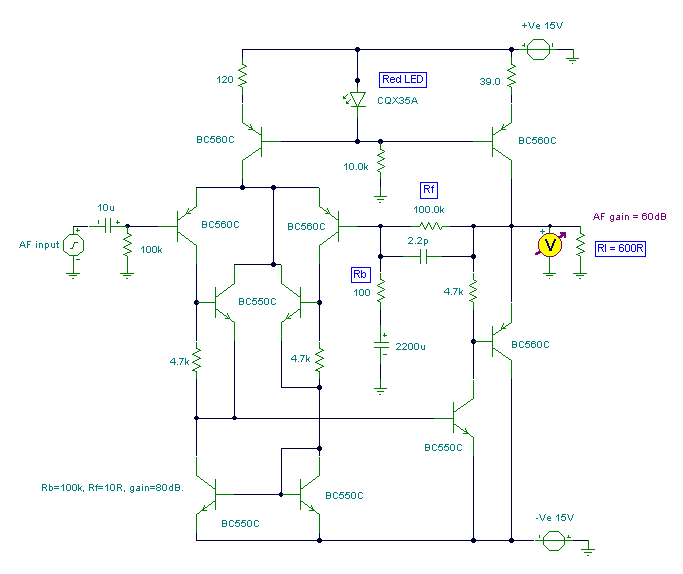
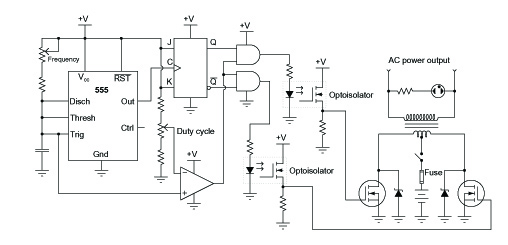
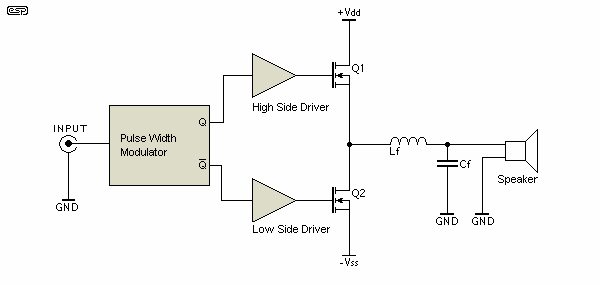
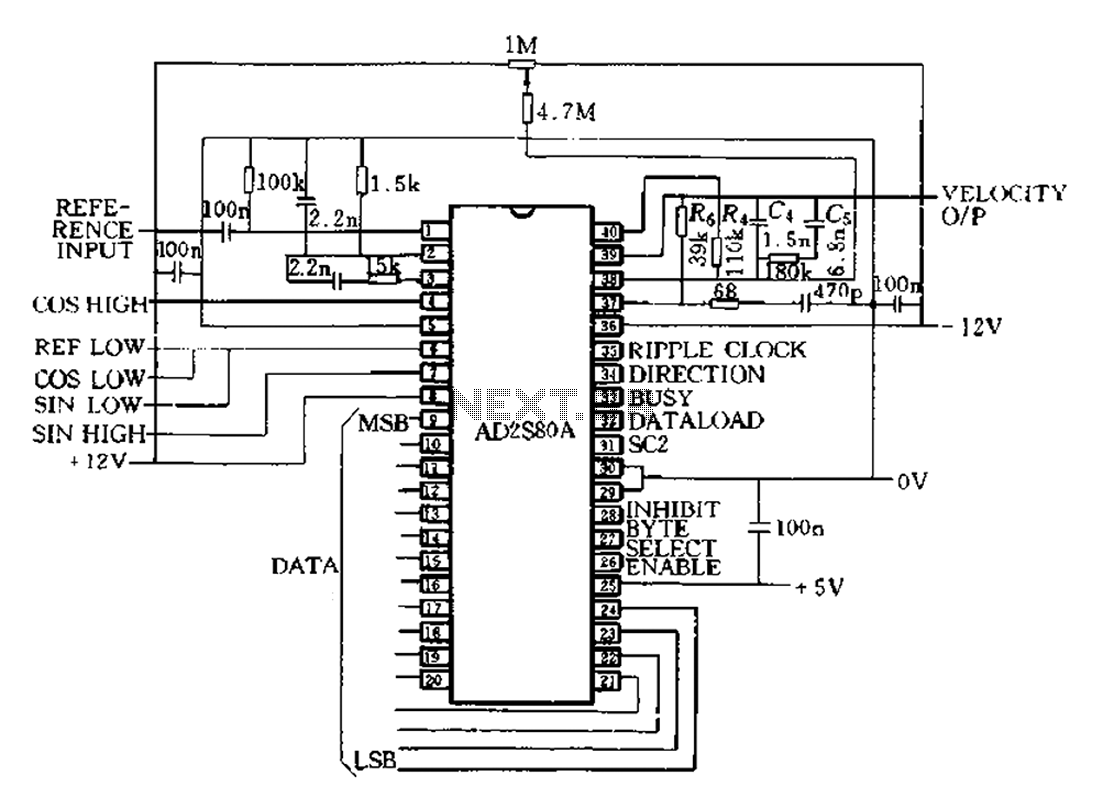
Extended common mode range of the instrumentation amplifier (INA101) circuit
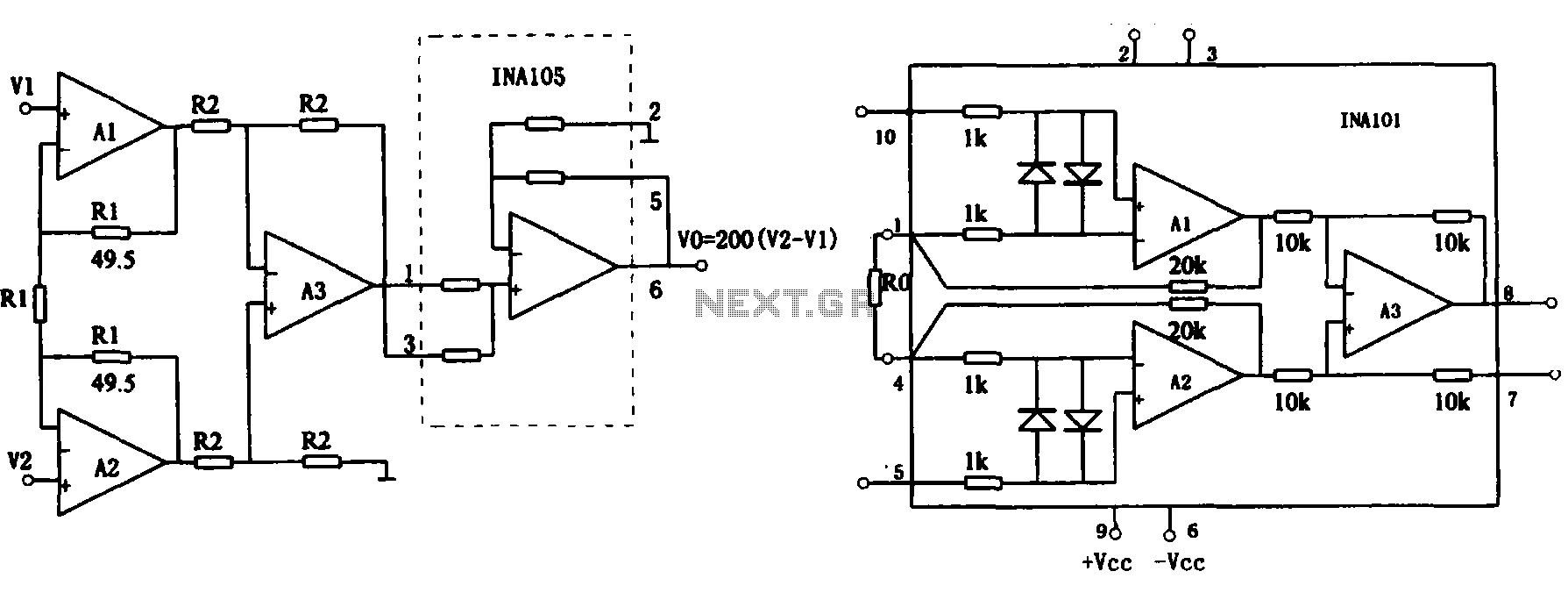
This document describes the extended common mode input voltage range of an instrument amplifier circuit. The circuit consists of three precision instrument amplifiers, A1, A2, and A3, which can be INA101 or INA102 models. The figure illustrates that A1, A2, and A3 provide a voltage magnification of 100 times. A precision unity gain amplifier, INA105, is connected to the inverting input of the amplifier in output follower mode. Four resistors are configured in parallel within the internal circuit, resulting in an INA105 amplifier voltage amplification factor of 2 and a high input impedance in the megohm range. The total voltage amplification of the circuit is 200 times. Additionally, figure (b) depicts the internal structure of the INA101.
The described instrument amplifier circuit is designed to handle a wide common mode input voltage range, making it suitable for various applications requiring high precision. The use of INA101 or INA102 as the primary amplifiers (A1, A2, A3) ensures that the circuit maintains high accuracy and low noise characteristics. These amplifiers are known for their low offset voltage and drift, which are critical in sensitive measurement applications.
The configuration of the INA105 as a unity gain amplifier in output follower mode is significant for maintaining the integrity of the signal while providing additional voltage gain. The parallel arrangement of the four resistors within the INA105 circuit contributes to achieving a voltage amplification factor of 2, while ensuring that the input impedance remains high, thus minimizing the loading effect on the source.
The total amplification of 200 times indicates that the circuit is capable of significantly boosting weak signals, making it ideal for applications in instrumentation where the detection of small changes in voltage is necessary. The high input impedance (in the megohm range) further enhances the circuit's performance by allowing it to interface effectively with high-impedance sensors without affecting their operation.
The internal structure of the INA101, as shown in figure (b), provides insights into the design and functionality of the amplifier, revealing the arrangement of transistors, resistors, and other components that contribute to its operational characteristics. This detailed understanding of the internal architecture can aid in troubleshooting and optimizing the circuit for specific applications.Shown for the extended common mode input voltage range of the instrument amplifier circuit. The circuit A1, A2 and A3 can be precision instrument amplifier INA101 or INA102 constitution. The figure shows, A1, A2 and A3 voltage magnification l00 times, then using precision amplifier unity gain amplifier INA105, connection to the amplifier inverting input, output follower mode, four resistors were about to internal circuit in parallel, thus obtained INA105 amplifier voltage amplification factor of 2 and a high input impedance (megohm). Total voltage of the circuit 200-fold magnification. Figure (b) is the internal structure of the INA101.
The described instrument amplifier circuit is designed to handle a wide common mode input voltage range, making it suitable for various applications requiring high precision. The use of INA101 or INA102 as the primary amplifiers (A1, A2, A3) ensures that the circuit maintains high accuracy and low noise characteristics. These amplifiers are known for their low offset voltage and drift, which are critical in sensitive measurement applications.
The configuration of the INA105 as a unity gain amplifier in output follower mode is significant for maintaining the integrity of the signal while providing additional voltage gain. The parallel arrangement of the four resistors within the INA105 circuit contributes to achieving a voltage amplification factor of 2, while ensuring that the input impedance remains high, thus minimizing the loading effect on the source.
The total amplification of 200 times indicates that the circuit is capable of significantly boosting weak signals, making it ideal for applications in instrumentation where the detection of small changes in voltage is necessary. The high input impedance (in the megohm range) further enhances the circuit's performance by allowing it to interface effectively with high-impedance sensors without affecting their operation.
The internal structure of the INA101, as shown in figure (b), provides insights into the design and functionality of the amplifier, revealing the arrangement of transistors, resistors, and other components that contribute to its operational characteristics. This detailed understanding of the internal architecture can aid in troubleshooting and optimizing the circuit for specific applications.Shown for the extended common mode input voltage range of the instrument amplifier circuit. The circuit A1, A2 and A3 can be precision instrument amplifier INA101 or INA102 constitution. The figure shows, A1, A2 and A3 voltage magnification l00 times, then using precision amplifier unity gain amplifier INA105, connection to the amplifier inverting input, output follower mode, four resistors were about to internal circuit in parallel, thus obtained INA105 amplifier voltage amplification factor of 2 and a high input impedance (megohm). Total voltage of the circuit 200-fold magnification. Figure (b) is the internal structure of the INA101.