High-quality ultra-linear 10W tube amp
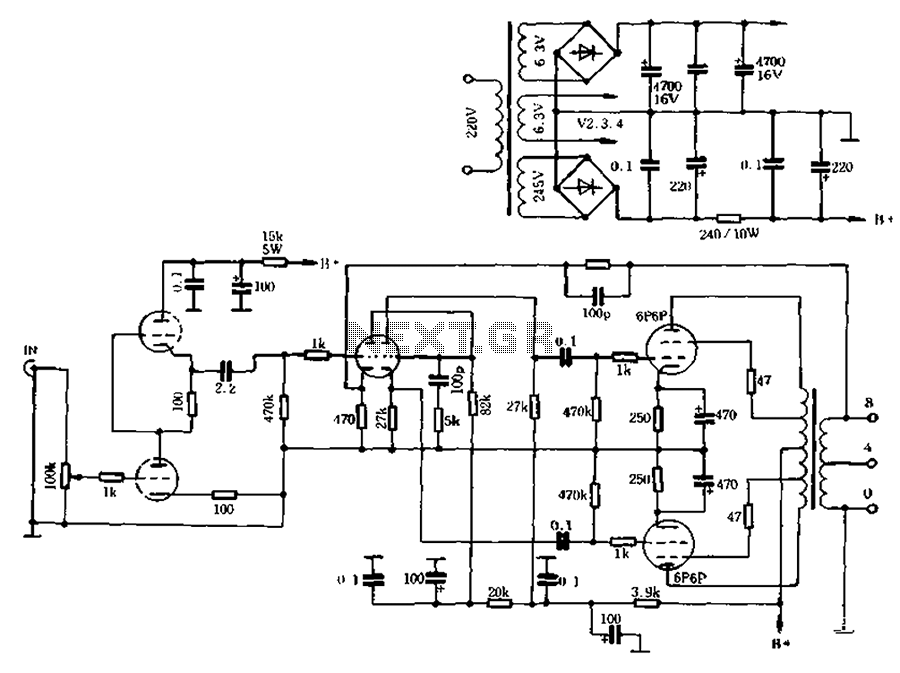
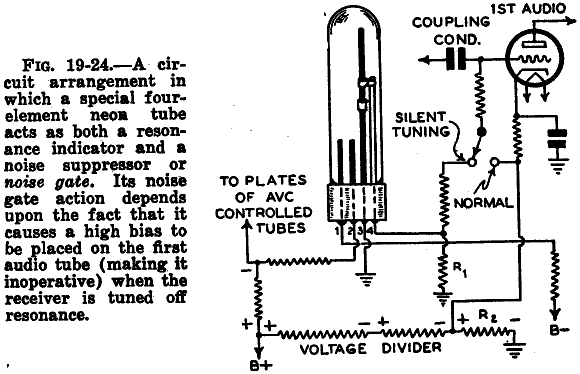
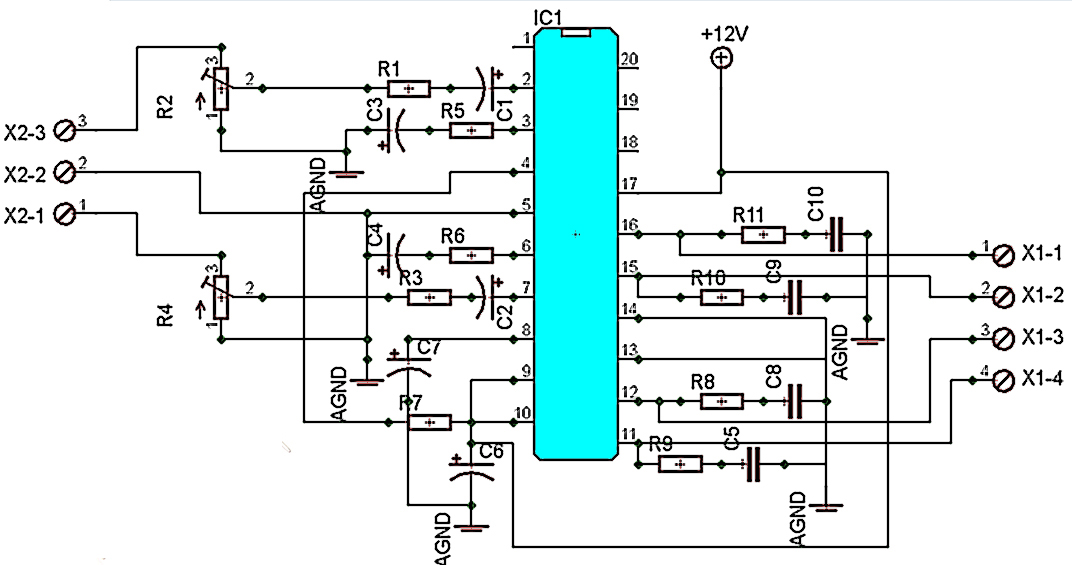
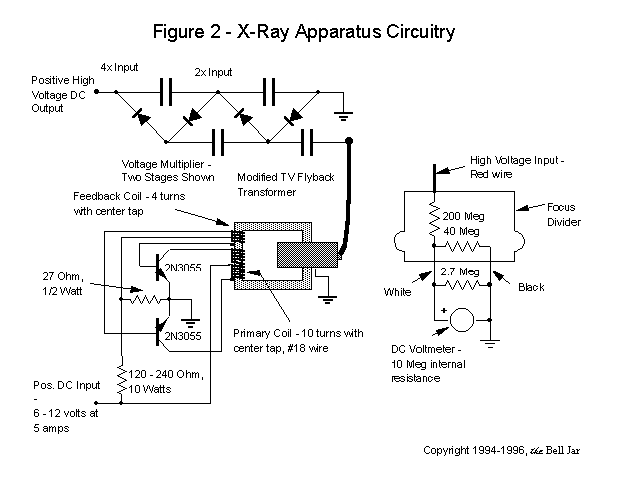
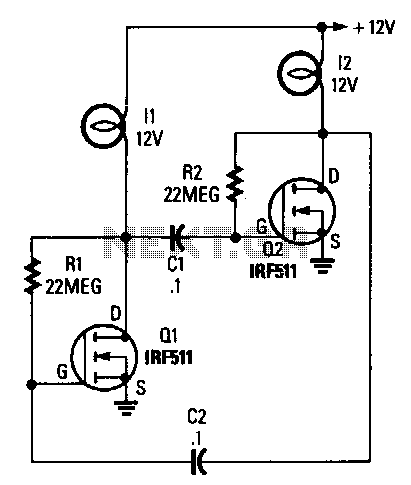
The self-generated bias amplifier tube is designed for each tube individually to alleviate the challenges faced by amateur conditions in paired amplifiers. It includes a separate DC filament power supply, which minimizes the risk of induced cross-linking and enhances the signal-to-noise ratio.
The self-generated bias amplifier circuit is an innovative approach to improve the performance of audio amplification systems, especially in environments where amateur conditions may lead to suboptimal operation. Each amplifier tube is equipped with its own biasing mechanism, ensuring that variations in tube characteristics do not adversely affect the overall sound quality. This method allows for precise control over the operating point of each tube, leading to better linearity and reduced distortion.
The inclusion of a dedicated DC filament power supply is a critical feature of this design. By providing stable and clean power to the filament, the circuit minimizes the potential for noise and interference that can occur when multiple tubes share a common power supply. This separation is essential in maintaining a high signal-to-noise ratio, which is vital for achieving clear and accurate audio reproduction.
Furthermore, the design incorporates protective measures to reduce the chance of induced cross-linking between the tubes. This is particularly important in high-gain applications where feedback and interaction between stages can lead to unwanted oscillations or noise. By isolating the biasing and power supply components for each tube, the circuit enhances the overall reliability and performance of the amplifier.
In summary, the self-generated bias amplifier tube circuit represents a sophisticated solution for audio amplification, particularly in challenging conditions. Its individual tube biasing, dedicated DC filament power supply, and measures to prevent cross-linking collectively contribute to a high-quality audio experience with improved signal integrity.As can be seen from the figure, the self-generated bias amplifier tube for each tube separately to reduce the demanding amateur conditions paired amplifiers camp. Pre-alone DC filament power supply, reducing the chance of induced cross-linking, and raise high signal to noise ratio.
The self-generated bias amplifier circuit is an innovative approach to improve the performance of audio amplification systems, especially in environments where amateur conditions may lead to suboptimal operation. Each amplifier tube is equipped with its own biasing mechanism, ensuring that variations in tube characteristics do not adversely affect the overall sound quality. This method allows for precise control over the operating point of each tube, leading to better linearity and reduced distortion.
The inclusion of a dedicated DC filament power supply is a critical feature of this design. By providing stable and clean power to the filament, the circuit minimizes the potential for noise and interference that can occur when multiple tubes share a common power supply. This separation is essential in maintaining a high signal-to-noise ratio, which is vital for achieving clear and accurate audio reproduction.
Furthermore, the design incorporates protective measures to reduce the chance of induced cross-linking between the tubes. This is particularly important in high-gain applications where feedback and interaction between stages can lead to unwanted oscillations or noise. By isolating the biasing and power supply components for each tube, the circuit enhances the overall reliability and performance of the amplifier.
In summary, the self-generated bias amplifier tube circuit represents a sophisticated solution for audio amplification, particularly in challenging conditions. Its individual tube biasing, dedicated DC filament power supply, and measures to prevent cross-linking collectively contribute to a high-quality audio experience with improved signal integrity.As can be seen from the figure, the self-generated bias amplifier tube for each tube separately to reduce the demanding amateur conditions paired amplifiers camp. Pre-alone DC filament power supply, reducing the chance of induced cross-linking, and raise high signal to noise ratio.