Water Level Alert Circuit
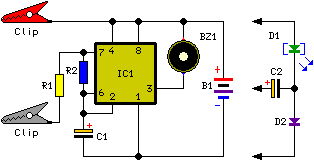
This circuit emits an intermittent beep or flashes an LED when the water level in a container reaches a predetermined height. It is designed to be mounted on top of the container, such as a plastic tank, using two crocodile clips that also function as probes. For deeper sensing, the clips can be extended with two pieces of stiff wire.
The circuit operates using a water level sensing mechanism that typically involves a pair of conductive probes, represented by the crocodile clips. When the water level rises to the height of the probes, it completes an electrical circuit, triggering the circuit to emit an audible beep or activate an LED indicator.
The configuration can be adjusted for different water levels by changing the position of the clips or extending them with stiff wires, allowing for flexibility in installation depending on the depth of the tank. The design may include a comparator circuit, where the probes are connected to an operational amplifier configured to detect the change in resistance when submerged in water.
The output of the comparator can drive a transistor, which in turn controls the LED and/or the buzzer. The LED provides a visual indication of the water level, while the buzzer gives an audible alert. The circuit may also incorporate resistors to limit current and ensure the components operate within safe parameters.
Powering the circuit can be accomplished using a battery or an external power source, and provisions should be made for ensuring the circuit is waterproof or protected from moisture to maintain functionality and safety. Overall, this water level detection circuit serves as a practical solution for monitoring liquid levels in various applications, enhancing safety and efficiency in fluid management.This circuit will emit an intermittent beep (or will flash a LED) when the water contained into a recipient has reached the desired level. It should be mounted on top of the recipient (e.g. a plastic tank) by means of two crocodile clips, acting also as probes. If a deeper sensing level is needed, the clips can be extended by means of two pieces of stiff wire (see pictures)..
🔗 External reference
The circuit operates using a water level sensing mechanism that typically involves a pair of conductive probes, represented by the crocodile clips. When the water level rises to the height of the probes, it completes an electrical circuit, triggering the circuit to emit an audible beep or activate an LED indicator.
The configuration can be adjusted for different water levels by changing the position of the clips or extending them with stiff wires, allowing for flexibility in installation depending on the depth of the tank. The design may include a comparator circuit, where the probes are connected to an operational amplifier configured to detect the change in resistance when submerged in water.
The output of the comparator can drive a transistor, which in turn controls the LED and/or the buzzer. The LED provides a visual indication of the water level, while the buzzer gives an audible alert. The circuit may also incorporate resistors to limit current and ensure the components operate within safe parameters.
Powering the circuit can be accomplished using a battery or an external power source, and provisions should be made for ensuring the circuit is waterproof or protected from moisture to maintain functionality and safety. Overall, this water level detection circuit serves as a practical solution for monitoring liquid levels in various applications, enhancing safety and efficiency in fluid management.This circuit will emit an intermittent beep (or will flash a LED) when the water contained into a recipient has reached the desired level. It should be mounted on top of the recipient (e.g. a plastic tank) by means of two crocodile clips, acting also as probes. If a deeper sensing level is needed, the clips can be extended by means of two pieces of stiff wire (see pictures)..
🔗 External reference