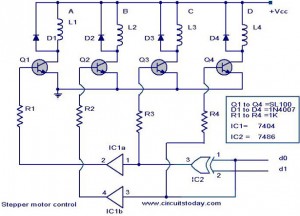
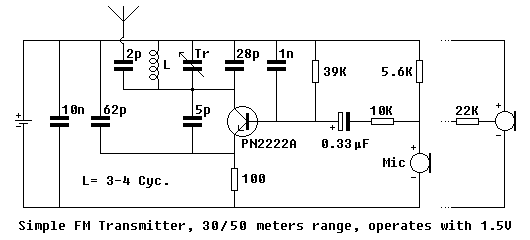
YENKA simple series circuit voltage diagram. voltages calculated problem
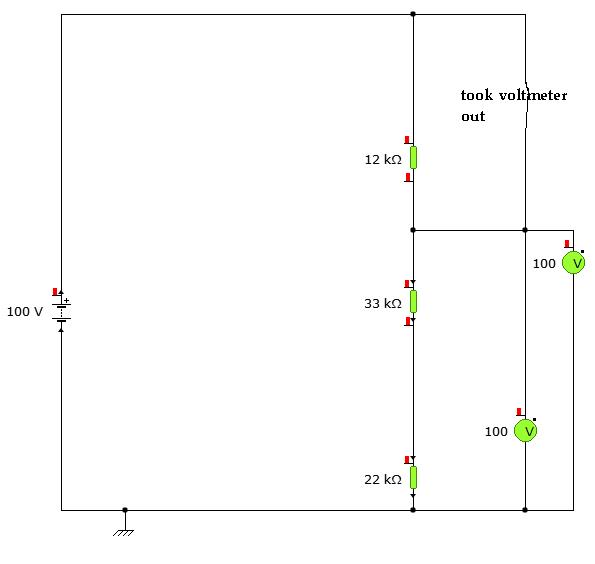
A user is utilizing YENKA software to diagram circuits but is experiencing confusion regarding the voltage calculations in a basic series circuit, as illustrated in the attached image.
In a basic series circuit, components are connected end-to-end, forming a single path for current flow. The total voltage supplied by the power source is distributed across the components. According to Ohm's Law, the voltage drop across each component can be determined by the formula V = I * R, where V represents the voltage drop, I is the current flowing through the circuit, and R is the resistance of the component.
In a series circuit, the current remains constant throughout all components, while the total resistance is the sum of the individual resistances. The total voltage across the circuit is equal to the sum of the individual voltage drops across each component. For example, if a series circuit consists of a 12V power supply and two resistors of 4Ω and 8Ω, the total resistance would be 12Ω. The current flowing through the circuit can be calculated using Ohm's Law: I = V / R = 12V / 12Ω = 1A.
The voltage drop across each resistor can then be calculated: for the 4Ω resistor, V1 = I * R1 = 1A * 4Ω = 4V, and for the 8Ω resistor, V2 = I * R2 = 1A * 8Ω = 8V. The sum of the voltage drops (4V + 8V) equals the total voltage supplied (12V), confirming the principle of conservation of energy in the circuit.
YENKA software can facilitate the visualization of these calculations and the overall circuit behavior, providing a dynamic environment for exploring circuit theory and practical applications. Understanding these principles is crucial for accurate circuit design and analysis.hi, i am using YENKA to diagram circuits. i dont get what it is doing when working out voltages in a basic series circuit. the picattached showsthe.. 🔗 External reference
In a basic series circuit, components are connected end-to-end, forming a single path for current flow. The total voltage supplied by the power source is distributed across the components. According to Ohm's Law, the voltage drop across each component can be determined by the formula V = I * R, where V represents the voltage drop, I is the current flowing through the circuit, and R is the resistance of the component.
In a series circuit, the current remains constant throughout all components, while the total resistance is the sum of the individual resistances. The total voltage across the circuit is equal to the sum of the individual voltage drops across each component. For example, if a series circuit consists of a 12V power supply and two resistors of 4Ω and 8Ω, the total resistance would be 12Ω. The current flowing through the circuit can be calculated using Ohm's Law: I = V / R = 12V / 12Ω = 1A.
The voltage drop across each resistor can then be calculated: for the 4Ω resistor, V1 = I * R1 = 1A * 4Ω = 4V, and for the 8Ω resistor, V2 = I * R2 = 1A * 8Ω = 8V. The sum of the voltage drops (4V + 8V) equals the total voltage supplied (12V), confirming the principle of conservation of energy in the circuit.
YENKA software can facilitate the visualization of these calculations and the overall circuit behavior, providing a dynamic environment for exploring circuit theory and practical applications. Understanding these principles is crucial for accurate circuit design and analysis.hi, i am using YENKA to diagram circuits. i dont get what it is doing when working out voltages in a basic series circuit. the picattached showsthe.. 🔗 External reference