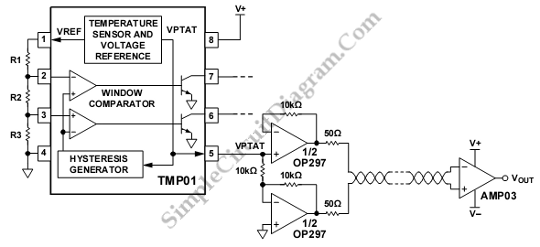
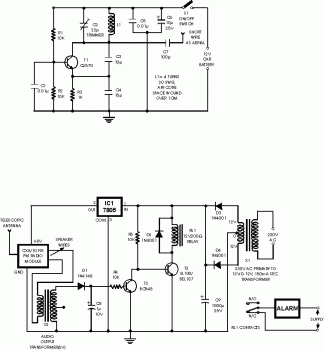
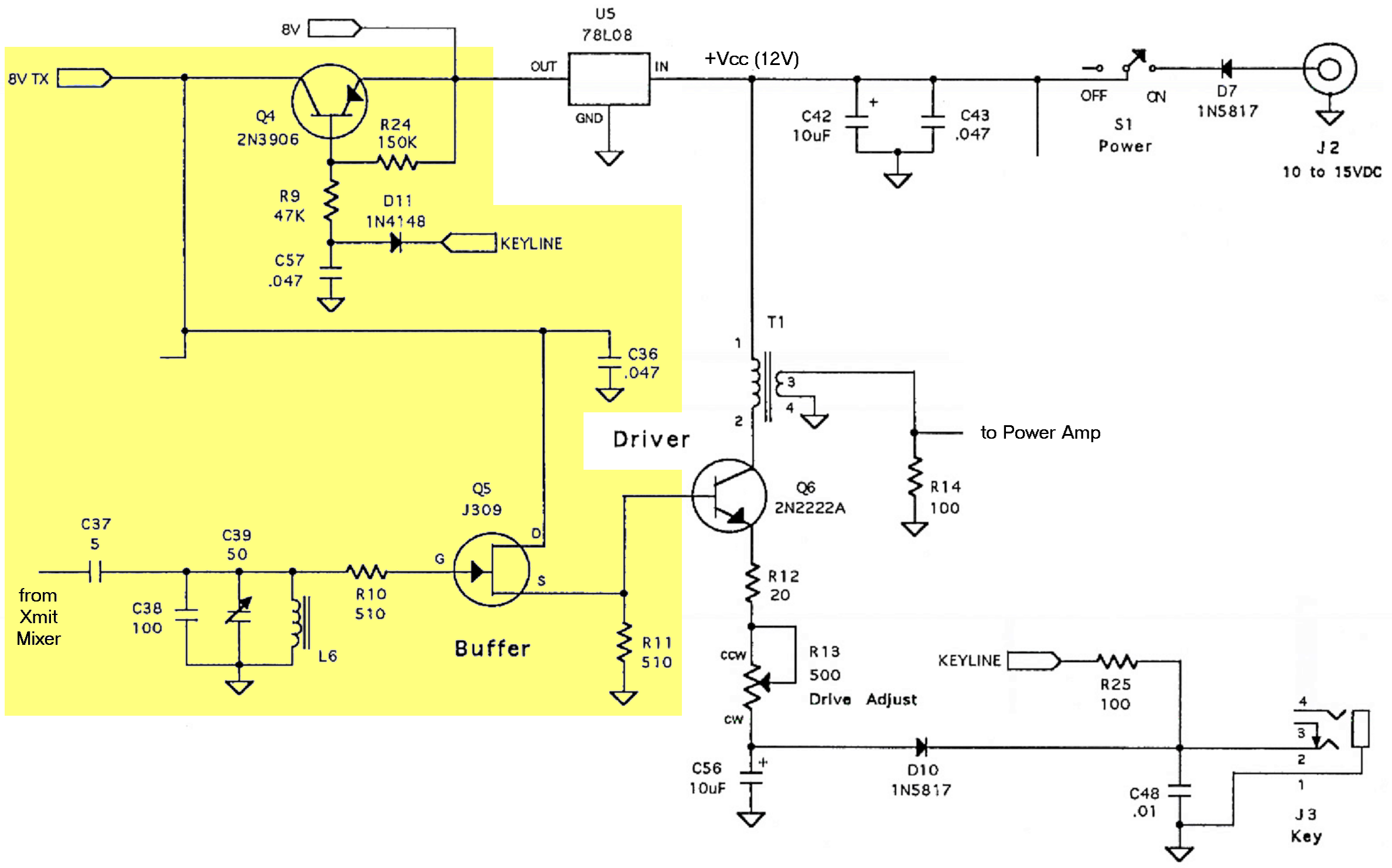
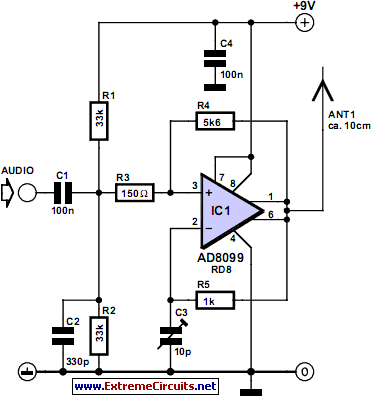
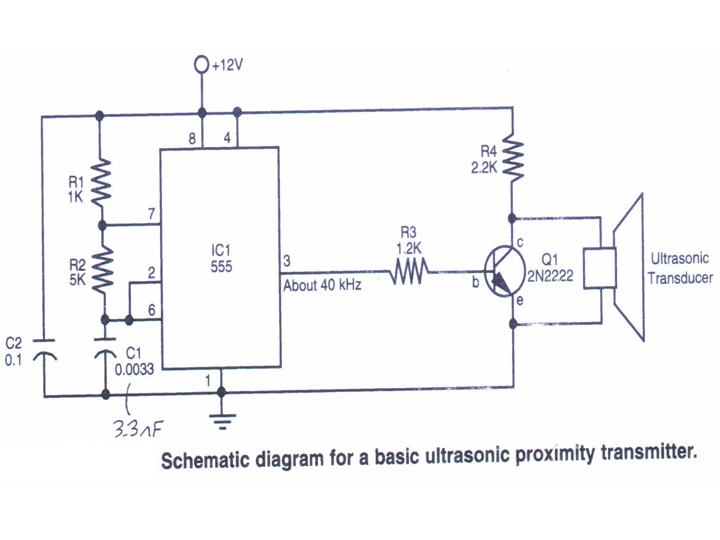
Wireless IR headphone transmitter
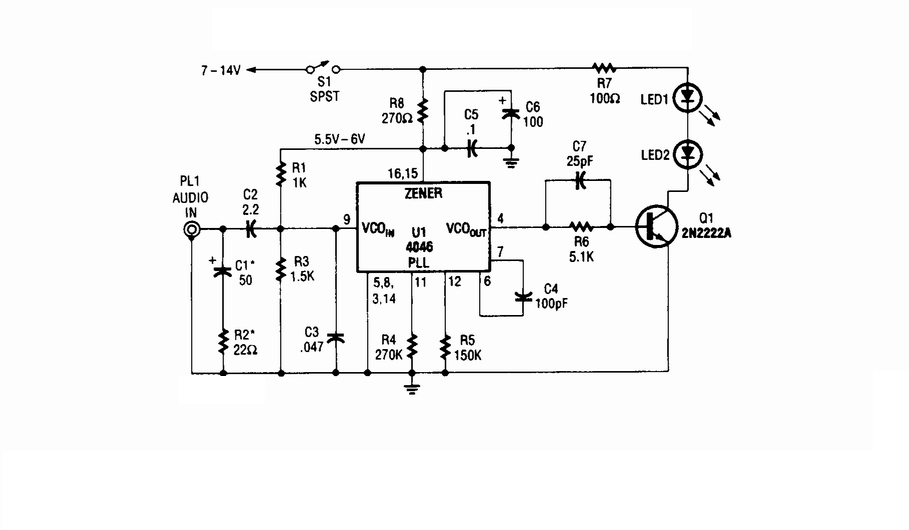
Wireless infrared headphone transmitter. Audio input from PL1 frequency modulates the voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) section of a 4046 phase-locked loop (PLL) chip. The VCO output drives Q1, a switching transistor, which in turn drives two infrared (IR) LEDs.
The wireless infrared headphone transmitter operates by converting audio signals into modulated infrared light signals. The audio input is connected to PL1, which serves as the input jack for audio sources. This signal is fed into the VCO section of the 4046 PLL chip, where it is frequency modulated. The VCO generates a signal that varies in frequency according to the amplitude of the audio input.
The output of the VCO is then used to control Q1, a switching transistor. This transistor acts as an electronic switch, allowing the modulated signal to drive two infrared LEDs. The modulation of the current through these LEDs corresponds to the audio input, resulting in an infrared light signal that carries the audio information.
The two IR LEDs are positioned to emit infrared light in a direction where the receiving headphones can capture the signal. The headphones contain a photodetector that demodulates the IR light back into an audio signal, allowing the user to hear the transmitted audio wirelessly.
This design ensures efficient transmission of audio signals over a short distance, making it suitable for applications such as home theater systems or personal audio devices. The use of infrared light for transmission provides a line-of-sight communication method, minimizing interference from other electronic devices.Wireless IR headphone transmitter. Audio input from PL1 frequency modulates the VCO section of a 4046 PLL chip. The VCO output drives Q1, a switching transistor. Q1 drives two IR LEDs. The. 🔗 External reference
The wireless infrared headphone transmitter operates by converting audio signals into modulated infrared light signals. The audio input is connected to PL1, which serves as the input jack for audio sources. This signal is fed into the VCO section of the 4046 PLL chip, where it is frequency modulated. The VCO generates a signal that varies in frequency according to the amplitude of the audio input.
The output of the VCO is then used to control Q1, a switching transistor. This transistor acts as an electronic switch, allowing the modulated signal to drive two infrared LEDs. The modulation of the current through these LEDs corresponds to the audio input, resulting in an infrared light signal that carries the audio information.
The two IR LEDs are positioned to emit infrared light in a direction where the receiving headphones can capture the signal. The headphones contain a photodetector that demodulates the IR light back into an audio signal, allowing the user to hear the transmitted audio wirelessly.
This design ensures efficient transmission of audio signals over a short distance, making it suitable for applications such as home theater systems or personal audio devices. The use of infrared light for transmission provides a line-of-sight communication method, minimizing interference from other electronic devices.Wireless IR headphone transmitter. Audio input from PL1 frequency modulates the VCO section of a 4046 PLL chip. The VCO output drives Q1, a switching transistor. Q1 drives two IR LEDs. The. 🔗 External reference