voltage-controlled gain amplifier operates by modulating the resistance of the FET based on an input voltage signal. This configuration allows for precise control of the gain of the amplifier, making it suitable for applications requiring variable amplification levels. The FET, acting as a voltage-controlled resistor, provides a linear relationship between the control voltage and the resistance, ensuring predictable performance across a range of input conditions.
The circuit typically comprises an op-amp configured in a non-inverting or inverting configuration, depending on the desired gain characteristics. The FET's source and drain terminals are connected to the op-amp inputs, while the gate terminal receives the control voltage. As the control voltage varies, the resistance of the FET alters, thereby changing the gain of the op-amp circuit in a linear fashion.
The performance of the VGA can be further enhanced by selecting appropriate op-amps and FETs that exhibit low distortion and high linearity. Additionally, feedback networks can be incorporated to stabilize the gain and improve bandwidth. Such configurations are widely used in audio processing, instrumentation, and communication systems, where adjustable gain is essential for signal integrity and processing efficiency.
Overall, the design and implementation of a voltage-controlled gain amplifier using a FET as a variable resistor provide an effective means of achieving dynamic control over amplification, making it a valuable component in various electronic applications.1.53 voltage controlled gain amplifier FET connected between the two inputs to the op amp as voltage-controlled resistance, resistance changes linearly with voltage, varies fro m several dozen square, with excellent control characteristics. Each of the resistance depends on the op amp.
The voltage-controlled gain amplifier operates by modulating the resistance of the FET based on an input voltage signal. This configuration allows for precise control of the gain of the amplifier, making it suitable for applications requiring variable amplification levels. The FET, acting as a voltage-controlled resistor, provides a linear relationship between the control voltage and the resistance, ensuring predictable performance across a range of input conditions.
The circuit typically comprises an op-amp configured in a non-inverting or inverting configuration, depending on the desired gain characteristics. The FET's source and drain terminals are connected to the op-amp inputs, while the gate terminal receives the control voltage. As the control voltage varies, the resistance of the FET alters, thereby changing the gain of the op-amp circuit in a linear fashion.
The performance of the VGA can be further enhanced by selecting appropriate op-amps and FETs that exhibit low distortion and high linearity. Additionally, feedback networks can be incorporated to stabilize the gain and improve bandwidth. Such configurations are widely used in audio processing, instrumentation, and communication systems, where adjustable gain is essential for signal integrity and processing efficiency.
Overall, the design and implementation of a voltage-controlled gain amplifier using a FET as a variable resistor provide an effective means of achieving dynamic control over amplification, making it a valuable component in various electronic applications.1.53 voltage controlled gain amplifier FET connected between the two inputs to the op amp as voltage-controlled resistance, resistance changes linearly with voltage, varies fro m several dozen square, with excellent control characteristics. Each of the resistance depends on the op amp.