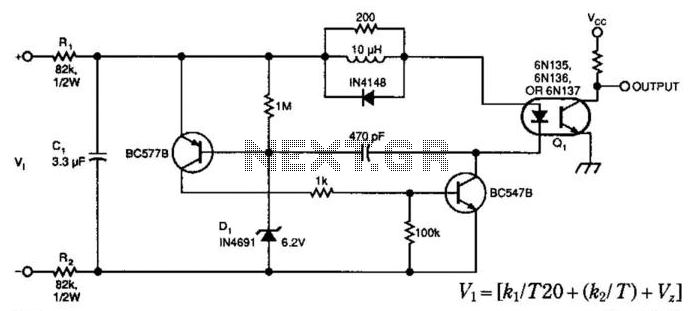
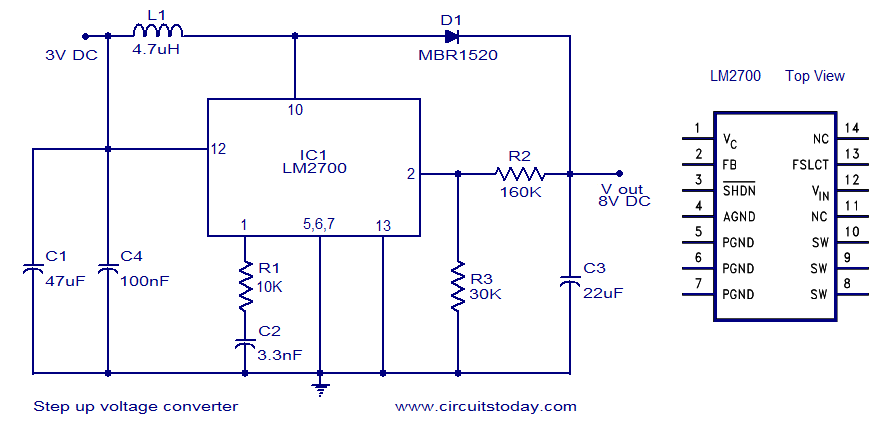
VOLTAGE TO CURRENT CONVERTER
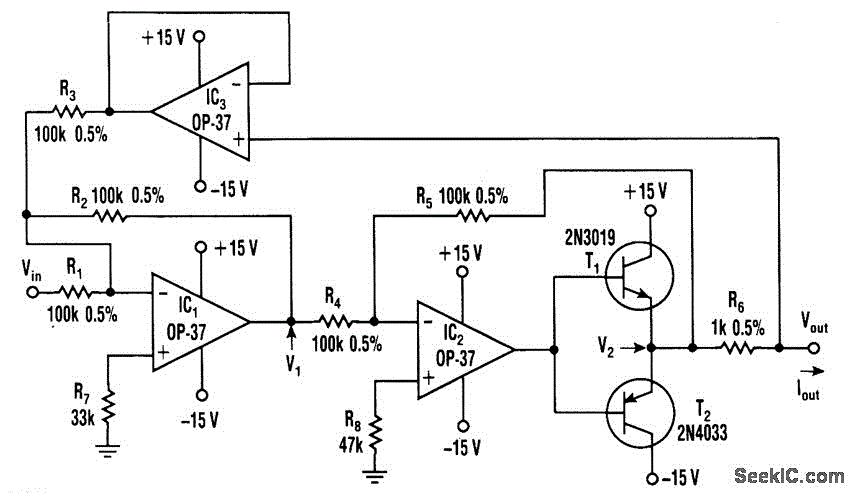
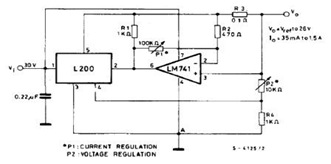
This voltage-to-current converter utilizes three operational amplifiers to control a pair of power transistors. The output current is determined by the formula: IOUT = Vin/R6. The output resistance exceeds 50 MΩ, and the output current can vary from 1 mA up to the current ratings of transistors T1 and T2.
The voltage-to-current converter circuit employs three operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured to provide precise control over the output current. The primary function of this circuit is to convert an input voltage (Vin) into a proportional output current (IOUT) based on the resistance value of R6. The relationship between the input voltage and output current is defined by the equation IOUT = Vin/R6, where R6 serves as a critical component in setting the current output.
In this configuration, the first op-amp is typically used for voltage amplification, ensuring that the input signal is adequately processed. The second op-amp may be configured as a differential amplifier to enhance the accuracy of the output current, while the third op-amp is employed as a buffer to drive the power transistors (T1 and T2) effectively. This arrangement allows for improved linearity and stability of the output current across varying load conditions.
The output resistance of the circuit is exceptionally high, exceeding 50 MΩ, which is advantageous for applications requiring minimal loading on the input source. The ability to adjust the output current from a minimum of 1 mA to the maximum ratings of the power transistors (T1 and T2) makes this converter suitable for a wide range of applications, including signal processing and driving high-impedance loads.
In summary, this voltage-to-current converter design offers a robust solution for converting voltage signals into precise current outputs, leveraging the capabilities of multiple operational amplifiers and power transistors to achieve high performance and adaptability in various electronic applications.This voltage to current converter uses three op amps to drive a pair of power transistors. The current output is calculated as: IOUT=Vin/R6 Output resistance is over 50 M?. IOUT can range from 1 mA to the current ratings of T1 and T2.. 🔗 External reference
The voltage-to-current converter circuit employs three operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured to provide precise control over the output current. The primary function of this circuit is to convert an input voltage (Vin) into a proportional output current (IOUT) based on the resistance value of R6. The relationship between the input voltage and output current is defined by the equation IOUT = Vin/R6, where R6 serves as a critical component in setting the current output.
In this configuration, the first op-amp is typically used for voltage amplification, ensuring that the input signal is adequately processed. The second op-amp may be configured as a differential amplifier to enhance the accuracy of the output current, while the third op-amp is employed as a buffer to drive the power transistors (T1 and T2) effectively. This arrangement allows for improved linearity and stability of the output current across varying load conditions.
The output resistance of the circuit is exceptionally high, exceeding 50 MΩ, which is advantageous for applications requiring minimal loading on the input source. The ability to adjust the output current from a minimum of 1 mA to the maximum ratings of the power transistors (T1 and T2) makes this converter suitable for a wide range of applications, including signal processing and driving high-impedance loads.
In summary, this voltage-to-current converter design offers a robust solution for converting voltage signals into precise current outputs, leveraging the capabilities of multiple operational amplifiers and power transistors to achieve high performance and adaptability in various electronic applications.This voltage to current converter uses three op amps to drive a pair of power transistors. The current output is calculated as: IOUT=Vin/R6 Output resistance is over 50 M?. IOUT can range from 1 mA to the current ratings of T1 and T2.. 🔗 External reference