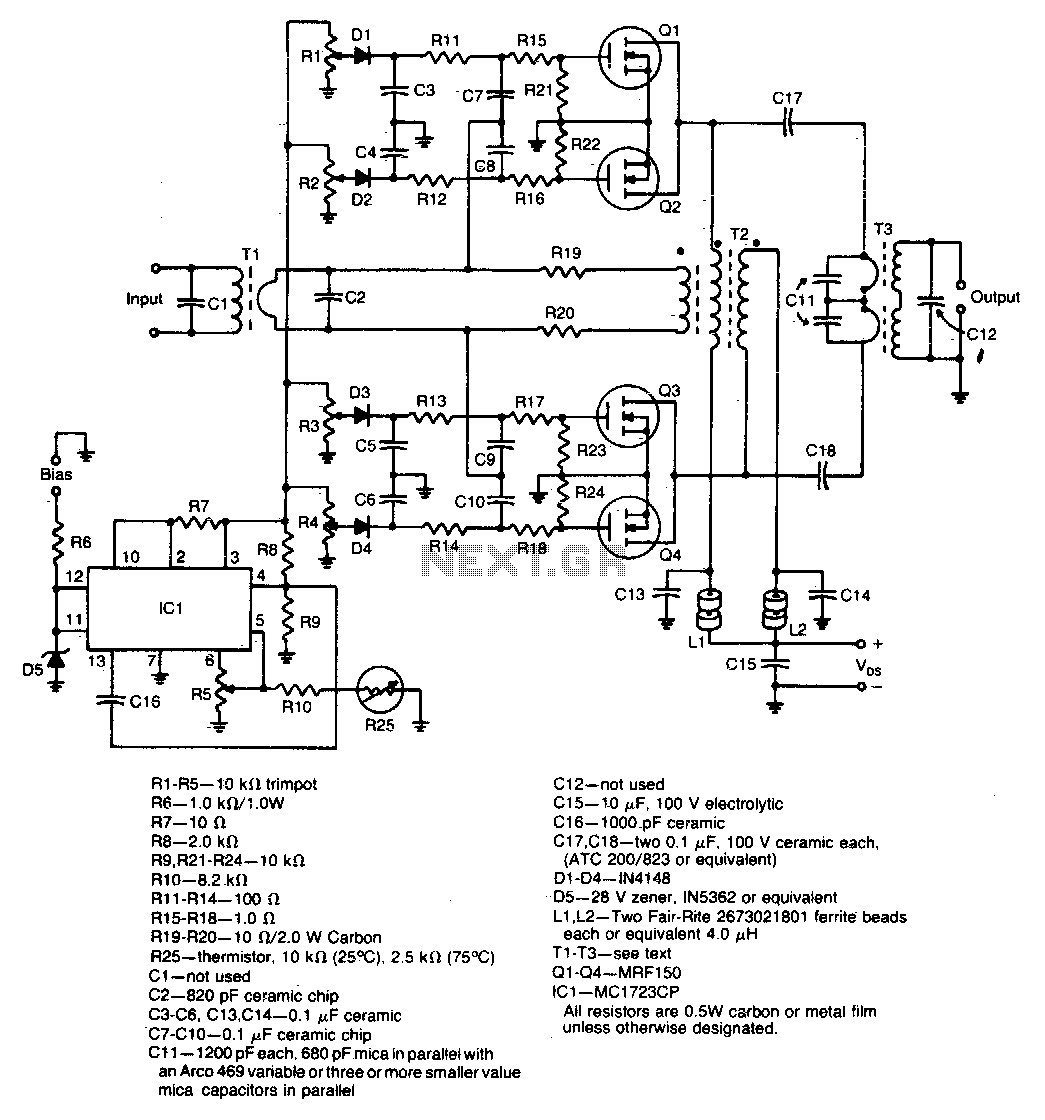
12 volt 2 a switching power supply
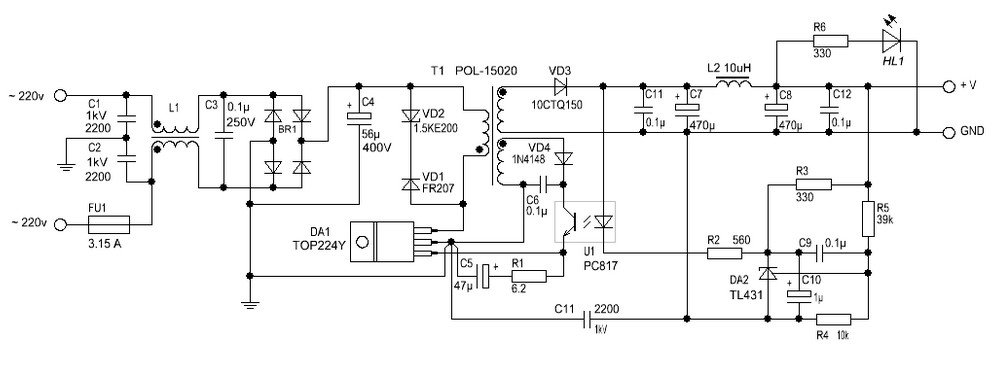
12 Volt / 2 A Switching Power Supply. Refer to the corresponding page for an explanation regarding the circuit diagram related to the above power supply.
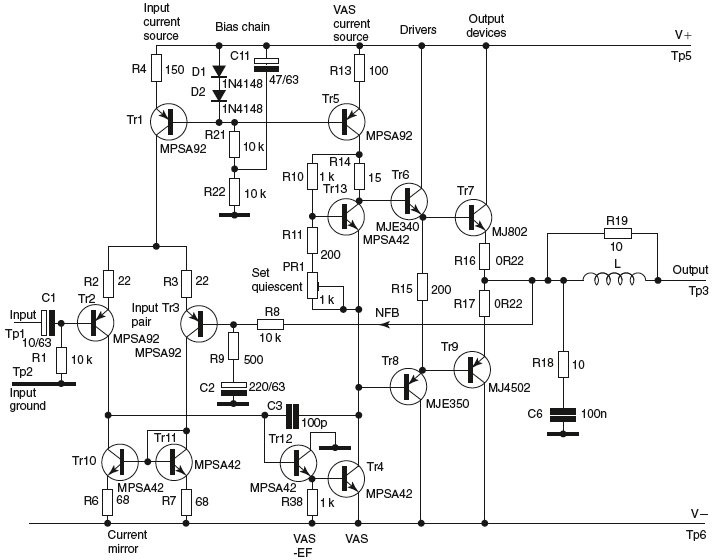
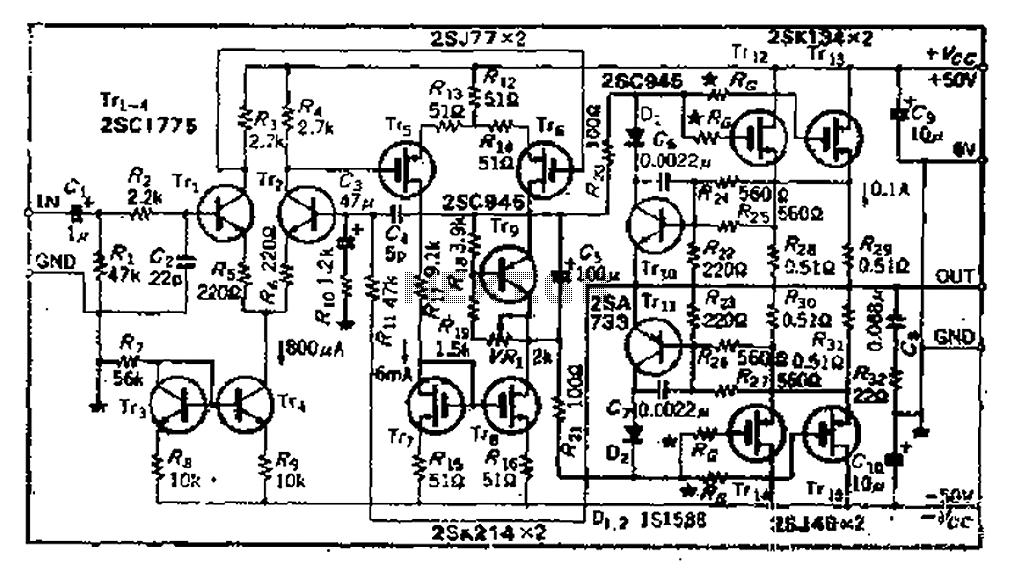
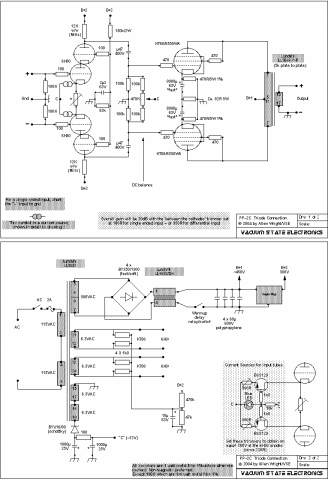
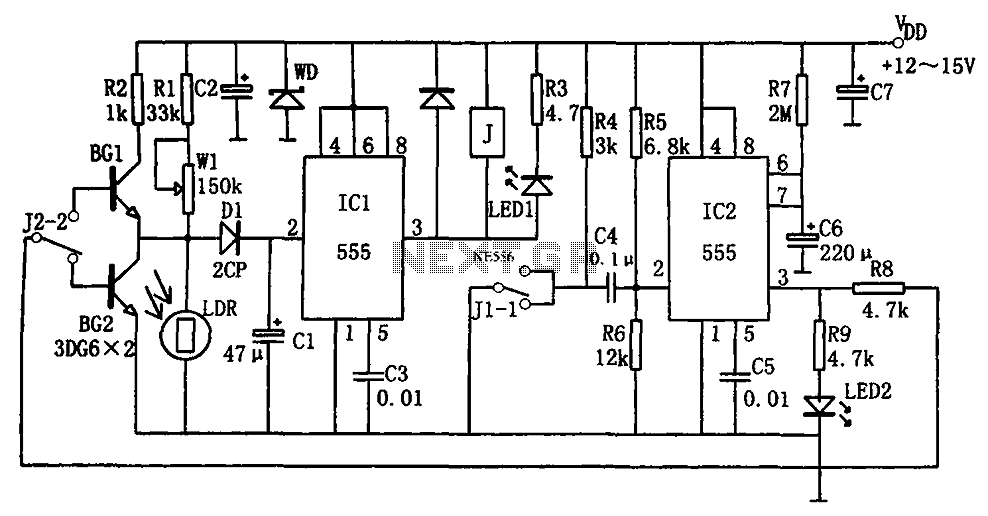
The 12 Volt / 2 A Switching Power Supply is designed to convert a higher input voltage into a stable 12 V output with a maximum current of 2 A. This type of power supply utilizes a switching regulator to achieve high efficiency and compact size. The primary components of the circuit typically include a transformer, rectifier, filter capacitors, and a control circuit.
The operation begins with the input AC voltage being transformed down to a lower AC voltage by the transformer. The output from the transformer is then rectified using a bridge rectifier configuration, which converts the AC voltage to DC. The rectified voltage is smoothed out by filter capacitors to reduce ripple, providing a more stable DC voltage.
The switching regulator, often based on integrated circuits (ICs) such as the LM2596 or similar, is responsible for maintaining the output voltage at 12 V. It does this by rapidly switching the input voltage on and off, controlling the average voltage delivered to the load. Feedback mechanisms are implemented to monitor the output voltage and adjust the duty cycle of the switching to ensure consistent output under varying load conditions.
Protection features may include over-voltage protection, over-current protection, and thermal shutdown to prevent damage to the power supply and connected devices. The design can be further enhanced with additional components such as inductors for filtering and improving transient response.
Overall, the 12 Volt / 2 A Switching Power Supply is a versatile and efficient solution for powering various electronic devices, making it a common choice in consumer electronics, industrial applications, and DIY projects.12 Volt / 2 A Switching Power Supply power supply. Go to that page to read the explanation about above power supply related circuit diagram. 🔗 External reference
The 12 Volt / 2 A Switching Power Supply is designed to convert a higher input voltage into a stable 12 V output with a maximum current of 2 A. This type of power supply utilizes a switching regulator to achieve high efficiency and compact size. The primary components of the circuit typically include a transformer, rectifier, filter capacitors, and a control circuit.
The operation begins with the input AC voltage being transformed down to a lower AC voltage by the transformer. The output from the transformer is then rectified using a bridge rectifier configuration, which converts the AC voltage to DC. The rectified voltage is smoothed out by filter capacitors to reduce ripple, providing a more stable DC voltage.
The switching regulator, often based on integrated circuits (ICs) such as the LM2596 or similar, is responsible for maintaining the output voltage at 12 V. It does this by rapidly switching the input voltage on and off, controlling the average voltage delivered to the load. Feedback mechanisms are implemented to monitor the output voltage and adjust the duty cycle of the switching to ensure consistent output under varying load conditions.
Protection features may include over-voltage protection, over-current protection, and thermal shutdown to prevent damage to the power supply and connected devices. The design can be further enhanced with additional components such as inductors for filtering and improving transient response.
Overall, the 12 Volt / 2 A Switching Power Supply is a versatile and efficient solution for powering various electronic devices, making it a common choice in consumer electronics, industrial applications, and DIY projects.12 Volt / 2 A Switching Power Supply power supply. Go to that page to read the explanation about above power supply related circuit diagram. 🔗 External reference