Why are audio transformers required
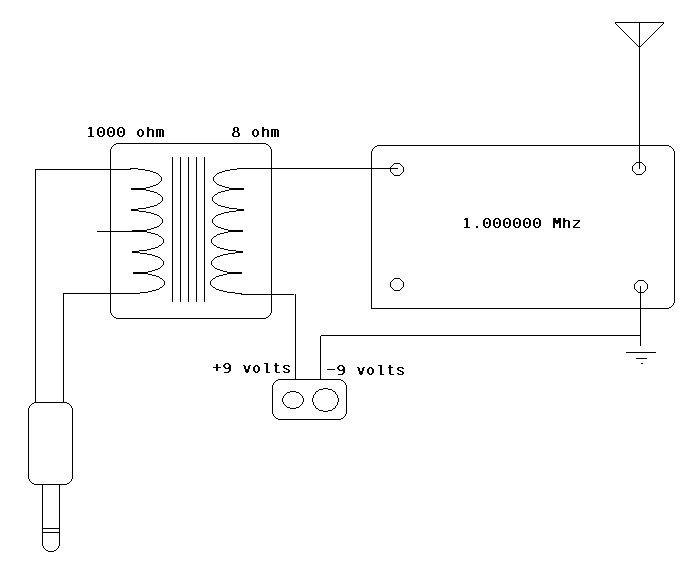
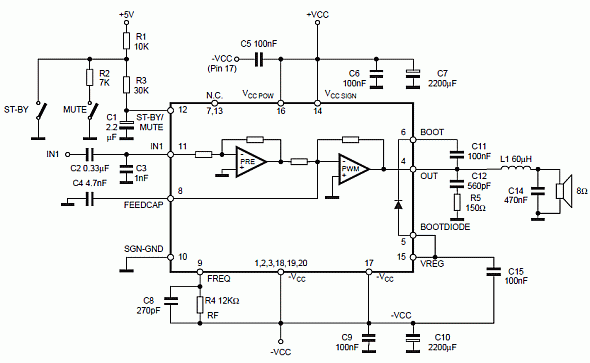
The circuit incorporates an audio transformer. There is an ongoing effort to understand the concept of impedance and its significance. Clarification is sought on the necessity of an audio transformer and its function in changing impedance. An inquiry is made regarding the implications of not using an audio transformer. It is noted that the design appears unusual, resembling configurations found in ZN414 receivers where power feed and audio signals are combined, and potentially RF signals in extreme cases. A link to the schematic has been shared, with an acknowledgment that it may be an atypical schematic, despite being intended as a learning resource.
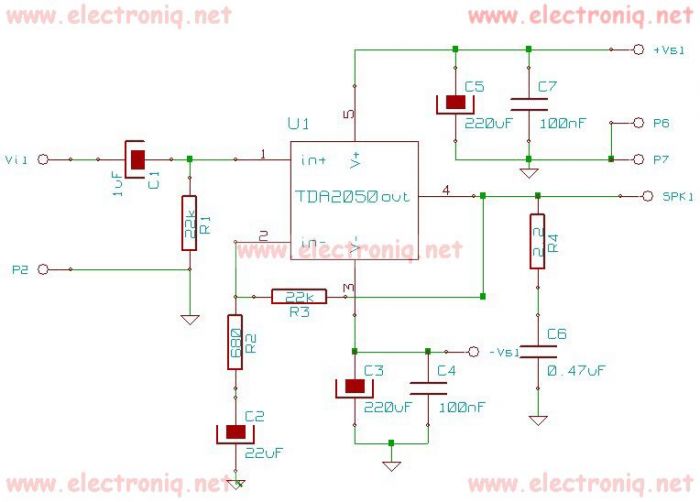
The audio transformer is a critical component in audio circuits, serving to match the impedance between different stages of an audio signal chain. Impedance matching is essential for maximizing power transfer and minimizing signal reflection, which can lead to distortion. An audio transformer typically consists of two coils of wire wound around a magnetic core, allowing the transfer of audio signals from one circuit to another while isolating the two circuits electrically.
When an audio transformer is used, it can step up or step down the voltage levels of the audio signal, depending on the turns ratio of the transformer. This adjustment in voltage can help in adapting the output of an audio source, such as a microphone or guitar pickup, to the input requirements of a downstream device, such as an amplifier or mixing console.
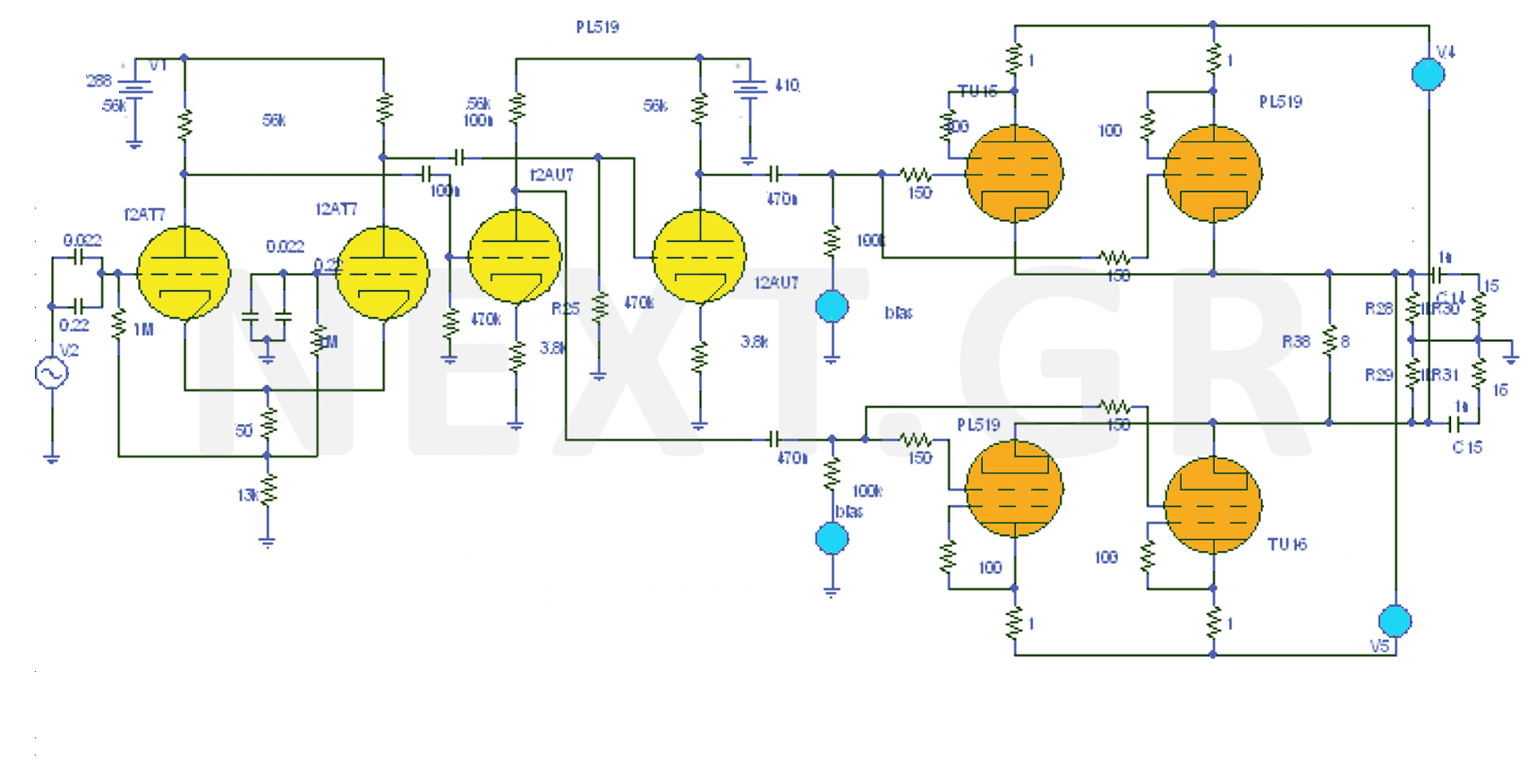
If an audio transformer is omitted, the direct connection between different circuit stages may lead to impedance mismatches. This can result in reduced audio quality, increased noise, or even damage to components due to excessive voltage levels. The unusual schematic referenced, which resembles that of ZN414 receivers, suggests a design that combines audio, power, and potentially RF signals. This complexity highlights the importance of carefully managing signal integrity and impedance throughout the circuit to ensure optimal performance.
In summary, the audio transformer not only serves a functional role in impedance matching but also provides electrical isolation, which can enhance the overall reliability and performance of audio circuits. Understanding its operation and necessity is crucial for effective circuit design and implementation.It has an audio transformer. I`m still attempting to grasp the concept of impedance and such, so can someone explain why this is necessary And how would such a transformer even work to change the impedance What would be the difference if you didn`t use an audio transformer @Leon Heller - It is unusual - looks like what you see with eg ZN414 receivers where power feed and audio are combined. And RF too in extreme cases :-). Russell McMahon Dec 14 `11 at 21:34 I`ve added the link to where I found that schematic. I didn`t realize it would be such an odd schematic since it was suppose to be a learning resource Earlz Dec 14 `11 at 22:10 🔗 External reference
The audio transformer is a critical component in audio circuits, serving to match the impedance between different stages of an audio signal chain. Impedance matching is essential for maximizing power transfer and minimizing signal reflection, which can lead to distortion. An audio transformer typically consists of two coils of wire wound around a magnetic core, allowing the transfer of audio signals from one circuit to another while isolating the two circuits electrically.
When an audio transformer is used, it can step up or step down the voltage levels of the audio signal, depending on the turns ratio of the transformer. This adjustment in voltage can help in adapting the output of an audio source, such as a microphone or guitar pickup, to the input requirements of a downstream device, such as an amplifier or mixing console.
If an audio transformer is omitted, the direct connection between different circuit stages may lead to impedance mismatches. This can result in reduced audio quality, increased noise, or even damage to components due to excessive voltage levels. The unusual schematic referenced, which resembles that of ZN414 receivers, suggests a design that combines audio, power, and potentially RF signals. This complexity highlights the importance of carefully managing signal integrity and impedance throughout the circuit to ensure optimal performance.
In summary, the audio transformer not only serves a functional role in impedance matching but also provides electrical isolation, which can enhance the overall reliability and performance of audio circuits. Understanding its operation and necessity is crucial for effective circuit design and implementation.It has an audio transformer. I`m still attempting to grasp the concept of impedance and such, so can someone explain why this is necessary And how would such a transformer even work to change the impedance What would be the difference if you didn`t use an audio transformer @Leon Heller - It is unusual - looks like what you see with eg ZN414 receivers where power feed and audio are combined. And RF too in extreme cases :-). Russell McMahon Dec 14 `11 at 21:34 I`ve added the link to where I found that schematic. I didn`t realize it would be such an odd schematic since it was suppose to be a learning resource Earlz Dec 14 `11 at 22:10 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713