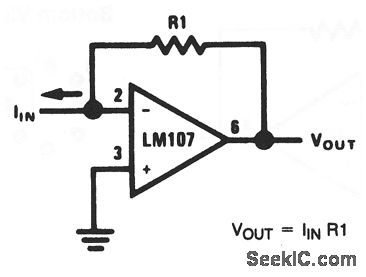
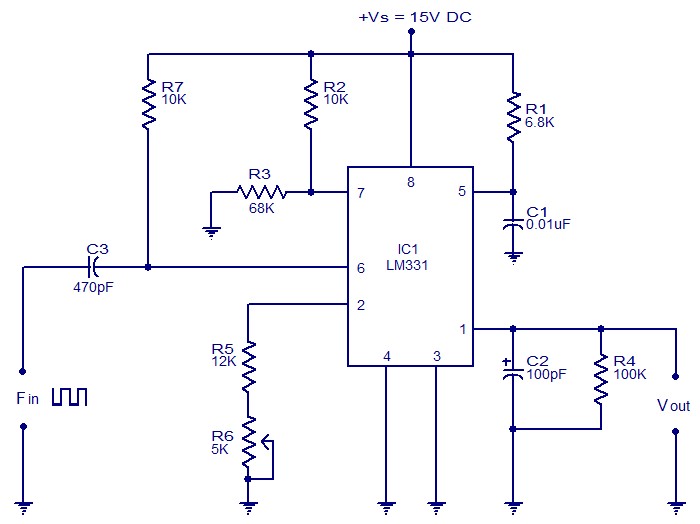
Voltage-to-pulse duration converter

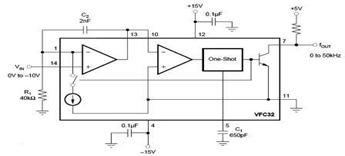
Accuracies better than 1% can be achieved with this circuit (a), and the output signals (b) maintain the original frequency, regardless of the input voltage. Voltage levels can be transformed into pulse durations by integrating an operational amplifier (op amp) with a timer integrated circuit (IC).
This circuit utilizes an operational amplifier to amplify input voltage levels, which are then processed by a timer IC to generate corresponding pulse durations. The op amp serves as a voltage comparator, where it compares the input voltage against a reference voltage. When the input exceeds the reference level, the op amp output switches states, creating a pulse.
The timer IC, such as the 555 timer, can be configured in monostable mode to produce a single output pulse of a specified duration when triggered by the op amp's output. This duration can be adjusted by varying the resistor and capacitor values connected to the timer, allowing for precise control over the pulse width in relation to the input voltage.
The design ensures that the output frequency remains constant, irrespective of variations in the input voltage, which is crucial for applications requiring stable signal processing. The overall accuracy of the system, exceeding 1%, is achieved through careful selection of components and calibration of the circuit to minimize errors from drift and noise.
This circuit can be employed in various applications, including analog-to-digital conversion, signal conditioning, and timing applications, where accurate pulse generation is essential. The combination of the op amp and timer IC provides a versatile solution for converting voltage levels into precise pulse durations while maintaining signal integrity. Accuracies to better than 1% can be obtained with this circuit (a), and the output signals (b) still retain the original frequency, independent of the input voltage. Voltage levels can be converted to pulse durations by combining an op amp and a timer IC. 🔗 External reference
This circuit utilizes an operational amplifier to amplify input voltage levels, which are then processed by a timer IC to generate corresponding pulse durations. The op amp serves as a voltage comparator, where it compares the input voltage against a reference voltage. When the input exceeds the reference level, the op amp output switches states, creating a pulse.
The timer IC, such as the 555 timer, can be configured in monostable mode to produce a single output pulse of a specified duration when triggered by the op amp's output. This duration can be adjusted by varying the resistor and capacitor values connected to the timer, allowing for precise control over the pulse width in relation to the input voltage.
The design ensures that the output frequency remains constant, irrespective of variations in the input voltage, which is crucial for applications requiring stable signal processing. The overall accuracy of the system, exceeding 1%, is achieved through careful selection of components and calibration of the circuit to minimize errors from drift and noise.
This circuit can be employed in various applications, including analog-to-digital conversion, signal conditioning, and timing applications, where accurate pulse generation is essential. The combination of the op amp and timer IC provides a versatile solution for converting voltage levels into precise pulse durations while maintaining signal integrity. Accuracies to better than 1% can be obtained with this circuit (a), and the output signals (b) still retain the original frequency, independent of the input voltage. Voltage levels can be converted to pulse durations by combining an op amp and a timer IC. 🔗 External reference