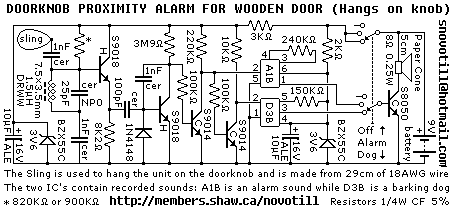
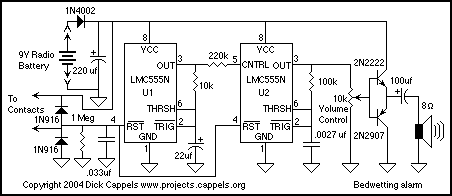
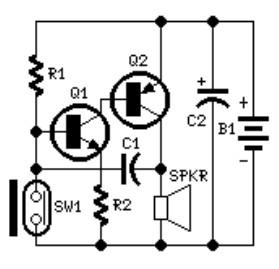
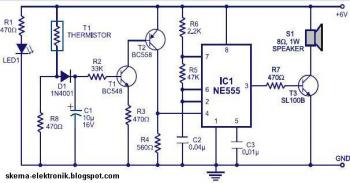
Water-Leak Alarm
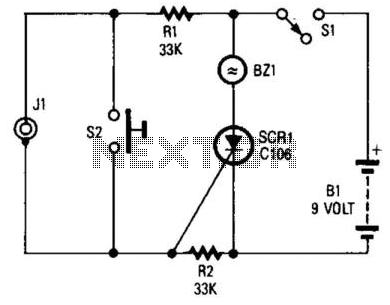
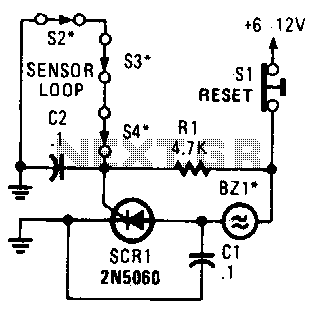
If you choose to create your own moisture sensor, this foil pattern will be useful. A sensor connected to J1 activates CR1, which sounds buzzer BZ1. The sensor consists of a printed circuit board (PCB) foil pattern grid. Multiple sensors can be connected in parallel to enhance coverage or monitor several locations at the same time.
The moisture sensor circuit utilizes a PCB foil pattern designed to detect moisture levels in the environment. The core of the sensor is a grid of conductive traces that change resistance based on the presence of moisture. When moisture is detected, the resistance between the conductive traces decreases, allowing current to flow through the circuit.
In this configuration, the sensor is connected to a terminal labeled J1. When moisture is detected, it triggers the conduction of CR1, which is likely a transistor or a relay, depending on the design specifics. This conduction activates the buzzer BZ1, providing an audible alert to indicate the presence of moisture.
The design allows for scalability; multiple sensors can be interconnected in parallel. This approach not only increases the effective area of moisture detection but also enables monitoring of different locations simultaneously. Each sensor can be independently wired to the same buzzer or to separate indicators, depending on the desired application.
For optimal performance, it is essential to consider the placement of the sensors, ensuring they are positioned in areas where moisture accumulation is likely. Additionally, the choice of materials for the PCB and the conductive traces should be made to withstand environmental conditions without degrading over time. Proper calibration of the sensors may also be necessary to ensure accurate moisture readings and effective response from the buzzer.
Overall, this moisture sensor design is versatile and can be adapted for various applications, including agricultural monitoring, leak detection, and environmental control systems. If you choose to make your own moisture sensor,; this foil pattern should come in handy. A sensor connected to J1 causes S CR1 to conduct, which sounds buzzer BZ1. The sensor is a PC-board foil pattern grid. Several sensors can be wired in parallel for increased coverage or to monitor several places simultaneously. 🔗 External reference
The moisture sensor circuit utilizes a PCB foil pattern designed to detect moisture levels in the environment. The core of the sensor is a grid of conductive traces that change resistance based on the presence of moisture. When moisture is detected, the resistance between the conductive traces decreases, allowing current to flow through the circuit.
In this configuration, the sensor is connected to a terminal labeled J1. When moisture is detected, it triggers the conduction of CR1, which is likely a transistor or a relay, depending on the design specifics. This conduction activates the buzzer BZ1, providing an audible alert to indicate the presence of moisture.
The design allows for scalability; multiple sensors can be interconnected in parallel. This approach not only increases the effective area of moisture detection but also enables monitoring of different locations simultaneously. Each sensor can be independently wired to the same buzzer or to separate indicators, depending on the desired application.
For optimal performance, it is essential to consider the placement of the sensors, ensuring they are positioned in areas where moisture accumulation is likely. Additionally, the choice of materials for the PCB and the conductive traces should be made to withstand environmental conditions without degrading over time. Proper calibration of the sensors may also be necessary to ensure accurate moisture readings and effective response from the buzzer.
Overall, this moisture sensor design is versatile and can be adapted for various applications, including agricultural monitoring, leak detection, and environmental control systems. If you choose to make your own moisture sensor,; this foil pattern should come in handy. A sensor connected to J1 causes S CR1 to conduct, which sounds buzzer BZ1. The sensor is a PC-board foil pattern grid. Several sensors can be wired in parallel for increased coverage or to monitor several places simultaneously. 🔗 External reference