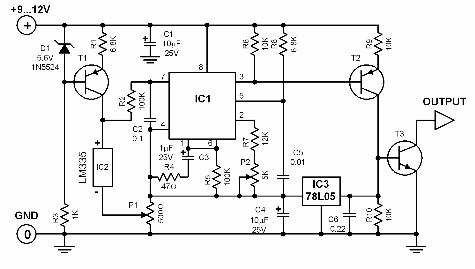
Voltage-to-Pulse Duration Converter
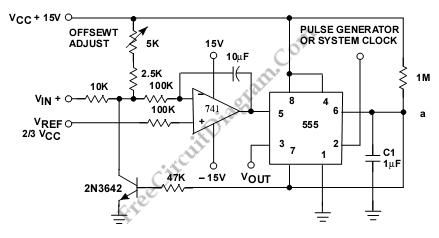
This is a circuit for a Voltage-to-Pulse Duration Converter. The circuit is designed to convert voltage into pulse duration by integrating a timer IC and an operational amplifier (OP Amp).
The Voltage-to-Pulse Duration Converter circuit utilizes a timer IC, typically the 555 timer, configured in monostable mode. In this configuration, the timer generates a pulse of a specified duration in response to a triggering voltage input. The duration of the output pulse is determined by the resistor and capacitor values connected to the timer.
An operational amplifier is employed to condition the input voltage signal. The OP Amp can be configured as a comparator to compare the input voltage against a reference voltage. When the input voltage exceeds the reference level, the OP Amp output triggers the timer IC, initiating the pulse generation.
In designing the circuit, it is essential to select appropriate resistor and capacitor values to achieve the desired pulse duration. The relationship between the pulse width (T) and the RC network can be described by the formula T = 1.1 * R * C, where R is the resistance in ohms and C is the capacitance in farads.
The operational amplifier's gain settings may also need adjustment to ensure proper triggering of the timer IC. Additionally, power supply considerations are critical, as both the OP Amp and timer IC require stable voltage levels for accurate operation.
Overall, this circuit is useful in applications where voltage levels need to be translated into time-based signals, such as in digital communication systems or pulse-width modulation (PWM) applications.This is a circuit of Voltage-to-Pulse Duration Converter. This circuit is used to convert voltage into pulse duration by combining a timer IC and an OP Amp 🔗 External reference
The Voltage-to-Pulse Duration Converter circuit utilizes a timer IC, typically the 555 timer, configured in monostable mode. In this configuration, the timer generates a pulse of a specified duration in response to a triggering voltage input. The duration of the output pulse is determined by the resistor and capacitor values connected to the timer.
An operational amplifier is employed to condition the input voltage signal. The OP Amp can be configured as a comparator to compare the input voltage against a reference voltage. When the input voltage exceeds the reference level, the OP Amp output triggers the timer IC, initiating the pulse generation.
In designing the circuit, it is essential to select appropriate resistor and capacitor values to achieve the desired pulse duration. The relationship between the pulse width (T) and the RC network can be described by the formula T = 1.1 * R * C, where R is the resistance in ohms and C is the capacitance in farads.
The operational amplifier's gain settings may also need adjustment to ensure proper triggering of the timer IC. Additionally, power supply considerations are critical, as both the OP Amp and timer IC require stable voltage levels for accurate operation.
Overall, this circuit is useful in applications where voltage levels need to be translated into time-based signals, such as in digital communication systems or pulse-width modulation (PWM) applications.This is a circuit of Voltage-to-Pulse Duration Converter. This circuit is used to convert voltage into pulse duration by combining a timer IC and an OP Amp 🔗 External reference