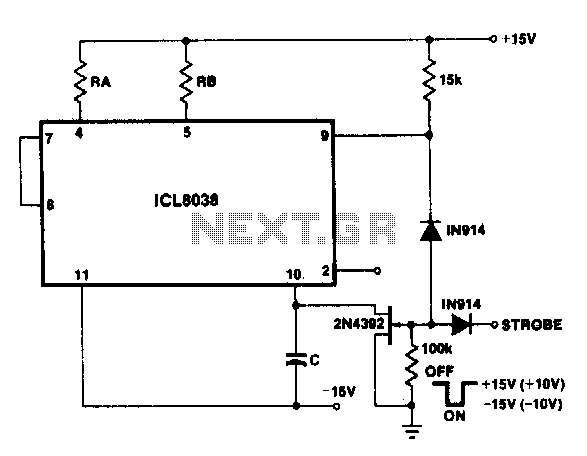
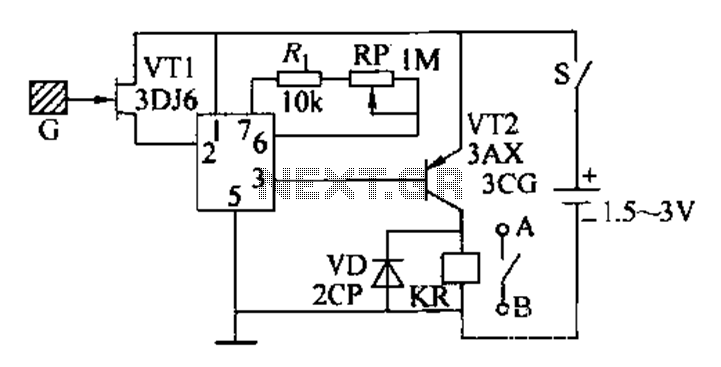
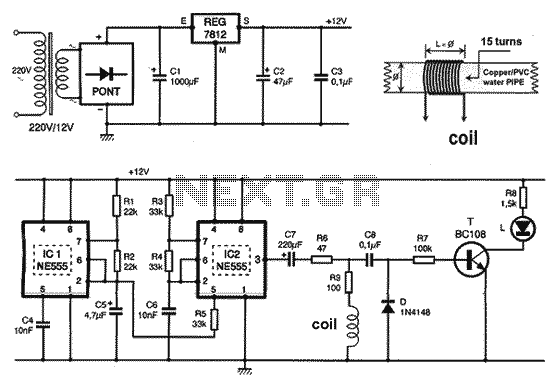
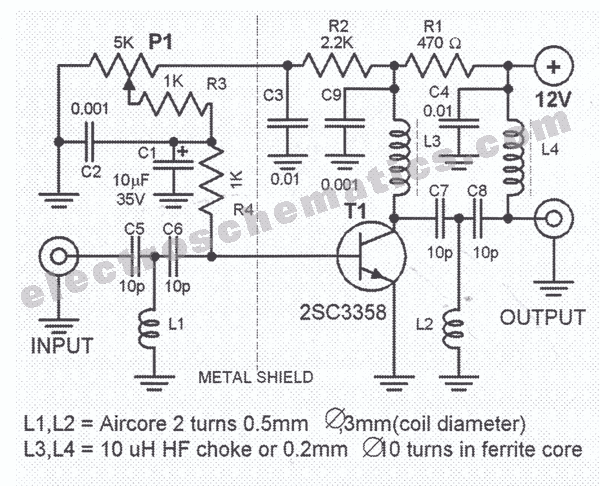
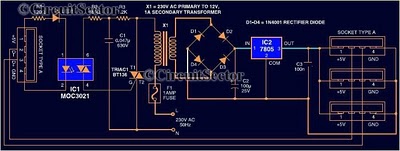
As one of the thyristor type delay circuit
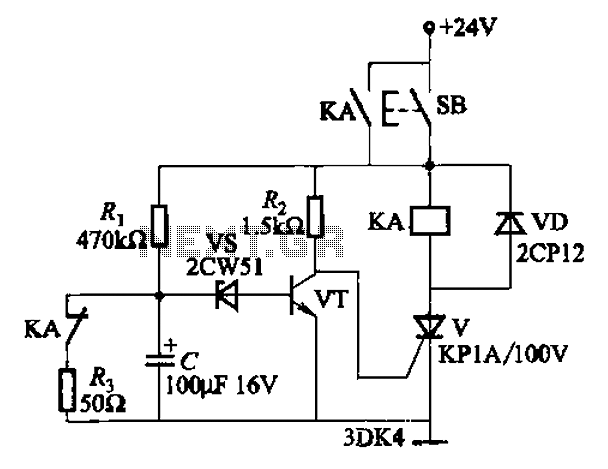
This circuit is a thyristor-based delay circuit known as a cut-off delay. It allows for a specified delay period after the thyristor is activated. The delay time of the circuit can be adjusted within 10 seconds by changing the resistor (Ri), capacitor (C), or voltage source (Vs).
The thyristor cut-off delay circuit functions by utilizing the properties of a thyristor, which is a semiconductor device that can control current flow. Upon receiving a trigger signal, the thyristor enters a conductive state, allowing current to flow through the load. The delay feature is achieved by incorporating passive components, specifically a resistor-capacitor (RC) network, which determines the time it takes for the circuit to respond after the thyristor is triggered.
In this configuration, the resistor (Ri) and capacitor (C) form an RC time constant that dictates the delay duration. The time constant (τ) can be calculated using the formula τ = Ri * C. By adjusting the value of Ri or C, or by modifying the supply voltage (Vs), the delay time can be finely tuned to meet specific requirements.
When the thyristor is triggered, the capacitor begins to charge through the resistor. The charging process continues until the voltage across the capacitor reaches a certain threshold, at which point the thyristor will turn off, effectively cutting off the current flow. The circuit can be used in various applications, such as timing circuits, motor control, and switching operations, where precise delay control is necessary.
Overall, the thyristor cut-off delay circuit is a versatile and effective solution for implementing time delays in electronic systems. Its simplicity and adjustability make it suitable for a wide range of applications in both industrial and consumer electronics.As one of the thyristor type delay circuit The so-called cut-off delay, that is, after a period of delay after the closure of the thyristor. The delay time of the circuit withi n lOs, change Ri (C or vs) can adjust the delay amount.
The thyristor cut-off delay circuit functions by utilizing the properties of a thyristor, which is a semiconductor device that can control current flow. Upon receiving a trigger signal, the thyristor enters a conductive state, allowing current to flow through the load. The delay feature is achieved by incorporating passive components, specifically a resistor-capacitor (RC) network, which determines the time it takes for the circuit to respond after the thyristor is triggered.
In this configuration, the resistor (Ri) and capacitor (C) form an RC time constant that dictates the delay duration. The time constant (τ) can be calculated using the formula τ = Ri * C. By adjusting the value of Ri or C, or by modifying the supply voltage (Vs), the delay time can be finely tuned to meet specific requirements.
When the thyristor is triggered, the capacitor begins to charge through the resistor. The charging process continues until the voltage across the capacitor reaches a certain threshold, at which point the thyristor will turn off, effectively cutting off the current flow. The circuit can be used in various applications, such as timing circuits, motor control, and switching operations, where precise delay control is necessary.
Overall, the thyristor cut-off delay circuit is a versatile and effective solution for implementing time delays in electronic systems. Its simplicity and adjustability make it suitable for a wide range of applications in both industrial and consumer electronics.As one of the thyristor type delay circuit The so-called cut-off delay, that is, after a period of delay after the closure of the thyristor. The delay time of the circuit withi n lOs, change Ri (C or vs) can adjust the delay amount.