Wien Bridge Oscillator Tutorial and Theory
A tutorial on the Wien Bridge Oscillator circuit, which utilizes an RC phase shift oscillator to generate sine waves.
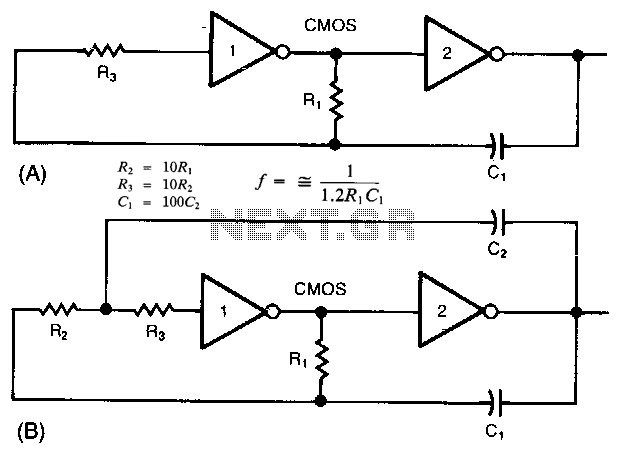
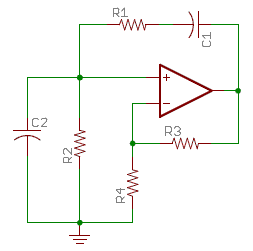
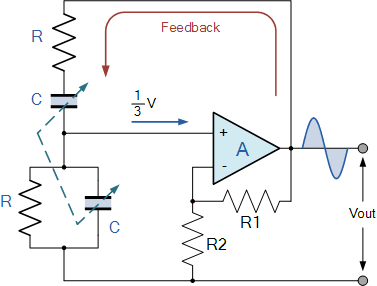
The Wien Bridge Oscillator is a well-known electronic circuit used to produce sine waves. It operates based on the principle of a feedback loop that incorporates both resistive (R) and capacitive (C) components to create a phase shift necessary for oscillation. The fundamental design consists of a bridge circuit that balances the impedances, allowing for stable oscillation at a specific frequency determined by the values of the resistors and capacitors used.
In its simplest form, the Wien Bridge Oscillator consists of four resistors and two capacitors arranged in a bridge configuration. The two resistors in series with the capacitors form the frequency-determining network. The output of the bridge is fed back to the input through an amplifier, which provides the necessary gain to sustain oscillation. The gain of the amplifier must be carefully controlled; traditionally, a light bulb or thermistor is used in the circuit to adjust the gain automatically, ensuring that it remains near unity for stable oscillation.
The frequency of oscillation (f) can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi R C} \]
where R is the resistance and C is the capacitance in the bridge network. By selecting appropriate values for R and C, the desired frequency of the output sine wave can be achieved.
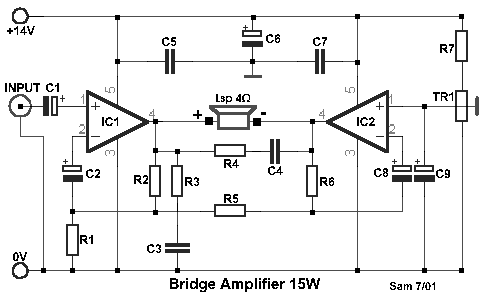
The Wien Bridge Oscillator is widely used in audio applications, function generators, and in various signal processing tasks due to its ability to generate low-distortion sine waves. It is also notable for its simplicity and ease of implementation, making it a popular choice in both educational and practical electronic applications.Wien Bridge Oscillator Tutorial about the Wien Bridge Oscillator Circuit which uses a RC Phase Shift Oscillator to produce sine waves.. 🔗 External reference
The Wien Bridge Oscillator is a well-known electronic circuit used to produce sine waves. It operates based on the principle of a feedback loop that incorporates both resistive (R) and capacitive (C) components to create a phase shift necessary for oscillation. The fundamental design consists of a bridge circuit that balances the impedances, allowing for stable oscillation at a specific frequency determined by the values of the resistors and capacitors used.
In its simplest form, the Wien Bridge Oscillator consists of four resistors and two capacitors arranged in a bridge configuration. The two resistors in series with the capacitors form the frequency-determining network. The output of the bridge is fed back to the input through an amplifier, which provides the necessary gain to sustain oscillation. The gain of the amplifier must be carefully controlled; traditionally, a light bulb or thermistor is used in the circuit to adjust the gain automatically, ensuring that it remains near unity for stable oscillation.
The frequency of oscillation (f) can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi R C} \]
where R is the resistance and C is the capacitance in the bridge network. By selecting appropriate values for R and C, the desired frequency of the output sine wave can be achieved.
The Wien Bridge Oscillator is widely used in audio applications, function generators, and in various signal processing tasks due to its ability to generate low-distortion sine waves. It is also notable for its simplicity and ease of implementation, making it a popular choice in both educational and practical electronic applications.Wien Bridge Oscillator Tutorial about the Wien Bridge Oscillator Circuit which uses a RC Phase Shift Oscillator to produce sine waves.. 🔗 External reference