Wien Bridge Sine Wave Oscillator Circuit
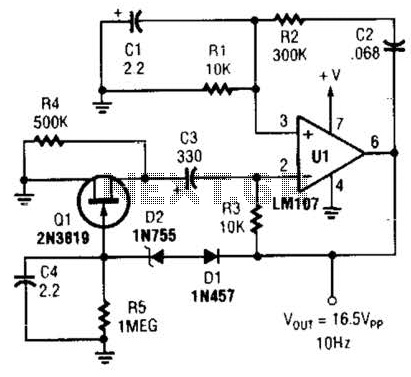
This Wien-bridge sine-wave oscillator utilizes a 2N3819 as an amplitude stabilizer. The 2N3819 functions as a variable-resistance element within the Wien bridge.
The Wien-bridge oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates sine waves. It employs a bridge circuit consisting of resistors and capacitors, which allows for the precise control of frequency. In this configuration, the 2N3819, a JFET (Junction Field Effect Transistor), plays a crucial role in maintaining a stable amplitude of the output waveform.
The oscillator circuit typically consists of four resistors and two capacitors arranged in a bridge configuration. The 2N3819 is integrated into the feedback loop of the oscillator, where it adjusts the resistance dynamically to ensure consistent oscillation amplitude. This is essential because, in a traditional Wien-bridge oscillator, the amplitude can vary due to component tolerances or temperature changes.
The operation begins with the application of power to the circuit, allowing the capacitors to charge and the oscillation to commence. As the oscillation builds, the 2N3819's variable resistance helps to control the gain of the amplifier stage, thereby stabilizing the output amplitude. The frequency of oscillation is determined by the values of the resistors and capacitors in the bridge, which can be calculated using the formula f = 1 / (2πRC), where R is the resistance and C is the capacitance.
Overall, the inclusion of the 2N3819 in the Wien-bridge oscillator circuit enhances its performance by providing a reliable means of amplitude stabilization, resulting in a clean, sinusoidal output that is suitable for various applications, including signal generation and waveform synthesis in electronic systems. This Wien-bridge sine-wave oscillator uses a 2N3819 as an amplitude stabilizer. The 2N3819 acts as a variable-resistance element in the Wien bridge. 🔗 External reference
The Wien-bridge oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates sine waves. It employs a bridge circuit consisting of resistors and capacitors, which allows for the precise control of frequency. In this configuration, the 2N3819, a JFET (Junction Field Effect Transistor), plays a crucial role in maintaining a stable amplitude of the output waveform.
The oscillator circuit typically consists of four resistors and two capacitors arranged in a bridge configuration. The 2N3819 is integrated into the feedback loop of the oscillator, where it adjusts the resistance dynamically to ensure consistent oscillation amplitude. This is essential because, in a traditional Wien-bridge oscillator, the amplitude can vary due to component tolerances or temperature changes.
The operation begins with the application of power to the circuit, allowing the capacitors to charge and the oscillation to commence. As the oscillation builds, the 2N3819's variable resistance helps to control the gain of the amplifier stage, thereby stabilizing the output amplitude. The frequency of oscillation is determined by the values of the resistors and capacitors in the bridge, which can be calculated using the formula f = 1 / (2πRC), where R is the resistance and C is the capacitance.
Overall, the inclusion of the 2N3819 in the Wien-bridge oscillator circuit enhances its performance by providing a reliable means of amplitude stabilization, resulting in a clean, sinusoidal output that is suitable for various applications, including signal generation and waveform synthesis in electronic systems. This Wien-bridge sine-wave oscillator uses a 2N3819 as an amplitude stabilizer. The 2N3819 acts as a variable-resistance element in the Wien bridge. 🔗 External reference