zener diode tester schematic
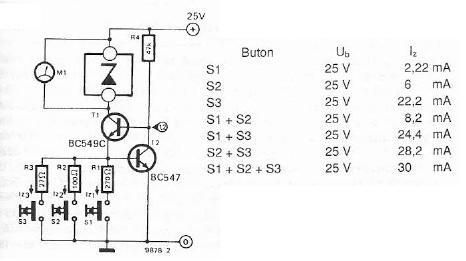
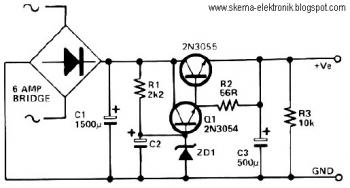
The electronic scheme provided can be used to design a Zener diode tester utilizing a few electronic components. This Zener tester, in conjunction with a multimeter, allows for the precise measurement of the threshold voltage of a Zener diode. The Zener voltage can be read using a DC voltmeter connected in parallel with the Zener diode. When contact S1 is closed, the resistors R1, T1, and the Zener diode allow current to flow. The base of transistor T1 is connected to the power supply through resistor R4, enabling the transistor to conduct. The Zener current is determined by the ratio of the base-emitter voltage of transistor Q2 to the resistance value of R1. With a supply voltage of 25 volts activated by switches S1 to S3, the current through the Zener diode can be approximately 2 mA, 6 mA, and 22 mA. Resistors R2 and R3, or a combination of R1, R2, and R3, can be connected in place of R1 using switches S2 and S3 to ensure a constant current flows through the Zener diode.
The Zener diode tester circuit comprises several essential components, including resistors, transistors, and switches, which work together to facilitate accurate measurements of the Zener diode's breakdown voltage. The core of the circuit is the Zener diode, which is connected in parallel with a voltmeter to enable direct voltage readings. When switch S1 is closed, current flows through the circuit, allowing the Zener diode to operate in its breakdown region.
Transistor T1 plays a crucial role in the circuit by regulating the current through the Zener diode. The base of T1 receives voltage from the power supply through resistor R4, which ensures that T1 remains in the 'on' state, allowing current to flow. The current through the Zener diode is influenced by the base-emitter voltage of transistor Q2, which is in turn affected by the value of resistor R1. This relationship allows for precise control of the Zener current, making it possible to measure different current levels accurately.
The circuit is designed to operate with a supply voltage of 25 volts, and by adjusting the configuration of resistors R1, R2, and R3 through switches S2 and S3, the current through the Zener diode can be varied. This adaptability enables the tester to measure Zener diodes with different specifications and characteristics. The ability to switch between different resistor combinations allows for a constant current to flow through the Zener diode, ensuring that the voltage readings obtained are stable and reliable.
Overall, this Zener diode tester circuit is a practical tool for electronics enthusiasts and professionals, providing a straightforward method for evaluating the performance of Zener diodes in various applications.Using electronic scheme below can be designed a zener diode tester using few electronic parts. Using this zener tester and a multimeter can be measured and determined with a high precision threshold voltage of a zener diode. Zener voltage can be read with a DC voltmeter connected in parallel with zener diode. If contact S1 is closed, the resistance R1, T1 and Zener diode current flow. Base transistor T1 is connected to power supply trough the R4, so the transistor conducts. Zener current is equal to the ratio of base-emitter voltage of Q2 and the resistance value R1. With a supply voltage of 25 volts at the actuation keys S1-S3, the current through zener diode take values of about 2. 2, 6 and 22mA. Resistances R2 and R3 or a combination of R1, R2, R3 can be connected in place of R1 with S2-S3 so that through the zener diode constant current flow.
🔗 External reference
The Zener diode tester circuit comprises several essential components, including resistors, transistors, and switches, which work together to facilitate accurate measurements of the Zener diode's breakdown voltage. The core of the circuit is the Zener diode, which is connected in parallel with a voltmeter to enable direct voltage readings. When switch S1 is closed, current flows through the circuit, allowing the Zener diode to operate in its breakdown region.
Transistor T1 plays a crucial role in the circuit by regulating the current through the Zener diode. The base of T1 receives voltage from the power supply through resistor R4, which ensures that T1 remains in the 'on' state, allowing current to flow. The current through the Zener diode is influenced by the base-emitter voltage of transistor Q2, which is in turn affected by the value of resistor R1. This relationship allows for precise control of the Zener current, making it possible to measure different current levels accurately.
The circuit is designed to operate with a supply voltage of 25 volts, and by adjusting the configuration of resistors R1, R2, and R3 through switches S2 and S3, the current through the Zener diode can be varied. This adaptability enables the tester to measure Zener diodes with different specifications and characteristics. The ability to switch between different resistor combinations allows for a constant current to flow through the Zener diode, ensuring that the voltage readings obtained are stable and reliable.
Overall, this Zener diode tester circuit is a practical tool for electronics enthusiasts and professionals, providing a straightforward method for evaluating the performance of Zener diodes in various applications.Using electronic scheme below can be designed a zener diode tester using few electronic parts. Using this zener tester and a multimeter can be measured and determined with a high precision threshold voltage of a zener diode. Zener voltage can be read with a DC voltmeter connected in parallel with zener diode. If contact S1 is closed, the resistance R1, T1 and Zener diode current flow. Base transistor T1 is connected to power supply trough the R4, so the transistor conducts. Zener current is equal to the ratio of base-emitter voltage of Q2 and the resistance value R1. With a supply voltage of 25 volts at the actuation keys S1-S3, the current through zener diode take values of about 2. 2, 6 and 22mA. Resistances R2 and R3 or a combination of R1, R2, R3 can be connected in place of R1 with S2-S3 so that through the zener diode constant current flow.
🔗 External reference