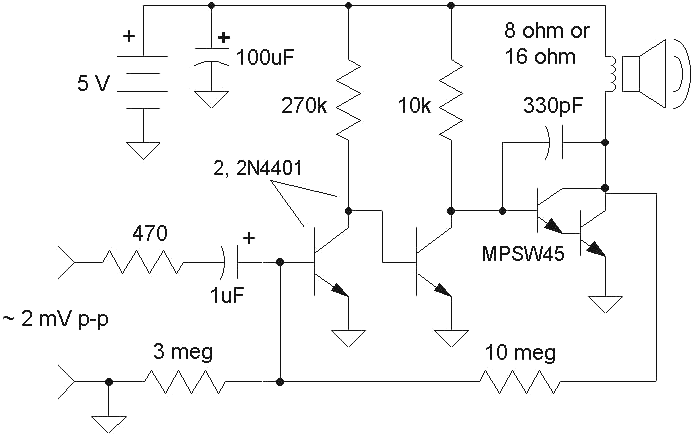
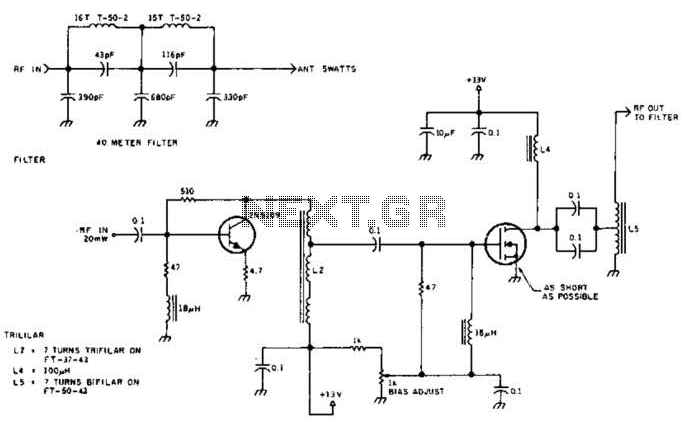
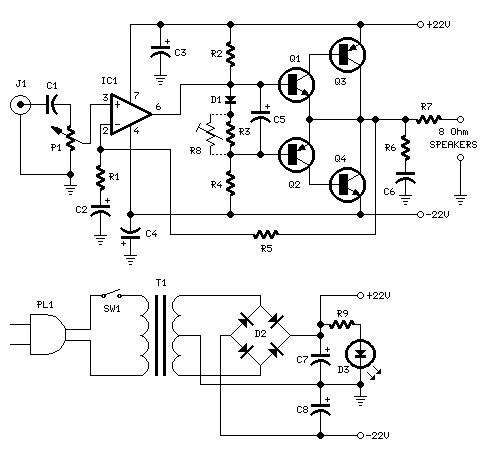
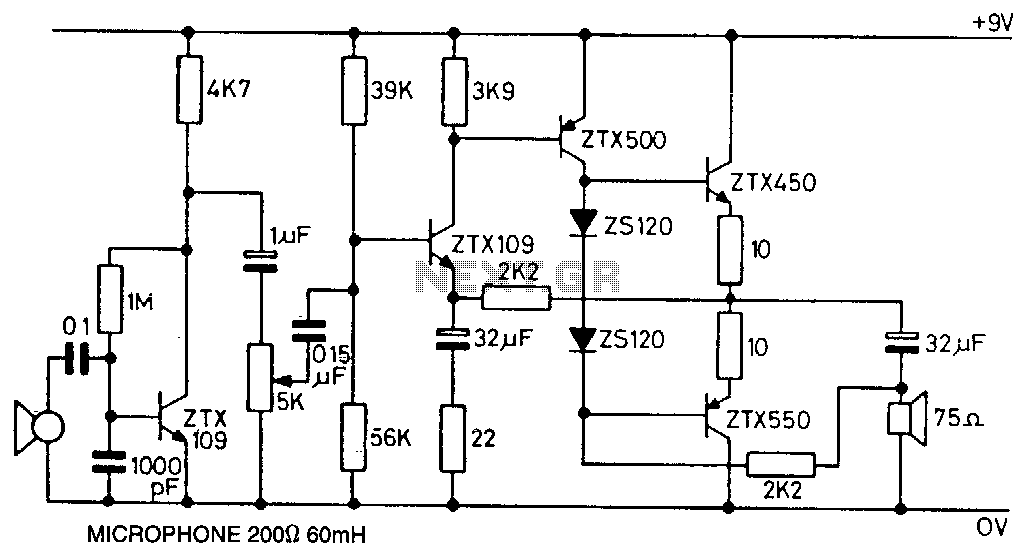
100W FM Linear Amplifier
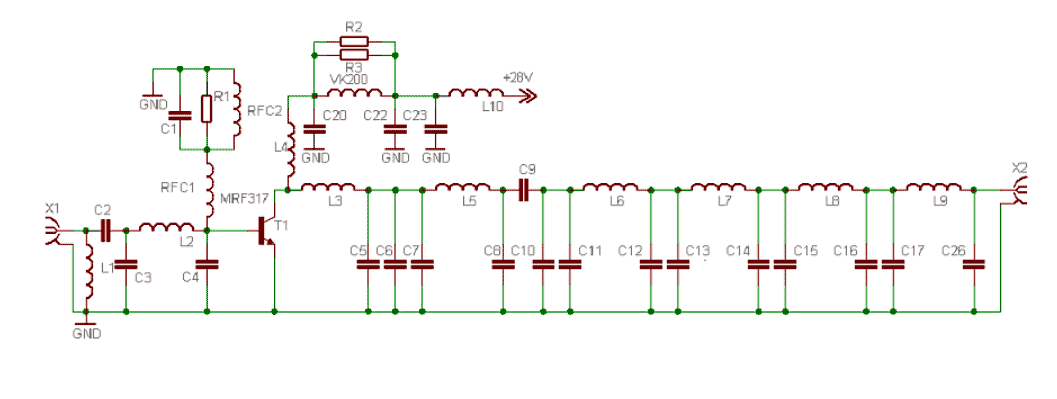
This power amplifier is equipped with a bipolar transistor, the famous MRF317. As in many FM amplifier applications, the power transistor is in a C class bias. All the impedance networks (input & output) have been determined by using the software: Mimp.EXE. A 9-element low pass filter ensures that we meet at least a 60 dB rejection from the carrier (RF simulation with RFSIM99). The FM amplifier has a 10 dB gain with a 60 to 65% efficiency. The input VSWR is around 1.4 and there's no problem reaching the maximum power in all the FM band.
The described power amplifier utilizes the MRF317 bipolar transistor, which is well-regarded for its performance in RF applications, particularly in FM broadcasting. The Class C biasing configuration employed in this circuit is optimal for high-efficiency applications, as it allows the transistor to conduct for less than half of the input signal cycle, thereby maximizing power output while minimizing heat generation.
The impedance matching networks for both the input and output stages are crucial for ensuring maximum power transfer and minimizing signal reflection. These networks have been designed using Mimp.EXE software, which aids in the precise calculation of component values to achieve the desired frequency response. The inclusion of a 9-element low pass filter at the output stage is particularly noteworthy, as it serves to attenuate unwanted harmonics and spurious signals, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards by providing at least 60 dB of rejection from the carrier frequency. The RF simulation performed with RFSIM99 further validates the design, allowing for adjustments based on simulated performance metrics.
The amplifier's gain of 10 dB indicates a substantial increase in signal strength, making it suitable for various FM transmission applications. The efficiency rating of 60 to 65% suggests that a significant portion of the input power is converted into useful output power, which is a critical factor in the design of power amplifiers to reduce operational costs and thermal management issues.
The input Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) of approximately 1.4 indicates good impedance matching, which minimizes reflections and maximizes power delivery from the source to the amplifier. This characteristic is essential for maintaining the integrity of the transmitted signal across the entire FM band, ensuring that the amplifier can operate effectively without distortion or loss of quality.
Overall, this power amplifier design is well-suited for FM broadcasting applications, providing a balance of efficiency, gain, and signal integrity.This Power amplifier is equiped with a bipolar transistor,the famous MRF317. As lots of FM amplifier application ,the power transistor is in a C class bias. All the impedance networks (Input & Output) have been determined by using the software: Mimp.EXE. A 9 elements low pass filter ensures that we meet at least a 60 dB rejection from the carrier.(RF Simulation with RFSIM99). The FM amplifier has a 10 dB gain with a 60 to 65% efficiency. The Input VSWR is around 1.4 and there's no problem to reach the max power in all the FM band.. 🔗 External reference
The described power amplifier utilizes the MRF317 bipolar transistor, which is well-regarded for its performance in RF applications, particularly in FM broadcasting. The Class C biasing configuration employed in this circuit is optimal for high-efficiency applications, as it allows the transistor to conduct for less than half of the input signal cycle, thereby maximizing power output while minimizing heat generation.
The impedance matching networks for both the input and output stages are crucial for ensuring maximum power transfer and minimizing signal reflection. These networks have been designed using Mimp.EXE software, which aids in the precise calculation of component values to achieve the desired frequency response. The inclusion of a 9-element low pass filter at the output stage is particularly noteworthy, as it serves to attenuate unwanted harmonics and spurious signals, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards by providing at least 60 dB of rejection from the carrier frequency. The RF simulation performed with RFSIM99 further validates the design, allowing for adjustments based on simulated performance metrics.
The amplifier's gain of 10 dB indicates a substantial increase in signal strength, making it suitable for various FM transmission applications. The efficiency rating of 60 to 65% suggests that a significant portion of the input power is converted into useful output power, which is a critical factor in the design of power amplifiers to reduce operational costs and thermal management issues.
The input Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) of approximately 1.4 indicates good impedance matching, which minimizes reflections and maximizes power delivery from the source to the amplifier. This characteristic is essential for maintaining the integrity of the transmitted signal across the entire FM band, ensuring that the amplifier can operate effectively without distortion or loss of quality.
Overall, this power amplifier design is well-suited for FM broadcasting applications, providing a balance of efficiency, gain, and signal integrity.This Power amplifier is equiped with a bipolar transistor,the famous MRF317. As lots of FM amplifier application ,the power transistor is in a C class bias. All the impedance networks (Input & Output) have been determined by using the software: Mimp.EXE. A 9 elements low pass filter ensures that we meet at least a 60 dB rejection from the carrier.(RF Simulation with RFSIM99). The FM amplifier has a 10 dB gain with a 60 to 65% efficiency. The Input VSWR is around 1.4 and there's no problem to reach the max power in all the FM band.. 🔗 External reference