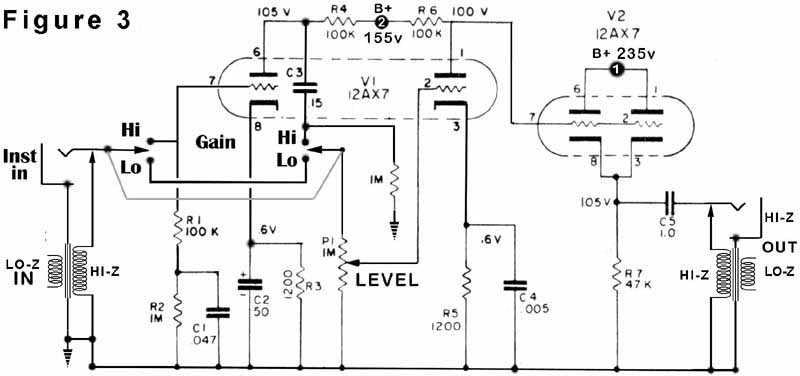
Vox box
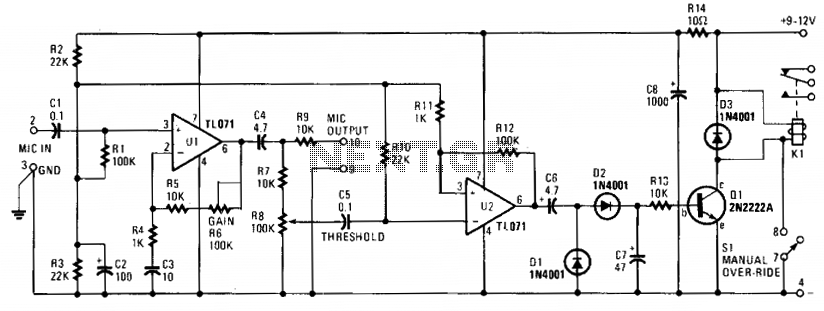
The electronic circuit in the VOX Box consists of three main components: a microphone preamplifier, a Schmitt trigger, and a relay driver. Input signals received at the microphone preamplifier (U1) are amplified and sent to a THRESHOLD control (R8). When the predetermined threshold voltage is surpassed, the output of the Schmitt trigger (U2) transitions to a high state. The signal from U2 is then rectified, and the voltage across capacitor C7 activates the relay energizer transistor (Q1). The action of this transistor allows current to flow through the coil of relay K1. The switching of the relay's SPDT contacts can be utilized to either connect or disconnect an external AC or DC circuit.
The circuit design begins with the microphone preamplifier (U1), which serves to amplify low-level audio signals captured by the microphone. The gain of this preamplifier can be adjusted using the THRESHOLD control (R8), setting a specific voltage level that must be exceeded for the subsequent stages to activate.
The Schmitt trigger (U2) functions as a voltage comparator with hysteresis, providing a stable output that prevents noise from causing false triggering. When the input voltage from the preamplifier exceeds the threshold, U2 rapidly transitions to a high output state, ensuring a fast response time for the circuit.
Following this, the output from U2 is rectified, typically using a diode, which allows only the positive half of the waveform to pass through. The rectified voltage is then stored in capacitor C7, which smooths out fluctuations and provides a stable voltage to drive the relay energizer transistor (Q1).
Once Q1 is activated by the voltage across C7, it allows current to flow through the coil of relay K1. This relay is configured as a Single Pole Double Throw (SPDT) switch, enabling it to either complete or break an external circuit, depending on the state of the relay. The relay can control various loads, including AC or DC devices, making this circuit versatile for applications such as voice-activated control systems or automated switching devices.
In summary, the VOX Box circuit effectively processes audio signals, converting them into control signals that can manipulate external devices through relay switching, showcasing a practical application of basic electronic components in signal processing and control.The electronic circuit in the VOX Box consists of three parts: a microphone preamplifier, a Schmitt trigger, and a relay driver. Input signals (MIC INPUT terminals) to the microphone preamplifier (Ul) are amplified and fed to a THRESHOLD control (R8).
When the preselected threshold voltage level is exceeded, the output of the Schmitt trigger (U2) immediately goes high. The signal from U2 is rectified and the voltage developed across C7 turns on the relay energizer transistor (Ql).
That transistor action passes pull-down current through the coil of relay Kl. The changing of the relay SPDT contacts can be used to either make or break an external ac or dc circuit. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design begins with the microphone preamplifier (U1), which serves to amplify low-level audio signals captured by the microphone. The gain of this preamplifier can be adjusted using the THRESHOLD control (R8), setting a specific voltage level that must be exceeded for the subsequent stages to activate.
The Schmitt trigger (U2) functions as a voltage comparator with hysteresis, providing a stable output that prevents noise from causing false triggering. When the input voltage from the preamplifier exceeds the threshold, U2 rapidly transitions to a high output state, ensuring a fast response time for the circuit.
Following this, the output from U2 is rectified, typically using a diode, which allows only the positive half of the waveform to pass through. The rectified voltage is then stored in capacitor C7, which smooths out fluctuations and provides a stable voltage to drive the relay energizer transistor (Q1).
Once Q1 is activated by the voltage across C7, it allows current to flow through the coil of relay K1. This relay is configured as a Single Pole Double Throw (SPDT) switch, enabling it to either complete or break an external circuit, depending on the state of the relay. The relay can control various loads, including AC or DC devices, making this circuit versatile for applications such as voice-activated control systems or automated switching devices.
In summary, the VOX Box circuit effectively processes audio signals, converting them into control signals that can manipulate external devices through relay switching, showcasing a practical application of basic electronic components in signal processing and control.The electronic circuit in the VOX Box consists of three parts: a microphone preamplifier, a Schmitt trigger, and a relay driver. Input signals (MIC INPUT terminals) to the microphone preamplifier (Ul) are amplified and fed to a THRESHOLD control (R8).
When the preselected threshold voltage level is exceeded, the output of the Schmitt trigger (U2) immediately goes high. The signal from U2 is rectified and the voltage developed across C7 turns on the relay energizer transistor (Ql).
That transistor action passes pull-down current through the coil of relay Kl. The changing of the relay SPDT contacts can be used to either make or break an external ac or dc circuit. 🔗 External reference