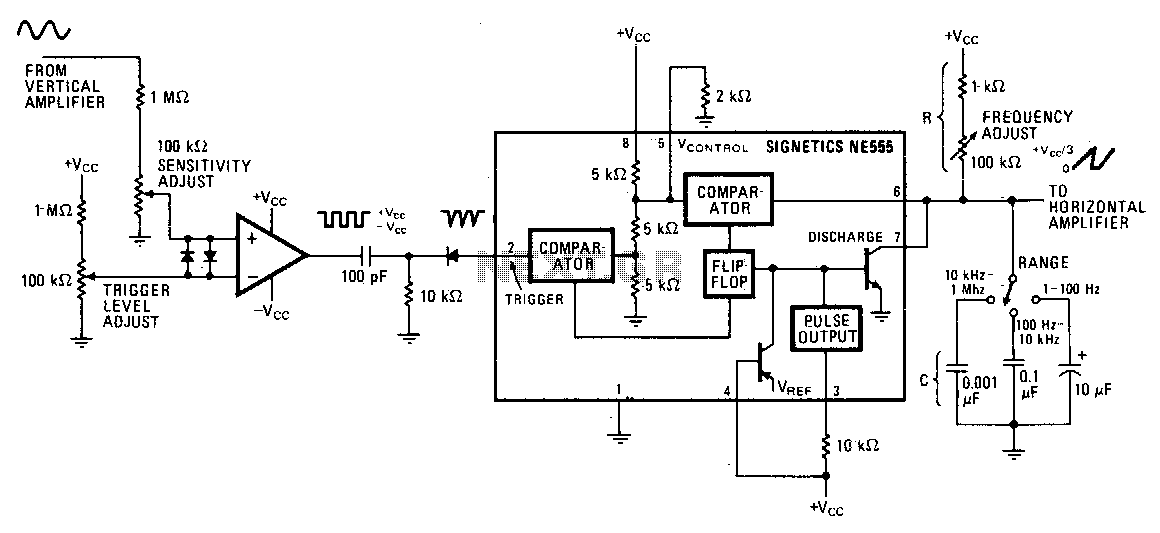
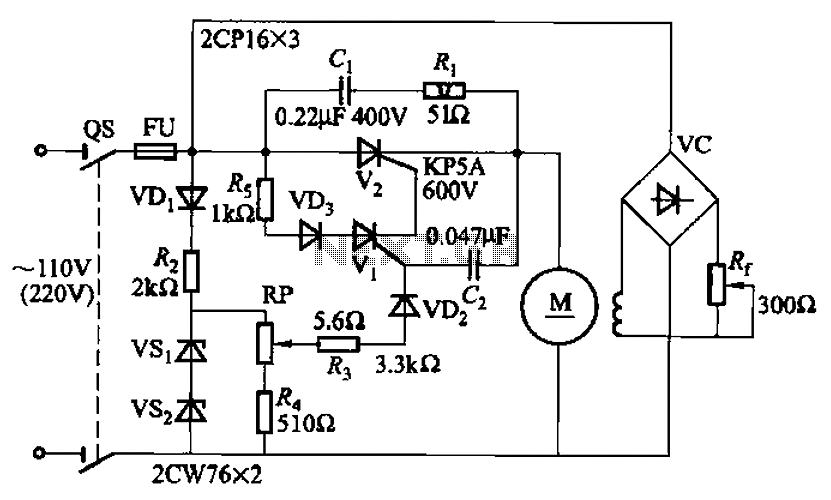
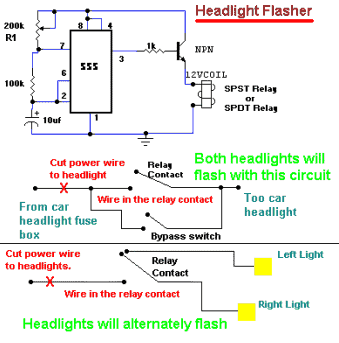
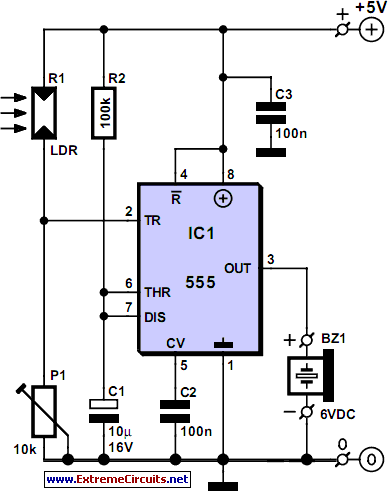
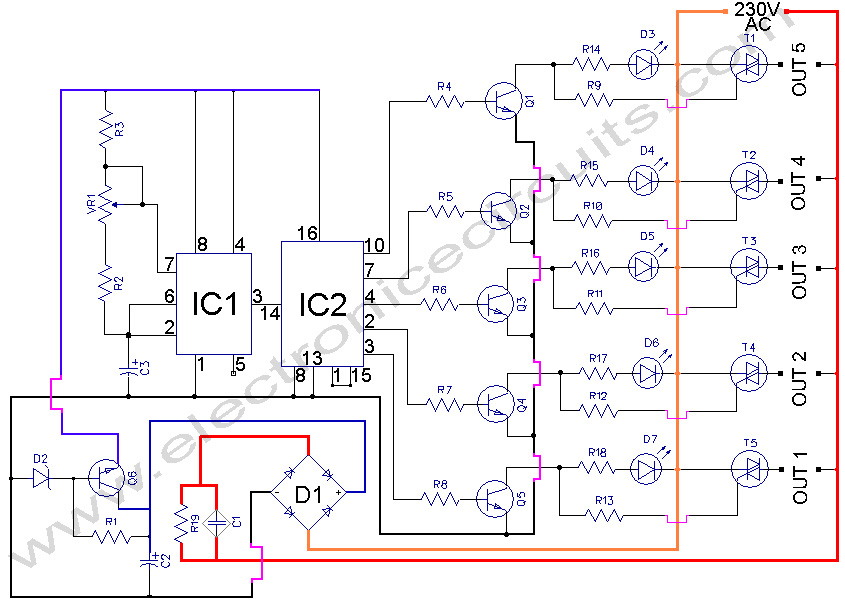
Slave Flash Trigger

Using any camera in a dull or dark environment generally requires the use of supplementary light. This is a standard technique, and even where adequate natural light is not available, additional lighting can enhance image quality.
In electronic circuit design for camera systems, the integration of supplementary lighting is crucial for improving visibility in low-light conditions. A common solution involves the use of LED (Light Emitting Diode) arrays, which provide efficient illumination while consuming minimal power. The circuit typically includes a power supply unit, a control circuit, and the LED array.
The power supply unit must be designed to convert the available voltage to the required level for the LEDs, taking into account the forward voltage and current specifications for the chosen LED components. A DC-DC converter can be employed for this purpose, ensuring that the LEDs receive a stable voltage and current, thus prolonging their lifespan and maintaining consistent brightness.
The control circuit can be implemented using a microcontroller or a simple transistor-based switch. If using a microcontroller, it can be programmed to adjust the brightness of the LEDs based on ambient light conditions, using a light-dependent resistor (LDR) as a sensor. The LDR detects the level of surrounding light and sends this information to the microcontroller, which then modulates the LED brightness accordingly. This allows for optimal illumination without excessive power consumption.
In summary, the design of a supplementary lighting circuit for cameras in low-light environments involves careful consideration of power management, control mechanisms, and component selection to ensure effective performance and energy efficiency.Using any camera in a dull or dark environment generally requires the use of supplementary light. This is a standard technique, and even where adequate na.. 🔗 External reference
In electronic circuit design for camera systems, the integration of supplementary lighting is crucial for improving visibility in low-light conditions. A common solution involves the use of LED (Light Emitting Diode) arrays, which provide efficient illumination while consuming minimal power. The circuit typically includes a power supply unit, a control circuit, and the LED array.
The power supply unit must be designed to convert the available voltage to the required level for the LEDs, taking into account the forward voltage and current specifications for the chosen LED components. A DC-DC converter can be employed for this purpose, ensuring that the LEDs receive a stable voltage and current, thus prolonging their lifespan and maintaining consistent brightness.
The control circuit can be implemented using a microcontroller or a simple transistor-based switch. If using a microcontroller, it can be programmed to adjust the brightness of the LEDs based on ambient light conditions, using a light-dependent resistor (LDR) as a sensor. The LDR detects the level of surrounding light and sends this information to the microcontroller, which then modulates the LED brightness accordingly. This allows for optimal illumination without excessive power consumption.
In summary, the design of a supplementary lighting circuit for cameras in low-light environments involves careful consideration of power management, control mechanisms, and component selection to ensure effective performance and energy efficiency.Using any camera in a dull or dark environment generally requires the use of supplementary light. This is a standard technique, and even where adequate na.. 🔗 External reference