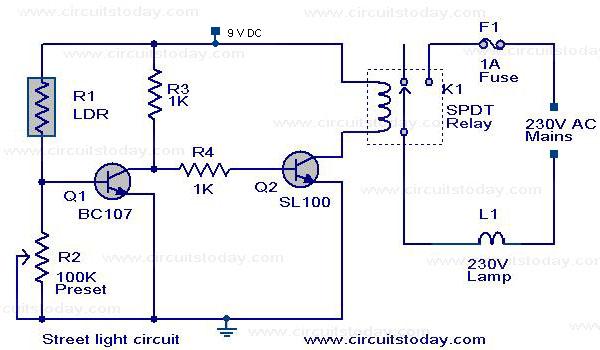
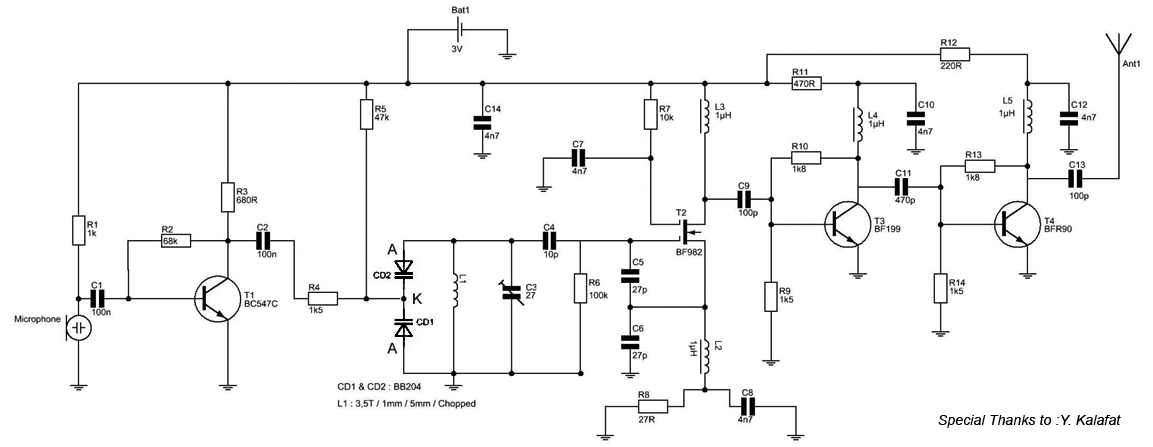
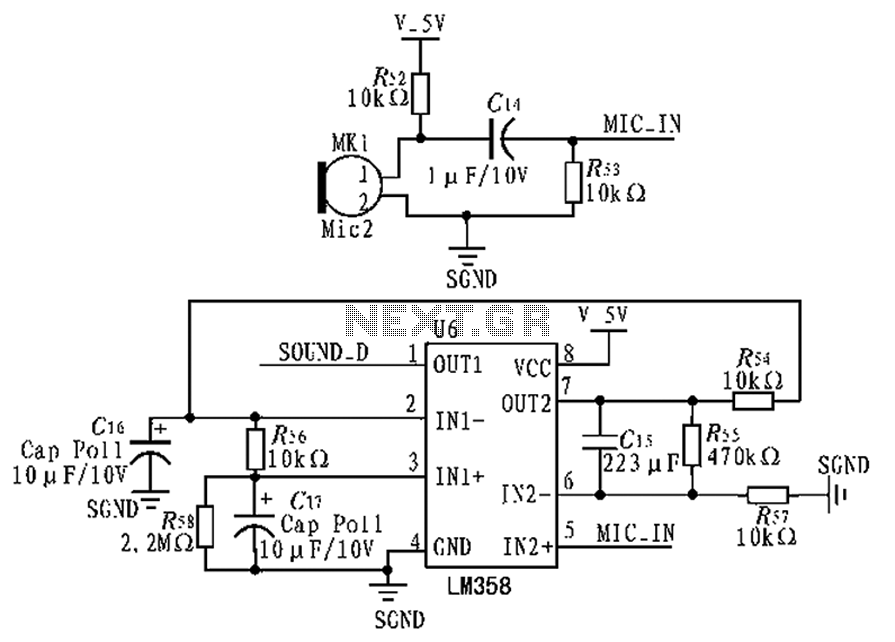
Real-time speech recognition system application circuit in family care robot
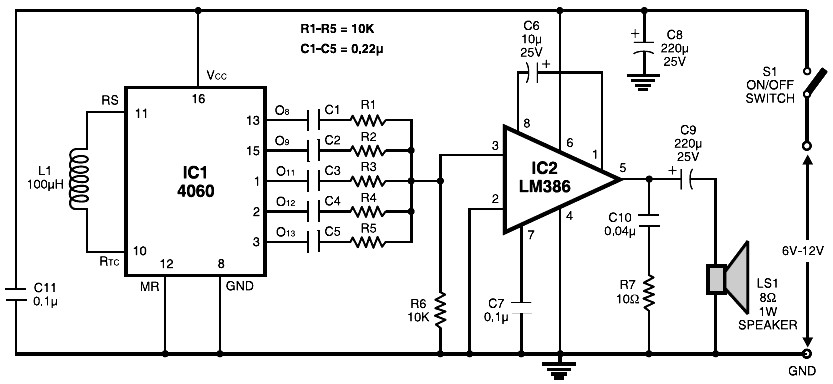
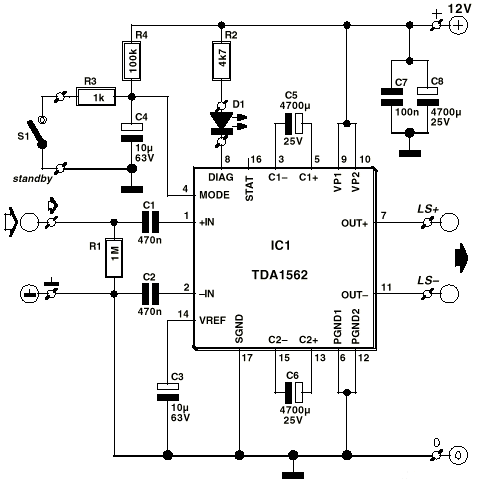
The circuit diagram focuses on the research and design features applied to mobile robots. The design considers small size, low power consumption, and ease of movement, catering to home users with a user-friendly display interface. For speech recognition, a processor is utilized to implement the speech recognition algorithm, along with a voice collection circuit and a voice output circuit. The processor executes arithmetic operations, functioning as the robot's brain; the voice acquisition circuit collects external sound signals, resembling the robot's ears; and the voice output circuit generates sound, acting as the robot's mouth. The schematic design is intended for mobile robots that require voice input, processing, and output. The voice input acquisition utilizes a sound sensor, microphone, and peripheral circuits. For the voice output section, a power amplifier is used in conjunction with a speaker, as illustrated in the schematic design of the speech component.
The described circuit diagram serves as a foundational element for the functionality of mobile robots, particularly in the realm of speech interaction. The design prioritizes compactness and efficiency, ensuring that the robot can operate effectively within a domestic environment.
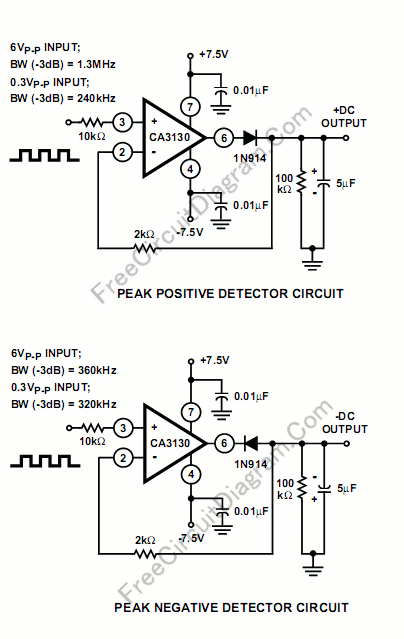
The processor at the heart of the speech recognition system is critical, as it executes complex algorithms that translate audio signals into actionable commands. This processor is typically a microcontroller or a dedicated digital signal processor (DSP) capable of handling real-time audio processing tasks. The efficiency of the speech recognition algorithm directly influences the robot's responsiveness and accuracy in understanding voice commands.
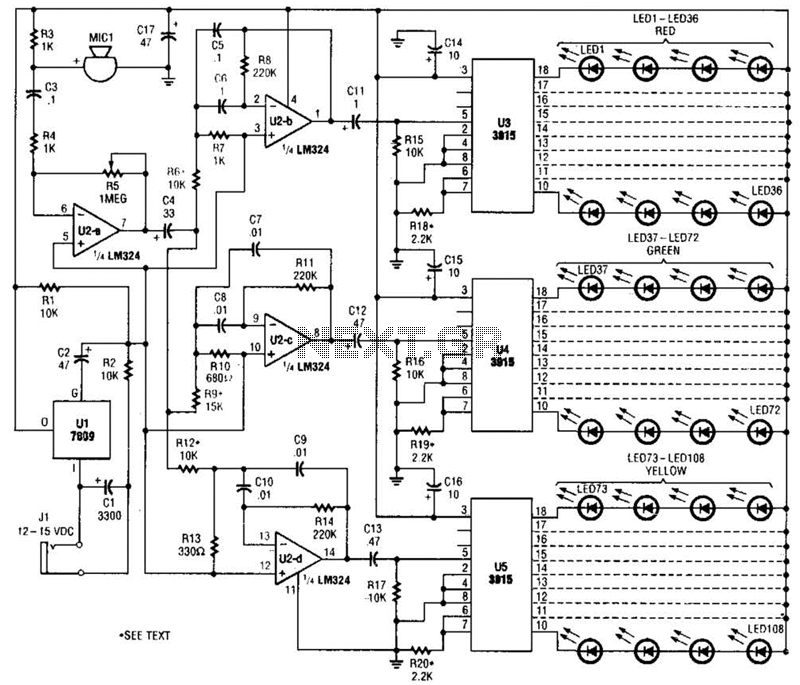
The voice acquisition circuit, which includes a microphone and associated circuitry, is designed to capture sound waves from the environment. This circuit may incorporate noise filtering techniques to enhance the clarity of the audio signal, thereby improving the recognition accuracy. The microphone converts acoustic energy into electrical signals, which are then processed by the processor.
The voice output circuit is equally important, as it transforms the processed data back into audible sound. The power amplifier amplifies the signal sufficiently to drive a speaker, ensuring that the robot can communicate effectively. The choice of speaker and amplifier affects the quality and volume of the output sound, which is essential for user interaction.
In summary, the schematic design for the mobile robot integrates these components into a cohesive system that enables voice input, processing, and output. The careful selection and arrangement of these elements are crucial for creating a responsive and interactive robotic system that meets user needs in a home environment. Circuit diagram in the research and design features, are applied on the mobile robot. Therefore the study design systems to take into account small size, low power, easy to mov e character, and home users need to have to facilitate the operation of the display-friendly interface. For the part of speech recognition, the need to use a processor for processing speech recognition algorithm, the voice collecting circuit and voice output circuit.
Wherein the processor of the speech recognition algorithm is responsible for operation of the arithmetic operation processing as the brain of the robot; voice acquisition circuit is responsible for collecting the external sound signal, corresponding ears of the robot; is responsible for the sound output voice output circuit words, the robot is equivalent to the mouth. The schematic design is used in mobile robots, requiring voice input, voice recognition processing and output.
For voice input acquisition, as used herein, a sound sensor, microphone and peripheral circuits. For voice output section, the use of a power amplifier used in conjunction speaker. Shown in the schematic design of the part of speech.
The described circuit diagram serves as a foundational element for the functionality of mobile robots, particularly in the realm of speech interaction. The design prioritizes compactness and efficiency, ensuring that the robot can operate effectively within a domestic environment.
The processor at the heart of the speech recognition system is critical, as it executes complex algorithms that translate audio signals into actionable commands. This processor is typically a microcontroller or a dedicated digital signal processor (DSP) capable of handling real-time audio processing tasks. The efficiency of the speech recognition algorithm directly influences the robot's responsiveness and accuracy in understanding voice commands.
The voice acquisition circuit, which includes a microphone and associated circuitry, is designed to capture sound waves from the environment. This circuit may incorporate noise filtering techniques to enhance the clarity of the audio signal, thereby improving the recognition accuracy. The microphone converts acoustic energy into electrical signals, which are then processed by the processor.
The voice output circuit is equally important, as it transforms the processed data back into audible sound. The power amplifier amplifies the signal sufficiently to drive a speaker, ensuring that the robot can communicate effectively. The choice of speaker and amplifier affects the quality and volume of the output sound, which is essential for user interaction.
In summary, the schematic design for the mobile robot integrates these components into a cohesive system that enables voice input, processing, and output. The careful selection and arrangement of these elements are crucial for creating a responsive and interactive robotic system that meets user needs in a home environment. Circuit diagram in the research and design features, are applied on the mobile robot. Therefore the study design systems to take into account small size, low power, easy to mov e character, and home users need to have to facilitate the operation of the display-friendly interface. For the part of speech recognition, the need to use a processor for processing speech recognition algorithm, the voice collecting circuit and voice output circuit.
Wherein the processor of the speech recognition algorithm is responsible for operation of the arithmetic operation processing as the brain of the robot; voice acquisition circuit is responsible for collecting the external sound signal, corresponding ears of the robot; is responsible for the sound output voice output circuit words, the robot is equivalent to the mouth. The schematic design is used in mobile robots, requiring voice input, voice recognition processing and output.
For voice input acquisition, as used herein, a sound sensor, microphone and peripheral circuits. For voice output section, the use of a power amplifier used in conjunction speaker. Shown in the schematic design of the part of speech.