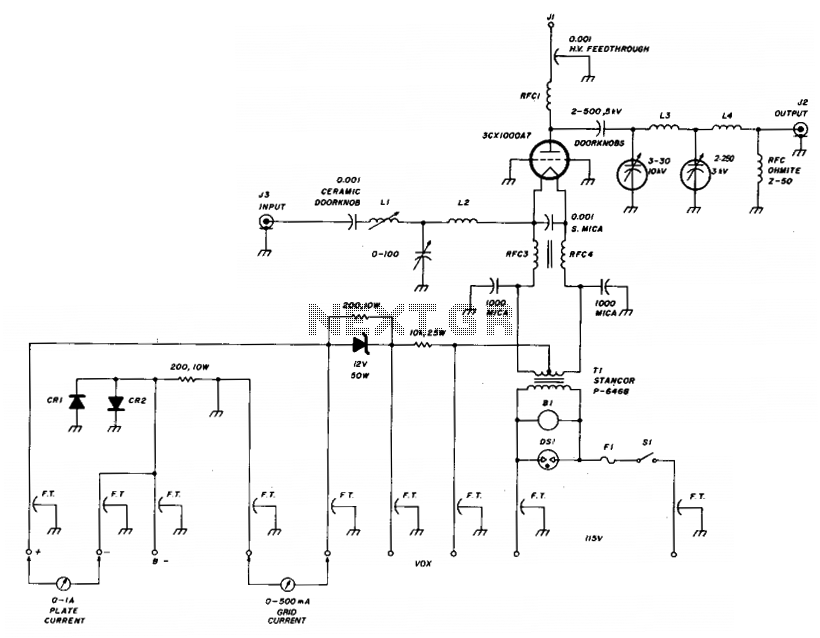
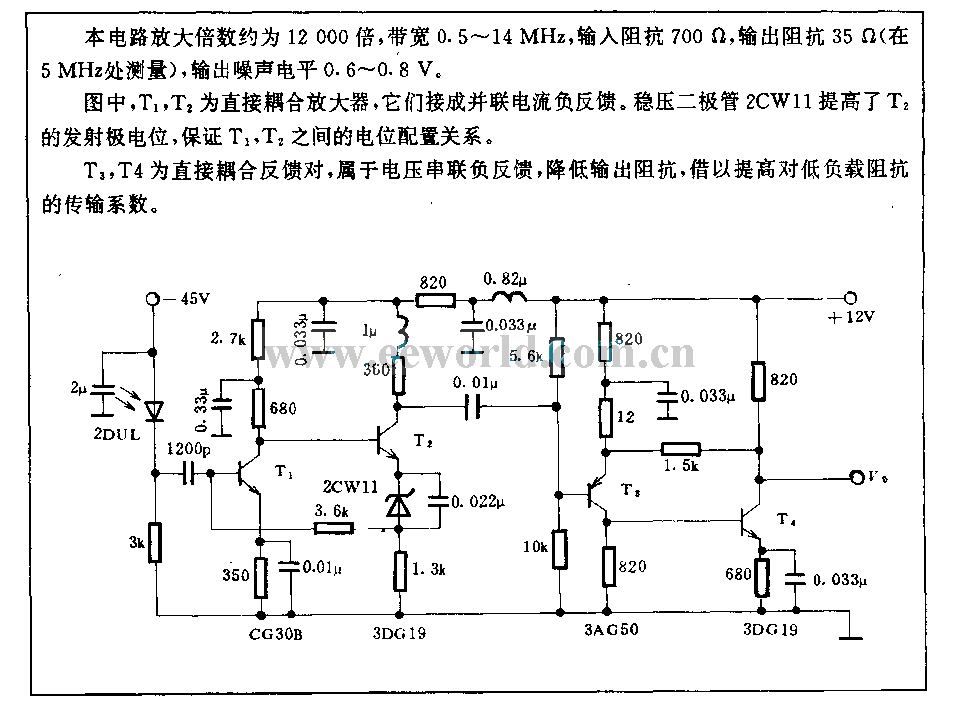
Light circuit diagram: Audio Graphic Equalizer Circuit Using Op Amp

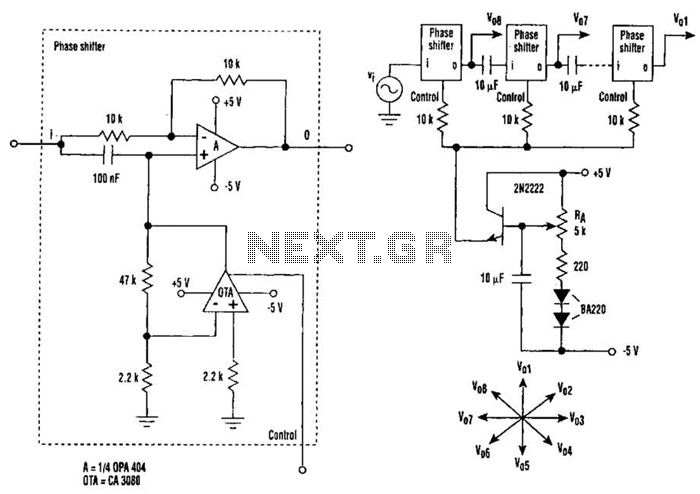
This design circuit is for audio graphic equalizers, which are commonly found in commercial products, yet circuits for them are rarely published. The circuit features a simple design that requires an operational amplifier (op-amp) to amplify the input signal. The figure of the circuit illustrates one gyrator stage; all seven gyrators are identical, with only the capacitors varying as indicated in the chart. Three of the seven faders are shown to demonstrate their placement. A gyrator is a circuit that employs active devices and transistors to simulate an inductor. In this instance, the gyrator consists of a transistor interacting with resistors R1, R3, and capacitor C2. A unity gain op-amp could also be utilized. The circuit includes three formulas: the first determines the center frequency (f) of the band, the second relates the quality factor (Q) to the capacitor ratio, and the third describes the impedance presented by the circuit. This impedance comprises three components: a purely resistive term, a capacitive contribution from C1, and an inductive term from the gyrator.
The audio graphic equalizer circuit is designed to manipulate audio signals across multiple frequency bands, allowing users to enhance or attenuate specific frequencies according to their preferences. The heart of the circuit is the operational amplifier, which serves as the primary amplification stage. The inclusion of gyrators in the design allows for the emulation of inductive behavior without the need for physical inductors, which can be bulky and expensive. Each gyrator stage is configured to create a bandpass filter, with the center frequency and quality factor adjustable through the selection of capacitors and resistors.
The operational amplifier may be configured in a non-inverting mode to ensure that the output signal remains in phase with the input signal, providing a clean amplification of the audio input. The gyrator's functionality is enhanced by the interaction between the resistors and capacitors, which defines the frequency response of each band. The three formulas included in the circuit design are crucial for understanding and optimizing its performance. The center frequency formula allows for precise tuning of each band, while the Q factor formula aids in determining the bandwidth of the filter. The impedance formula is essential for assessing how the circuit interacts with the connected audio components, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance.
In summary, this audio graphic equalizer circuit design emphasizes simplicity and effectiveness, utilizing operational amplifiers and gyrators to create a versatile tool for audio processing. The design's flexibility in adjusting frequency response and quality factors makes it suitable for various audio applications, from home audio systems to professional sound equipment.This is a design circuit for audio graphic equalizers, that are very common as commercial products but circuits for them are very rarely published. This circuit is a simple design circuit. The circuit is need an op-amp for amplifying the input signal. This is the figure of the circuit. Only one gyrator stage is shown: all 7 gyrators are the same c ircuit, only the capacitors change, as shown in the chart. I have shown three of the seven faders to show where they go. A gyrator is a circuit using active devices and transistors to simulate an inductor. In this case the gyrator is the transistor acting with R1, R3 and C2. It could just as easily be a unity gain op-amp. The circuit includes three formulae: one which gives f, the the centre frequency of the band. The second shows how the Q is related to the capacitor ratio. The third shows the impedance presented by the circuit. Note that this includes 3 terms, the first purely resistive, the second is the capacitive contribution from C1 and the third is an inductive term from the gyrator. 🔗 External reference
The audio graphic equalizer circuit is designed to manipulate audio signals across multiple frequency bands, allowing users to enhance or attenuate specific frequencies according to their preferences. The heart of the circuit is the operational amplifier, which serves as the primary amplification stage. The inclusion of gyrators in the design allows for the emulation of inductive behavior without the need for physical inductors, which can be bulky and expensive. Each gyrator stage is configured to create a bandpass filter, with the center frequency and quality factor adjustable through the selection of capacitors and resistors.
The operational amplifier may be configured in a non-inverting mode to ensure that the output signal remains in phase with the input signal, providing a clean amplification of the audio input. The gyrator's functionality is enhanced by the interaction between the resistors and capacitors, which defines the frequency response of each band. The three formulas included in the circuit design are crucial for understanding and optimizing its performance. The center frequency formula allows for precise tuning of each band, while the Q factor formula aids in determining the bandwidth of the filter. The impedance formula is essential for assessing how the circuit interacts with the connected audio components, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance.
In summary, this audio graphic equalizer circuit design emphasizes simplicity and effectiveness, utilizing operational amplifiers and gyrators to create a versatile tool for audio processing. The design's flexibility in adjusting frequency response and quality factors makes it suitable for various audio applications, from home audio systems to professional sound equipment.This is a design circuit for audio graphic equalizers, that are very common as commercial products but circuits for them are very rarely published. This circuit is a simple design circuit. The circuit is need an op-amp for amplifying the input signal. This is the figure of the circuit. Only one gyrator stage is shown: all 7 gyrators are the same c ircuit, only the capacitors change, as shown in the chart. I have shown three of the seven faders to show where they go. A gyrator is a circuit using active devices and transistors to simulate an inductor. In this case the gyrator is the transistor acting with R1, R3 and C2. It could just as easily be a unity gain op-amp. The circuit includes three formulae: one which gives f, the the centre frequency of the band. The second shows how the Q is related to the capacitor ratio. The third shows the impedance presented by the circuit. Note that this includes 3 terms, the first purely resistive, the second is the capacitive contribution from C1 and the third is an inductive term from the gyrator. 🔗 External reference