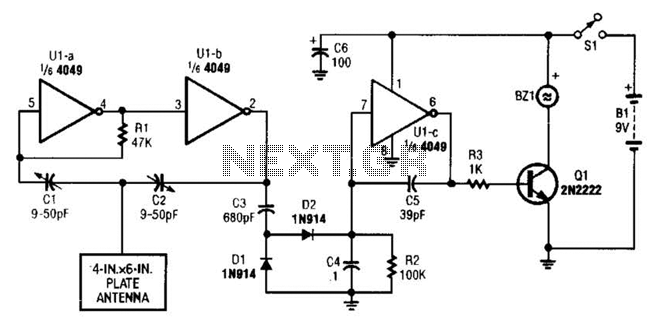
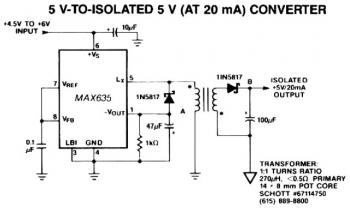
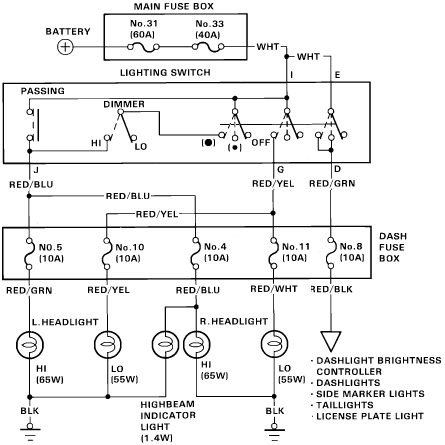
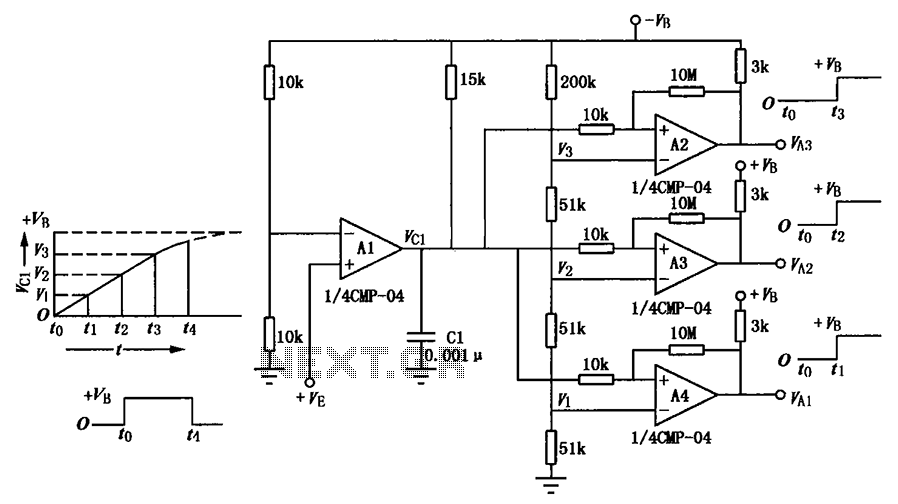
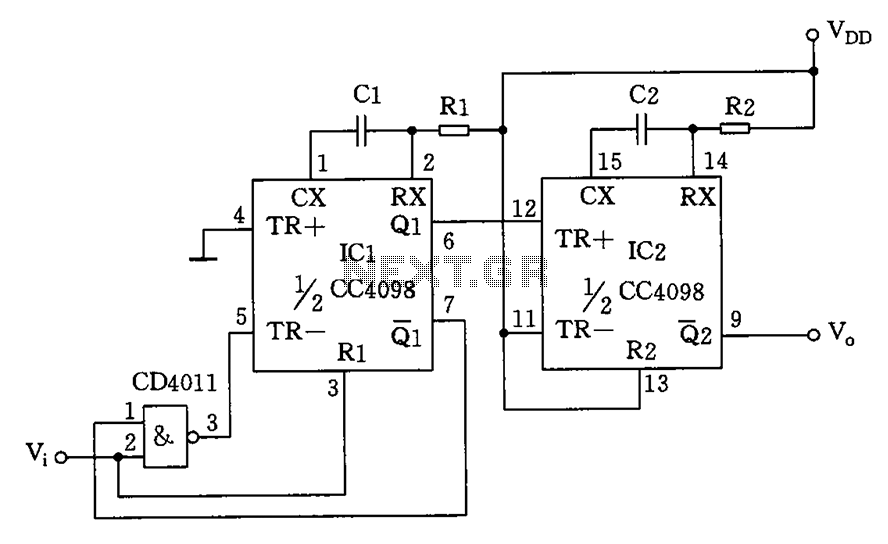
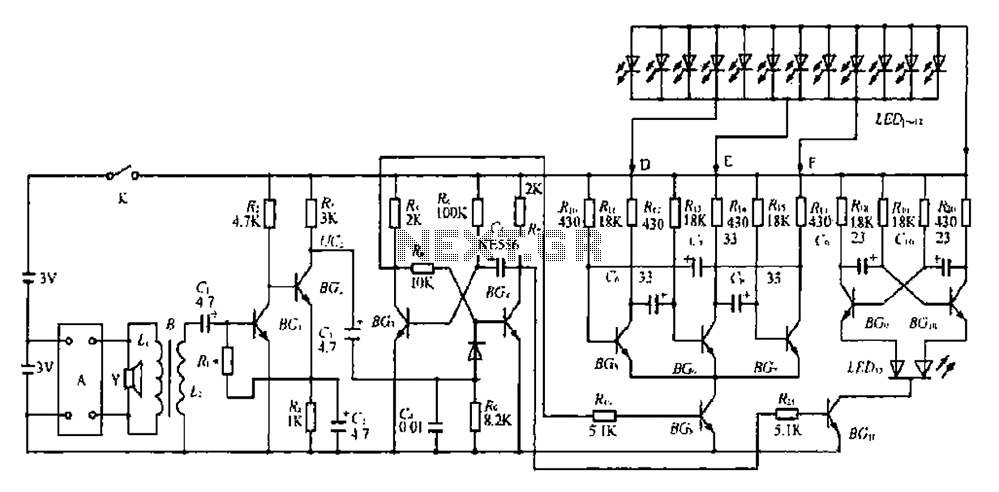
Panasonic M12H switching power supply circuit diagram
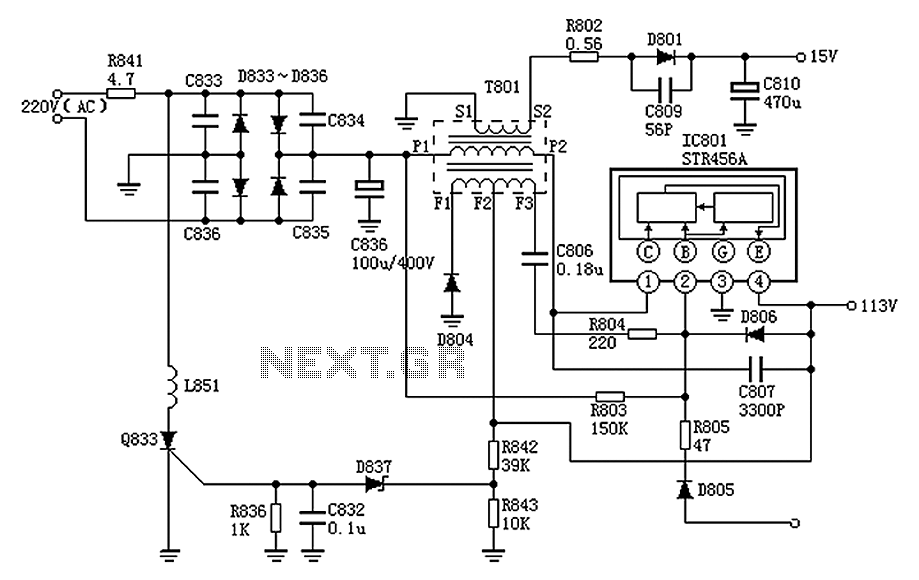
The Panasonic M12H switching power supply circuit is utilized in Panasonic models such as TC-230H, TC-2030DHN, TC-830D, and TC-840D. The circuit operates with an oscillation frequency that generates approximately 300V DC voltage at C836. The T801 transformer is involved in the switching process, where the primary winding P1 and P2 are connected to the internal switching tube of IC801. The operation begins when the switch B pole of IC801 conducts via R803, allowing current to flow from the E pole at pin 4 of IC801. As the current through the P1 winding of T801 increases, it induces a voltage in the F2 and F3 windings. This induced voltage has a positive polarity at F2 and a negative polarity at F3, which is coupled through C806 and R804 back to pins 2 and 4 of IC801, enhancing the switch current and creating a strong positive feedback loop that quickly saturates the switch.
Once saturation occurs, the voltage across the primary winding of T801 increases linearly, resulting in a DC voltage of 113V at pin 4 of IC801 while the transformer stores magnetic energy. As C806 continues to charge, the voltage at pin 2 of IC801 decreases, eventually causing the internal switch to exit saturation. When the switch is off, the current in the P1 and P2 windings of T801 decreases, causing the induced voltage polarities to reverse. This reduction in switch current leads to a rapid cycle of switching. After the switch turns off, the voltage at the S1 and S2 windings allows D801 to conduct, establishing a voltage of 16V across C810. Additionally, F1 and F3 windings allow D804 to conduct, releasing the stored magnetic energy from T801 to the 113V load. The discharging of the F2 and F3 windings through C806, R804, and D806 leads to a reverse charge at C806, which increases the voltage at pin 2 of IC801, facilitating the generation of flyback pulses through D805 and R805 that trigger the next oscillation cycle. The regulation of the circuit is managed automatically by the STR456A component. A protection circuit is included; if the 113V voltage rises excessively, R842 and R843 create a voltage drop that activates D837, leading to the conduction of SCR Q833, resulting in a short circuit of the 220V AC supply and blowing the fuse for safety.
This circuit design demonstrates a robust switching power supply mechanism, utilizing feedback loops for stabilization and regulation, while incorporating protective measures to prevent overvoltage conditions. The arrangement of components ensures efficient energy transfer and operational reliability across the specified Panasonic television models. As shown Panasonic M12H switching power supply circuit, the use of Panasonic movement M12H TV: Panasonic TC-230H, TC-2030DHN, TC-830D, TC-840D and the like. Oscillation Approxi mately 300V DC voltage on the C836, T801 all the way through the P1, P2 winding added IC801 (1) foot internal switching tube C pole, but added IC801 via R803 (2) foot internal switch B pole switch tube starts conducting, E pole current from IC801 (4) feet outflow. T801 of P1, P1 winding current increases, the induced voltage coupled to F2, F3 winding induced voltage polarity at this time F2, F3 winding is positive F2 F3 negative voltage through C806, R804 added IC801 (2 ), (4) feet, so that the switch current is further increased, a strong positive feedback switch rapidly saturated.
After saturation the switch, the voltage of the primary winding increases linearly T801, on the one hand in the IC801 (4) is formed pin 113V DC voltage, while T801 stored magnetic energy. With the C806 continue to be charged and the IC801 (2) pin voltage falling, and finally the internal switch out of saturation.
Once the switch out of saturation, T801 of P1, P2 winding current decreases, T801 each winding induced voltage polarity will flip, F2, F3 voltage winding and through C806, R804 to IC801 (2), (4 ) feet, so that switch current is further reduced, so the cycle to switch off quickly. After switching off, T801 S1, S2 voltage windings so D801 is turned on, the voltage on the establishment 16V C810; F1, F3 winding D804 also allows conduction, T801 stored magnetic energy is released by the D804 to 113V load, while the C806 through R804, D806, T801 of F2, F3 winding discharge, 300V voltage by R803 to C806 reverse charging, so (2) IC801 pin voltage rise, the line flyback pulses also through D805, R805 to IC801 (2) feet, IC801 advance turned on to start another cycle of oscillation.
Regulator circuit Regulator circuit is done automatically by STR456A inside. Protection circuit If 113V voltage increases, the R842, R843 partial pressure after D837 conduction, SCR Q833 conduction, 220V AC is short-circuited, the fuse burned.
Once saturation occurs, the voltage across the primary winding of T801 increases linearly, resulting in a DC voltage of 113V at pin 4 of IC801 while the transformer stores magnetic energy. As C806 continues to charge, the voltage at pin 2 of IC801 decreases, eventually causing the internal switch to exit saturation. When the switch is off, the current in the P1 and P2 windings of T801 decreases, causing the induced voltage polarities to reverse. This reduction in switch current leads to a rapid cycle of switching. After the switch turns off, the voltage at the S1 and S2 windings allows D801 to conduct, establishing a voltage of 16V across C810. Additionally, F1 and F3 windings allow D804 to conduct, releasing the stored magnetic energy from T801 to the 113V load. The discharging of the F2 and F3 windings through C806, R804, and D806 leads to a reverse charge at C806, which increases the voltage at pin 2 of IC801, facilitating the generation of flyback pulses through D805 and R805 that trigger the next oscillation cycle. The regulation of the circuit is managed automatically by the STR456A component. A protection circuit is included; if the 113V voltage rises excessively, R842 and R843 create a voltage drop that activates D837, leading to the conduction of SCR Q833, resulting in a short circuit of the 220V AC supply and blowing the fuse for safety.
This circuit design demonstrates a robust switching power supply mechanism, utilizing feedback loops for stabilization and regulation, while incorporating protective measures to prevent overvoltage conditions. The arrangement of components ensures efficient energy transfer and operational reliability across the specified Panasonic television models. As shown Panasonic M12H switching power supply circuit, the use of Panasonic movement M12H TV: Panasonic TC-230H, TC-2030DHN, TC-830D, TC-840D and the like. Oscillation Approxi mately 300V DC voltage on the C836, T801 all the way through the P1, P2 winding added IC801 (1) foot internal switching tube C pole, but added IC801 via R803 (2) foot internal switch B pole switch tube starts conducting, E pole current from IC801 (4) feet outflow. T801 of P1, P1 winding current increases, the induced voltage coupled to F2, F3 winding induced voltage polarity at this time F2, F3 winding is positive F2 F3 negative voltage through C806, R804 added IC801 (2 ), (4) feet, so that the switch current is further increased, a strong positive feedback switch rapidly saturated.
After saturation the switch, the voltage of the primary winding increases linearly T801, on the one hand in the IC801 (4) is formed pin 113V DC voltage, while T801 stored magnetic energy. With the C806 continue to be charged and the IC801 (2) pin voltage falling, and finally the internal switch out of saturation.
Once the switch out of saturation, T801 of P1, P2 winding current decreases, T801 each winding induced voltage polarity will flip, F2, F3 voltage winding and through C806, R804 to IC801 (2), (4 ) feet, so that switch current is further reduced, so the cycle to switch off quickly. After switching off, T801 S1, S2 voltage windings so D801 is turned on, the voltage on the establishment 16V C810; F1, F3 winding D804 also allows conduction, T801 stored magnetic energy is released by the D804 to 113V load, while the C806 through R804, D806, T801 of F2, F3 winding discharge, 300V voltage by R803 to C806 reverse charging, so (2) IC801 pin voltage rise, the line flyback pulses also through D805, R805 to IC801 (2) feet, IC801 advance turned on to start another cycle of oscillation.
Regulator circuit Regulator circuit is done automatically by STR456A inside. Protection circuit If 113V voltage increases, the R842, R843 partial pressure after D837 conduction, SCR Q833 conduction, 220V AC is short-circuited, the fuse burned.