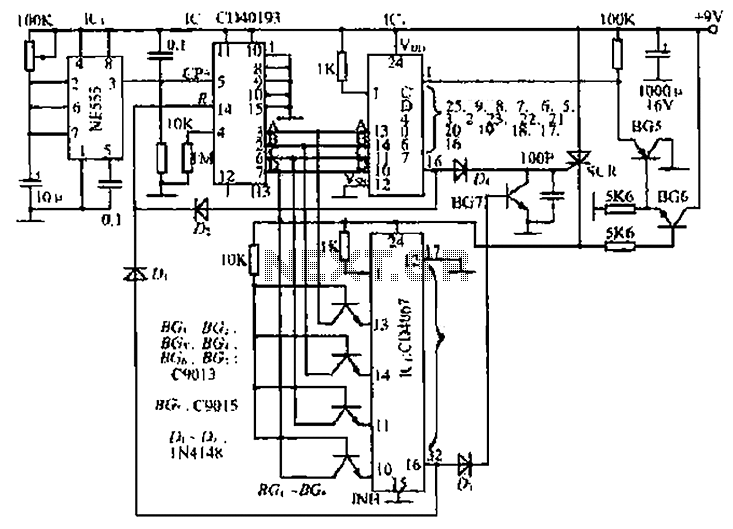
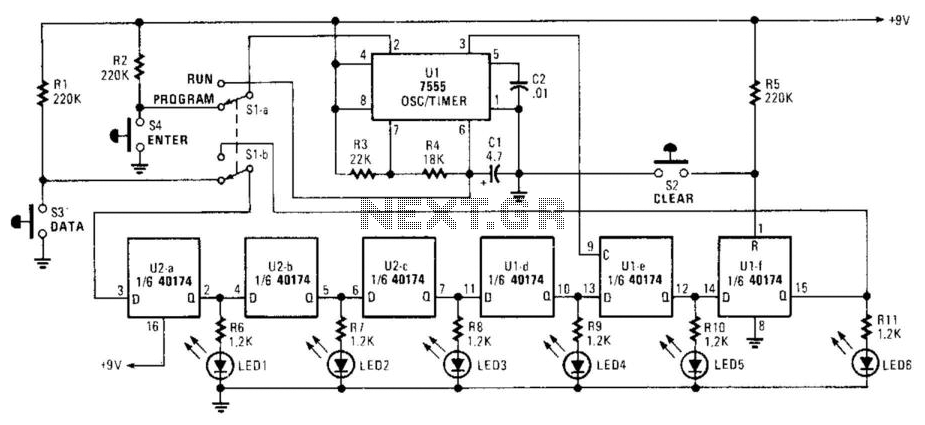
Warning light
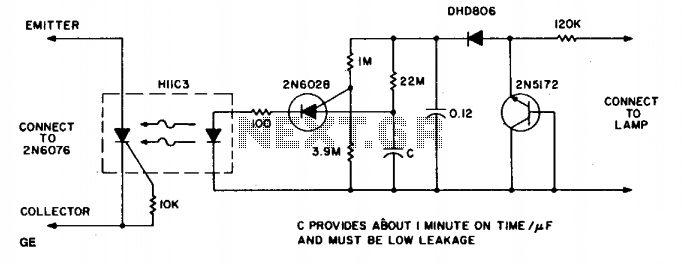
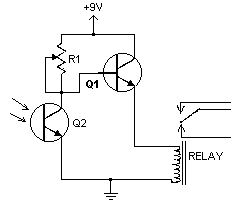
The circuit provides illumination when darkness falls. By utilizing the gain available in Darlington transistors, this circuit is simplified to employ only a photodarlington sensor, a Darlington amplifier, and three resistors. The illumination level will be slightly lower than normal, and a longer bulb life can be expected since the D40K saturation voltage reduces the lamp operating voltage slightly.
This circuit employs a photodarlington sensor, which is highly sensitive to light levels, making it ideal for detecting darkness. When ambient light levels drop below a predetermined threshold, the photodarlington sensor activates, triggering the Darlington amplifier. The Darlington amplifier, known for its high current gain, allows for a minimal input current to control a larger output current, effectively powering the illumination source, such as an LED or incandescent bulb.
The circuit includes three resistors that serve multiple purposes: one resistor is typically used to set the biasing conditions for the photodarlington sensor, ensuring it operates within its optimal range. Another resistor is often placed in the feedback loop of the Darlington amplifier to stabilize the gain and prevent oscillations. The third resistor may be employed to limit the current flowing through the illumination source, thereby protecting it from potential damage due to excessive current.
The D40K component is notable for its low saturation voltage, which means that when the circuit is activated, the voltage drop across the Darlington pair is minimized. This results in a slightly reduced operating voltage for the lamp, which not only lowers the illumination level but also contributes to an extended lifespan for the bulb. The overall design emphasizes efficiency and longevity, making it suitable for applications where automatic illumination is desired, such as in outdoor lighting systems or automatic night lights.The circuit provides illumination when darkness comes. By using the gain available in darlington transistors, this circuit is simplified to use just a photodarlington sensor, a darlington amplifier, and three resistors. The illumination level will be slightly lower than normal, and longer bulb life can be expected, since the D40K saturation voltage lowers the lamp operating voltage slightly. 🔗 External reference
This circuit employs a photodarlington sensor, which is highly sensitive to light levels, making it ideal for detecting darkness. When ambient light levels drop below a predetermined threshold, the photodarlington sensor activates, triggering the Darlington amplifier. The Darlington amplifier, known for its high current gain, allows for a minimal input current to control a larger output current, effectively powering the illumination source, such as an LED or incandescent bulb.
The circuit includes three resistors that serve multiple purposes: one resistor is typically used to set the biasing conditions for the photodarlington sensor, ensuring it operates within its optimal range. Another resistor is often placed in the feedback loop of the Darlington amplifier to stabilize the gain and prevent oscillations. The third resistor may be employed to limit the current flowing through the illumination source, thereby protecting it from potential damage due to excessive current.
The D40K component is notable for its low saturation voltage, which means that when the circuit is activated, the voltage drop across the Darlington pair is minimized. This results in a slightly reduced operating voltage for the lamp, which not only lowers the illumination level but also contributes to an extended lifespan for the bulb. The overall design emphasizes efficiency and longevity, making it suitable for applications where automatic illumination is desired, such as in outdoor lighting systems or automatic night lights.The circuit provides illumination when darkness comes. By using the gain available in darlington transistors, this circuit is simplified to use just a photodarlington sensor, a darlington amplifier, and three resistors. The illumination level will be slightly lower than normal, and longer bulb life can be expected, since the D40K saturation voltage lowers the lamp operating voltage slightly. 🔗 External reference