White LED Array Lamp
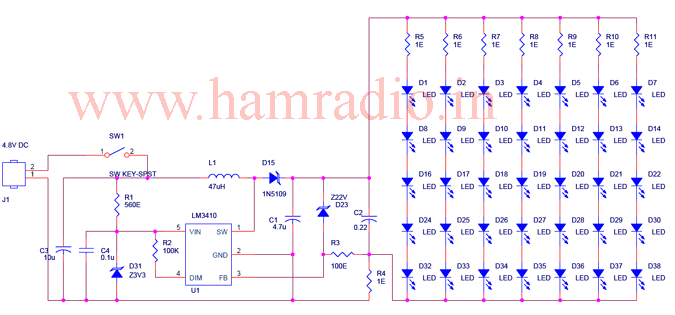
To create a battery-operated LED lamp, it is preferable to utilize a cluster of low-power discrete LED arrays instead of a single high-power LED. This configuration allows for scattered light production, significantly reducing irritation or potential damage to the eyes if accidentally viewed. Additionally, the light distribution is well-suited for room lighting, and no heat sink is required. The circuit is designed to operate a 3W, 5 x 7 white LED array powered by four NiMH cells. It employs a straightforward DC to DC boost circuit using an LM3410, which includes a 170 mΩ NMOS switch. The circuit is completed with a few external components. The switching frequency is internally set to either 525 kHz for LM3410-Y devices or 1.60 MHz for LM3410-X devices, allowing for the use of very small inductors and capacitors. The 525 kHz switching frequency is chosen due to the availability of suitable ferrite with lower core losses. The required inductor value for the circuit depends on the desired voltage and current output, with detailed calculations provided in the LM3410 datasheet. An efficiency of approximately 88% is achieved. The integrated circuit features an external shutdown option and a standby current of only 80 nA. The operating current for a single branch of the LED array is approximately 25 mA, resulting in a total output current of 190 mA drawn from the DC to DC converters, as there are 7 parallel paths. This current is regulated by a 10Ω resistor (R4), with the relationship I = 0.19/R4. An optional output over-voltage protection is implemented using a 22V zener diode (D23) and a resistor (R3) to safeguard the IC in case the LED load becomes an open circuit. Given that the absolute maximum input voltage to the IC is 5.5V, a voltage regulator utilizing R1 and a zener diode (D31) is necessary if the circuit is powered by a source exceeding 5.5V. The DIM input pin of the LM3410 can be utilized for either on/off control or brightness adjustment of the LED array. A PWM dimming signal with a duty cycle ranging from 0 to 100% and a frequency between 200 Hz and 1 kHz is optimal for brightness control, although a PWM frequency of up to 25 kHz can also be employed. In this application, the DIM pin is connected to VIN to achieve maximum brightness.
This battery-operated LED lamp circuit offers an efficient and effective solution for ambient lighting. The use of a low-power discrete LED array ensures a softer light output, making it more comfortable for prolonged viewing. The LM3410 integrated circuit provides robust performance with high efficiency, minimizing energy waste and extending battery life. The external components required for the circuit are minimal, making assembly straightforward. The choice of a 525 kHz switching frequency balances the need for compact components while ensuring low core losses in the inductor, which is crucial for maintaining high efficiency.
The design accommodates the need for brightness control through PWM dimming, allowing users to adjust the light output according to their preferences. The inclusion of over-voltage protection enhances the reliability of the circuit, ensuring that the LED array operates safely under various conditions. The standby current of only 80 nA is particularly advantageous for battery-operated applications, as it extends the operational life of the batteries between charges.
Overall, this LED lamp circuit is well-suited for applications where low power consumption, ease of assembly, and user-adjustable brightness are essential. Its design principles can be adapted for various lighting scenarios, making it a versatile choice for portable lighting solutions.To make a battery operated LED lamp, it may better to use a cluster of low power discrete LED array rather than a single high power LED. The light produced will be scattered and It considerably reduces irritation or damages to a naked eye, if accidentally looked on it.
Also the light spreads nicely so it is good for room lighting and no heat sink required for the LEDs! The circuit is designed to operate 3W, 5 x 7 white LED array powered from four NiMH cells. The design is straight forward DC to DC boost circuit using a LM3410 which includes a 170 m © NMOS switch. The circuit is completes with few external components. The switching frequency is internally set to either 525 kHz for LM3410-Y devices or 1. 60 MHz for LM3410-X, allowing the use of extremely small inductors and capacitors. The 525 kHz switching frequency is selected due to the availability of suitable ferrite having lower core losses.
The inductor value needed for the circuit depends upon the voltage and current output needed. A detailed calculation is described in the datasheet of the LM3410. A higher efficiency of approximately 88% is achieved. The IC is featured with an external shutdown and the standby current of only 80 nA. The operating current for a single branch the LED array is ~25mA, and since there are 7 parallel paths a total output current of 190mA is drawn from the DC to DC convertors. This current is set by the 1O resistor R4 (I = 0. 19/R4). An optional output over voltage protection is provided using a 22V zener diode D23 and a resistor R3.
This will protect the IC if the LED load becomes an open circuit. Since the absolute maximum input voltage to the IC is 5. 5 V, a voltage regulator using R1 and zener diode D31 is required if the circuit is operated from a voltage source more than 5. 5 V. The DIM input pin of LM3410 can be used for either on/off or brightness control of LED array. A PWM dimming signal whose duty cycle from 0 to 100% with a frequency of 200 ~ 1 kHz is best suited for this brightness control, although a PWM with maximum of 25 KHz can be used.
In this application DIM pin is tied to VIN for maximum brightness. 🔗 External reference
This battery-operated LED lamp circuit offers an efficient and effective solution for ambient lighting. The use of a low-power discrete LED array ensures a softer light output, making it more comfortable for prolonged viewing. The LM3410 integrated circuit provides robust performance with high efficiency, minimizing energy waste and extending battery life. The external components required for the circuit are minimal, making assembly straightforward. The choice of a 525 kHz switching frequency balances the need for compact components while ensuring low core losses in the inductor, which is crucial for maintaining high efficiency.
The design accommodates the need for brightness control through PWM dimming, allowing users to adjust the light output according to their preferences. The inclusion of over-voltage protection enhances the reliability of the circuit, ensuring that the LED array operates safely under various conditions. The standby current of only 80 nA is particularly advantageous for battery-operated applications, as it extends the operational life of the batteries between charges.
Overall, this LED lamp circuit is well-suited for applications where low power consumption, ease of assembly, and user-adjustable brightness are essential. Its design principles can be adapted for various lighting scenarios, making it a versatile choice for portable lighting solutions.To make a battery operated LED lamp, it may better to use a cluster of low power discrete LED array rather than a single high power LED. The light produced will be scattered and It considerably reduces irritation or damages to a naked eye, if accidentally looked on it.
Also the light spreads nicely so it is good for room lighting and no heat sink required for the LEDs! The circuit is designed to operate 3W, 5 x 7 white LED array powered from four NiMH cells. The design is straight forward DC to DC boost circuit using a LM3410 which includes a 170 m © NMOS switch. The circuit is completes with few external components. The switching frequency is internally set to either 525 kHz for LM3410-Y devices or 1. 60 MHz for LM3410-X, allowing the use of extremely small inductors and capacitors. The 525 kHz switching frequency is selected due to the availability of suitable ferrite having lower core losses.
The inductor value needed for the circuit depends upon the voltage and current output needed. A detailed calculation is described in the datasheet of the LM3410. A higher efficiency of approximately 88% is achieved. The IC is featured with an external shutdown and the standby current of only 80 nA. The operating current for a single branch the LED array is ~25mA, and since there are 7 parallel paths a total output current of 190mA is drawn from the DC to DC convertors. This current is set by the 1O resistor R4 (I = 0. 19/R4). An optional output over voltage protection is provided using a 22V zener diode D23 and a resistor R3.
This will protect the IC if the LED load becomes an open circuit. Since the absolute maximum input voltage to the IC is 5. 5 V, a voltage regulator using R1 and zener diode D31 is required if the circuit is operated from a voltage source more than 5. 5 V. The DIM input pin of LM3410 can be used for either on/off or brightness control of LED array. A PWM dimming signal whose duty cycle from 0 to 100% with a frequency of 200 ~ 1 kHz is best suited for this brightness control, although a PWM with maximum of 25 KHz can be used.
In this application DIM pin is tied to VIN for maximum brightness. 🔗 External reference