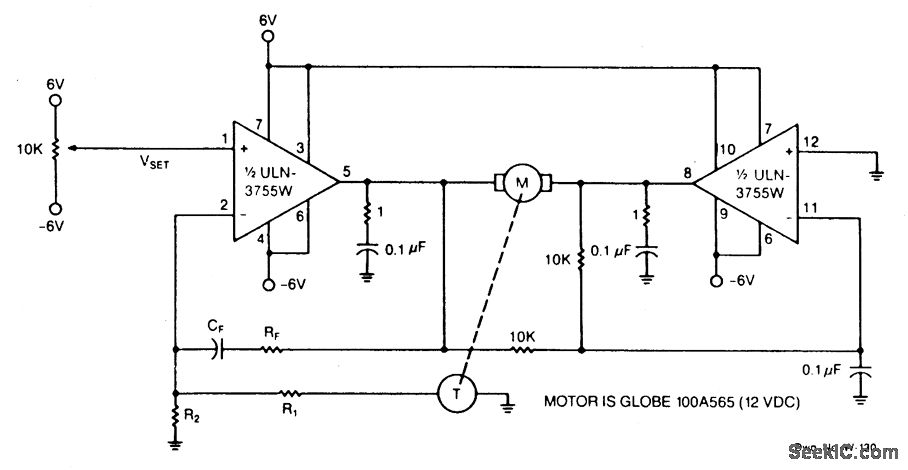
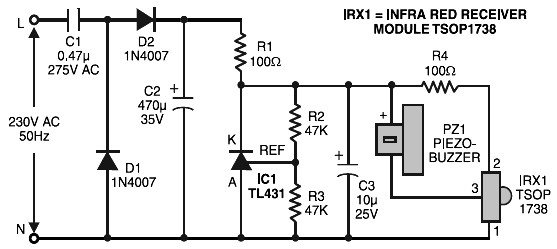
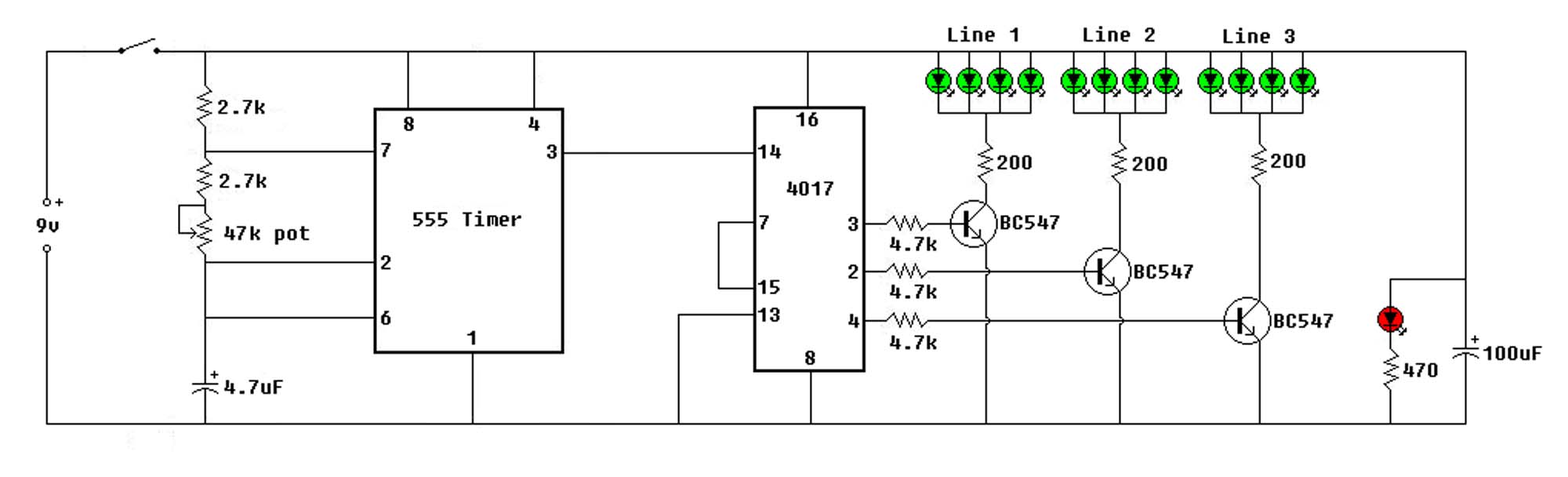
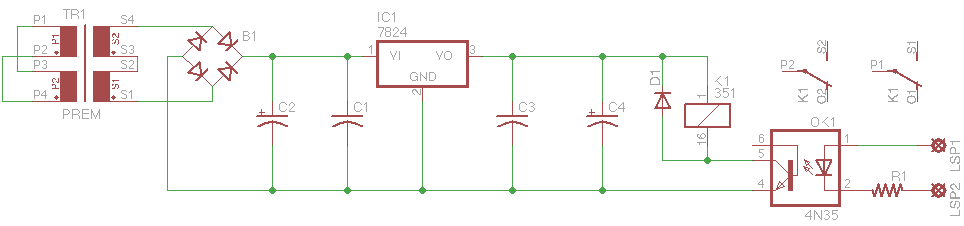
ld168 audio control circuit diagram of a voltage-controlled flash decoration
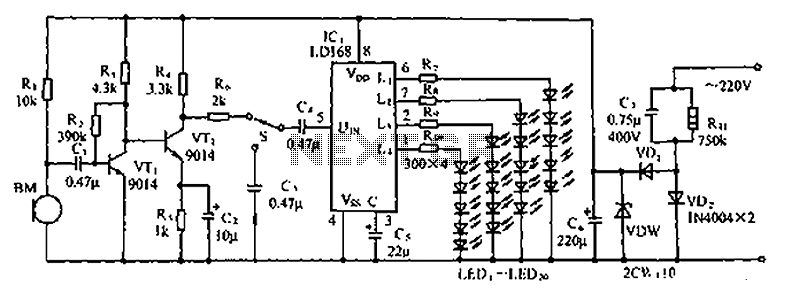
The circuit depicted in the figure involves the LD168, which functions as a sound level indicator for tape recorder speakers. It features four outputs capable of directly driving multiple light-emitting diodes. Additionally, the device can be activated by a thyristor drive for lantern light emission.
The LD168 circuit is designed to provide a visual representation of sound levels through the use of light-emitting diodes (LEDs). Each of the four outputs corresponds to different sound level thresholds, allowing for a clear indication of audio intensity. When the sound level reaches a specified point, the respective LED will illuminate, offering immediate feedback to the user regarding the audio output.
In terms of functionality, the LD168 can operate in two primary modes. The first mode utilizes direct LED drive, where the outputs are connected to the LEDs, allowing them to light up in response to the audio levels detected by the circuit. This mode is particularly useful in applications where real-time visual feedback is essential, such as in live sound environments or recording studios.
The second mode of operation involves the use of a thyristor drive, which enables the circuit to control higher power lantern lights. This feature is beneficial for applications that require more substantial lighting effects or where the use of standard LEDs would be insufficient. The thyristor acts as a switch, allowing the LD168 to handle higher voltage and current levels, thus expanding its usability in various settings.
Overall, the LD168 circuit is versatile and adaptable, making it suitable for a range of audio applications. Its ability to drive multiple outputs and integrate with different lighting technologies enhances its functionality, providing an effective solution for sound level indication. Circuit shown in Figure, LD168 is a flash of tape recorders speaker for sound level indication ASIC. It has four outputs can directly drive a plurality of light emitting diodes , the device can also be driven by lantern light emission thyristor drive.
The LD168 circuit is designed to provide a visual representation of sound levels through the use of light-emitting diodes (LEDs). Each of the four outputs corresponds to different sound level thresholds, allowing for a clear indication of audio intensity. When the sound level reaches a specified point, the respective LED will illuminate, offering immediate feedback to the user regarding the audio output.
In terms of functionality, the LD168 can operate in two primary modes. The first mode utilizes direct LED drive, where the outputs are connected to the LEDs, allowing them to light up in response to the audio levels detected by the circuit. This mode is particularly useful in applications where real-time visual feedback is essential, such as in live sound environments or recording studios.
The second mode of operation involves the use of a thyristor drive, which enables the circuit to control higher power lantern lights. This feature is beneficial for applications that require more substantial lighting effects or where the use of standard LEDs would be insufficient. The thyristor acts as a switch, allowing the LD168 to handle higher voltage and current levels, thus expanding its usability in various settings.
Overall, the LD168 circuit is versatile and adaptable, making it suitable for a range of audio applications. Its ability to drive multiple outputs and integrate with different lighting technologies enhances its functionality, providing an effective solution for sound level indication. Circuit shown in Figure, LD168 is a flash of tape recorders speaker for sound level indication ASIC. It has four outputs can directly drive a plurality of light emitting diodes , the device can also be driven by lantern light emission thyristor drive.