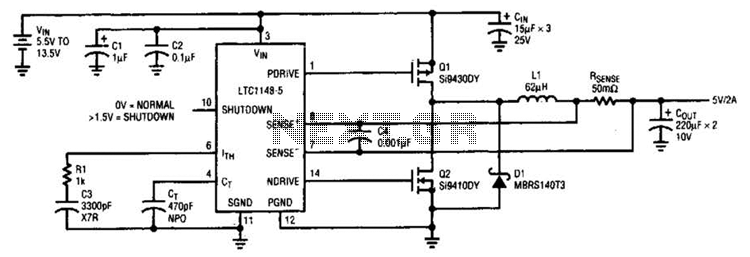
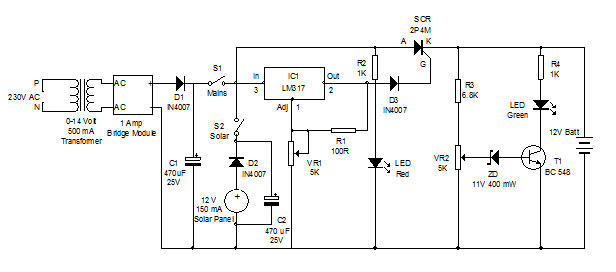
XQP frequency sensitive start-type control box circuit
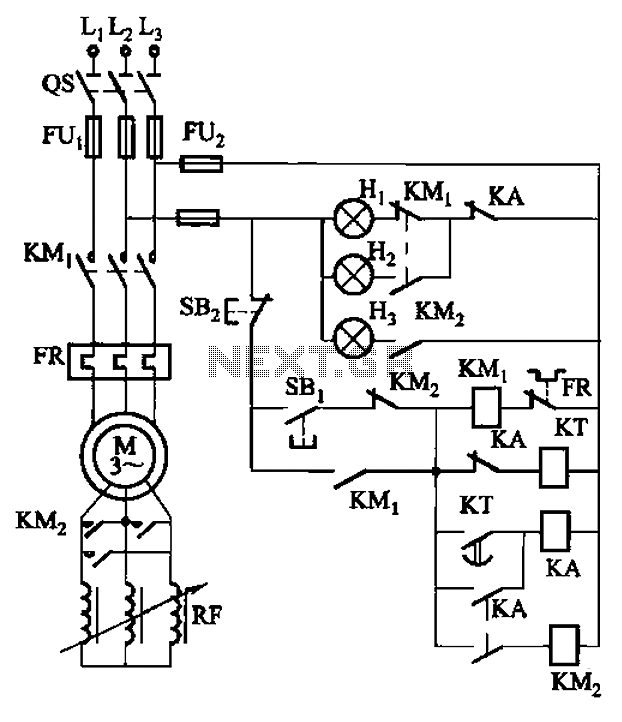
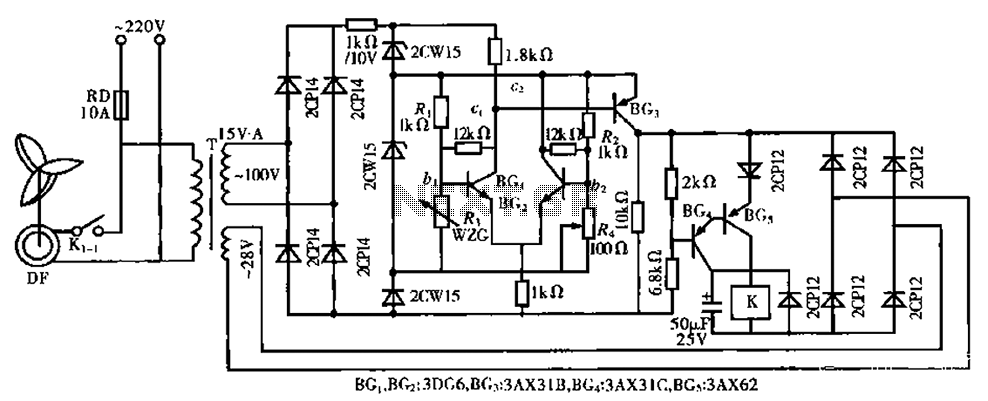
The circuit depicted in Figure 3-165 utilizes a time relay (KT) for controlling the start-up time. Indicator light Hi serves as the power indicator, H2 is designated for the start lights, and H3 functions as the running lights.
The circuit operates by employing a time relay (KT) that initiates the start-up sequence after a predetermined delay. This relay is crucial in managing the timing aspect of the circuit, ensuring that the system does not engage immediately upon power-up, which can help prevent potential damage or operational issues.
The power indicator light (Hi) provides a visual cue that the circuit is energized. This is essential for operators to confirm that the system is receiving power. The start lights (H2) illuminate to indicate that the system is in the process of starting up. This feature is particularly useful in applications where the start-up sequence may take some time, allowing users to monitor the status of the system easily.
Once the system has successfully started, the running lights (H3) activate, signaling that the circuit is operating as intended. This sequential lighting system not only enhances user awareness but also improves safety by clearly indicating the operational status of the equipment.
The overall design of this circuit ensures that each component plays a critical role in the functionality and user interaction with the system, providing a reliable and efficient operation. Proper attention to the timing relay's specifications and the indicator light ratings will further enhance the performance and longevity of the circuit. Circuit shown in Figure 3-165. Start-up time by the time relay KT control. Figure, Hi is the power indicator, H2 for the start lights, H3 for the running lights.
The circuit operates by employing a time relay (KT) that initiates the start-up sequence after a predetermined delay. This relay is crucial in managing the timing aspect of the circuit, ensuring that the system does not engage immediately upon power-up, which can help prevent potential damage or operational issues.
The power indicator light (Hi) provides a visual cue that the circuit is energized. This is essential for operators to confirm that the system is receiving power. The start lights (H2) illuminate to indicate that the system is in the process of starting up. This feature is particularly useful in applications where the start-up sequence may take some time, allowing users to monitor the status of the system easily.
Once the system has successfully started, the running lights (H3) activate, signaling that the circuit is operating as intended. This sequential lighting system not only enhances user awareness but also improves safety by clearly indicating the operational status of the equipment.
The overall design of this circuit ensures that each component plays a critical role in the functionality and user interaction with the system, providing a reliable and efficient operation. Proper attention to the timing relay's specifications and the indicator light ratings will further enhance the performance and longevity of the circuit. Circuit shown in Figure 3-165. Start-up time by the time relay KT control. Figure, Hi is the power indicator, H2 for the start lights, H3 for the running lights.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713