10w audio amplifier with bass

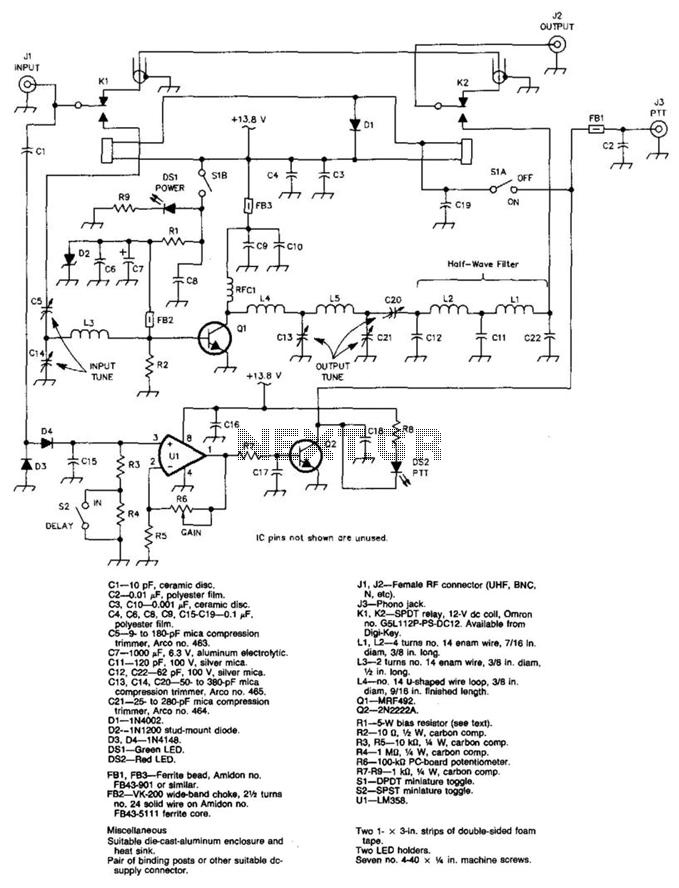
Proper grounding is essential for eliminating hum and ground loops. The ground connections for J1, P1, C2, C3, and C4 should all be connected to the same point. Additionally, connect C9 to the output ground.
In electronic circuits, grounding serves as a reference point for all voltage levels within the system and is critical for maintaining signal integrity. Ground loops can introduce unwanted noise, often manifesting as hum in audio applications. To mitigate these issues, it is recommended that all ground connections be consolidated to a single point.
In this particular schematic, the components J1 (likely a connector), P1 (possibly a power input), and capacitors C2, C3, and C4 must share a common ground connection. This ensures that any potential differences between the ground points of these components are eliminated, reducing the likelihood of interference.
Furthermore, C9 should be connected to the output ground. This capacitor may be used for filtering purposes, smoothing out voltage fluctuations at the output, thus enhancing the overall performance of the circuit. By ensuring that C9 is grounded properly, it can effectively minimize noise and stabilize the output signal.
Overall, careful consideration of grounding practices is vital in circuit design to ensure optimal functionality and reliability.A correct grounding is very important to eliminate hum and ground loops. Connect to the same point the ground sides of J1, P1, C2, C3 &C4. Connect C9 to the output ground. 🔗 External reference
In electronic circuits, grounding serves as a reference point for all voltage levels within the system and is critical for maintaining signal integrity. Ground loops can introduce unwanted noise, often manifesting as hum in audio applications. To mitigate these issues, it is recommended that all ground connections be consolidated to a single point.
In this particular schematic, the components J1 (likely a connector), P1 (possibly a power input), and capacitors C2, C3, and C4 must share a common ground connection. This ensures that any potential differences between the ground points of these components are eliminated, reducing the likelihood of interference.
Furthermore, C9 should be connected to the output ground. This capacitor may be used for filtering purposes, smoothing out voltage fluctuations at the output, thus enhancing the overall performance of the circuit. By ensuring that C9 is grounded properly, it can effectively minimize noise and stabilize the output signal.
Overall, careful consideration of grounding practices is vital in circuit design to ensure optimal functionality and reliability.A correct grounding is very important to eliminate hum and ground loops. Connect to the same point the ground sides of J1, P1, C2, C3 &C4. Connect C9 to the output ground. 🔗 External reference