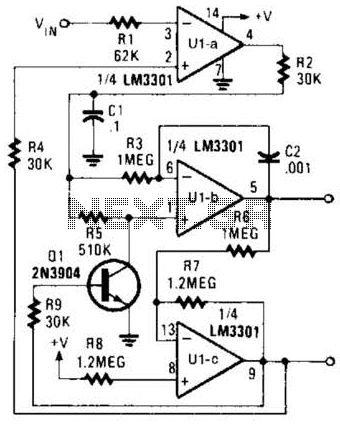
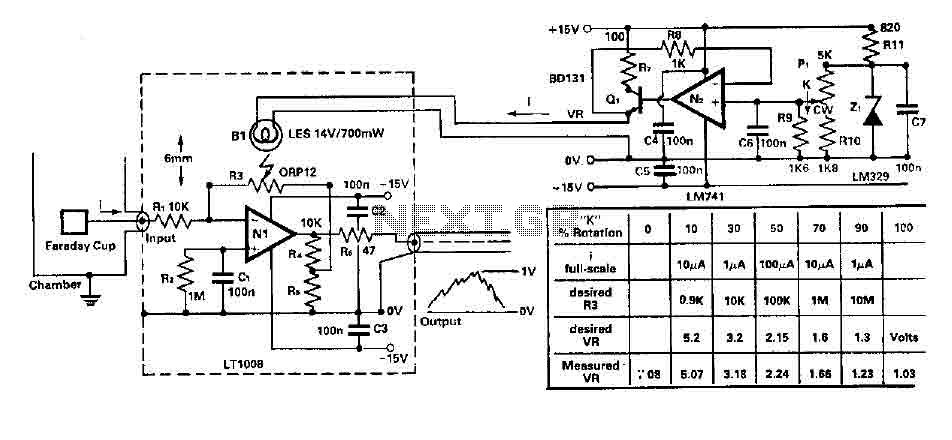
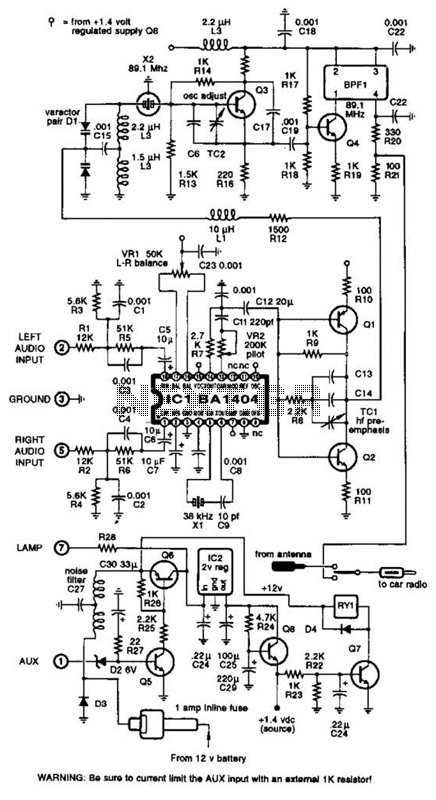
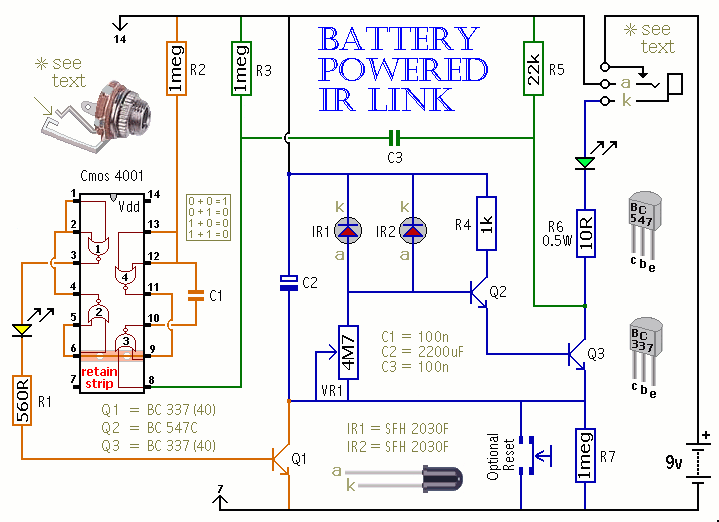
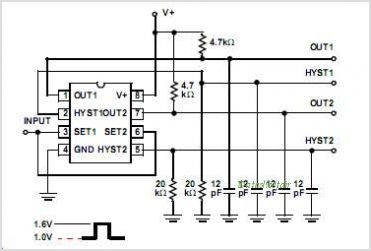
Basic circuit diagram connection of signal and power INA166
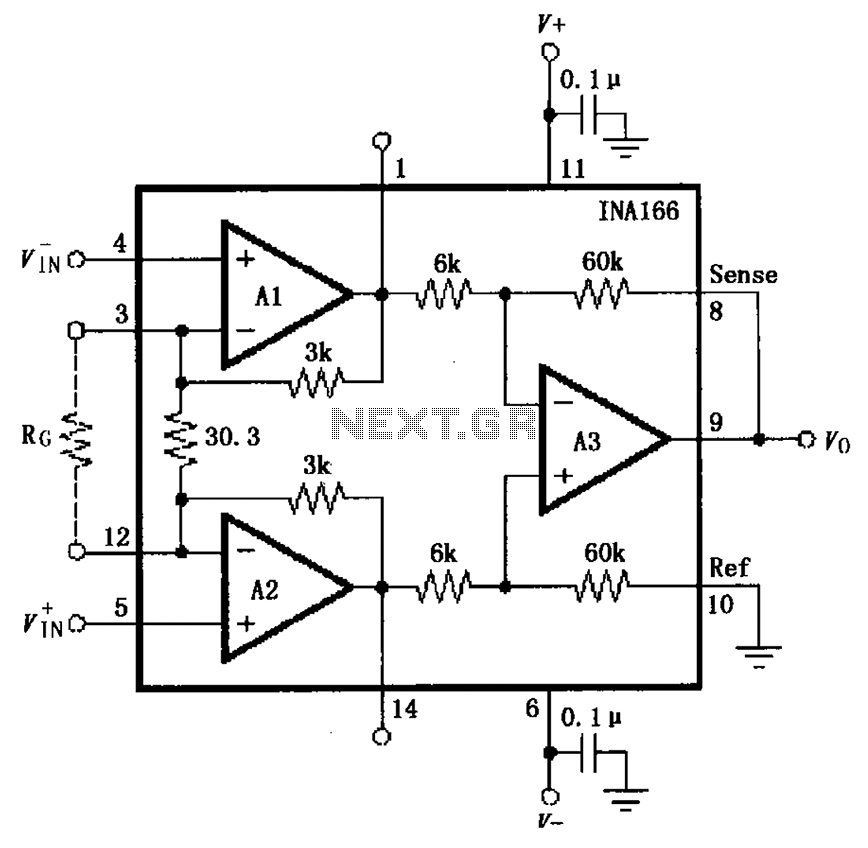
The basic connection circuit for the INA166 includes signal and power connections. A 0.1 µF tantalum capacitor should be used for filtering the chip's power supply terminal, and the PCB layout should be designed to position this capacitor as close to the chip as possible. The placement of the tantalum capacitor at the power pin is crucial. The sense output voltage detection terminal must be connected to the reference terminal (Ref) with low resistance to ensure a high common-mode rejection ratio; using a 5-ohm series resistor can decrease this ratio. The internal fixed gain of the INA166 is 2000, with the input stage amplifiers A1 and A2 having a gain of 200, and the output stage amplifier A3 having a gain of 10. A gain-setting resistor, RG, should be added between pins 3 and 12 to adjust the amplifier gain, calculated as G = 2000 + 60000/RG.
The INA166 is a precision instrumentation amplifier designed for high common-mode rejection and low noise operation. The circuit configuration requires careful attention to component placement and values to optimize performance. The use of a 0.1 µF tantalum capacitor at the power supply terminal is essential for stabilizing the power input and filtering out high-frequency noise, which can adversely affect the amplifier's performance. The PCB layout should minimize the distance between the capacitor and the chip to reduce inductive effects, which can introduce voltage drops and noise.
For the sense output voltage detection, the reference terminal must be connected with low resistance to maintain the integrity of the common-mode rejection ratio. This is critical in applications where the amplifier is subjected to varying common-mode voltages, as a higher common-mode rejection results in improved accuracy and signal fidelity. The specification indicates that introducing a 5-ohm series resistor can significantly reduce the common-mode rejection ratio, which must be avoided to ensure optimal performance.
The internal gain structure of the INA166 is designed to provide a high overall gain of 2000, with the first two stages contributing significantly to this gain. The input stages A1 and A2 have a gain of 200, while the output stage A3 amplifies the signal with a gain of 10. The addition of a gain-setting resistor RG between pins 3 and 12 allows for further customization of the amplifier's gain, making it adaptable to various applications. The gain formula, G = 2000 + 60000/RG, illustrates how the choice of RG directly influences the overall gain, allowing for precise adjustments based on the specific requirements of the circuit.
Overall, careful consideration of component selection, placement, and circuit design is essential for maximizing the performance of the INA166 in precision measurement applications. Proper adherence to these guidelines will ensure that the amplifier operates effectively, providing accurate and reliable signal amplification. As shown for the basic connection circuit INA166 signals and power. Chip power supply terminal to use 0.1 F tantalum capacitor filter, PCB layout should be as close to the chip tantalum capacitor power pin placement. Sense output voltage detection terminal connection, the connection must be reference terminal Ref low resistance connections to ensure a high common mode rejection ratio, if 5 series resistor will result in the common-mode rejection ratio decreased. Internal fixed gain of 2000, wherein the input stage A1, A2 gain 200, the gain of the output stage 10 A3.
Between 3 feet and 12 feet to increase a gain setting resistor, RG can change the amplifier gain, the gain G 2000 + 60000/RG.
The INA166 is a precision instrumentation amplifier designed for high common-mode rejection and low noise operation. The circuit configuration requires careful attention to component placement and values to optimize performance. The use of a 0.1 µF tantalum capacitor at the power supply terminal is essential for stabilizing the power input and filtering out high-frequency noise, which can adversely affect the amplifier's performance. The PCB layout should minimize the distance between the capacitor and the chip to reduce inductive effects, which can introduce voltage drops and noise.
For the sense output voltage detection, the reference terminal must be connected with low resistance to maintain the integrity of the common-mode rejection ratio. This is critical in applications where the amplifier is subjected to varying common-mode voltages, as a higher common-mode rejection results in improved accuracy and signal fidelity. The specification indicates that introducing a 5-ohm series resistor can significantly reduce the common-mode rejection ratio, which must be avoided to ensure optimal performance.
The internal gain structure of the INA166 is designed to provide a high overall gain of 2000, with the first two stages contributing significantly to this gain. The input stages A1 and A2 have a gain of 200, while the output stage A3 amplifies the signal with a gain of 10. The addition of a gain-setting resistor RG between pins 3 and 12 allows for further customization of the amplifier's gain, making it adaptable to various applications. The gain formula, G = 2000 + 60000/RG, illustrates how the choice of RG directly influences the overall gain, allowing for precise adjustments based on the specific requirements of the circuit.
Overall, careful consideration of component selection, placement, and circuit design is essential for maximizing the performance of the INA166 in precision measurement applications. Proper adherence to these guidelines will ensure that the amplifier operates effectively, providing accurate and reliable signal amplification. As shown for the basic connection circuit INA166 signals and power. Chip power supply terminal to use 0.1 F tantalum capacitor filter, PCB layout should be as close to the chip tantalum capacitor power pin placement. Sense output voltage detection terminal connection, the connection must be reference terminal Ref low resistance connections to ensure a high common mode rejection ratio, if 5 series resistor will result in the common-mode rejection ratio decreased. Internal fixed gain of 2000, wherein the input stage A1, A2 gain 200, the gain of the output stage 10 A3.
Between 3 feet and 12 feet to increase a gain setting resistor, RG can change the amplifier gain, the gain G 2000 + 60000/RG.