12VDC to 220VAC Inverter Circuit Using IC 555
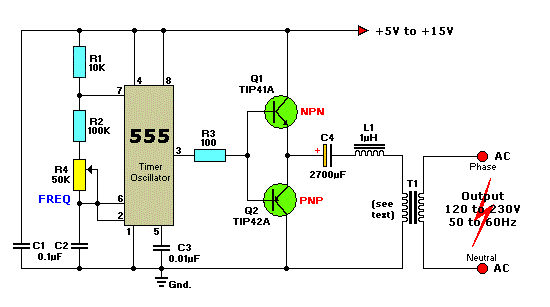
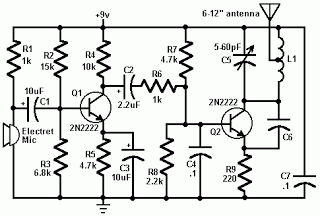
This circuit is a simple 12V DC to 220V AC inverter that produces an AC output at line frequency, specifically 220V AC, or other voltages by selecting transformer T1. The 555 integrated circuit (IC) is configured as a low-frequency oscillator, adjustable over the frequency range of 50 to 60 Hz using the frequency potentiometer R4. The output from the 555 IC is amplified by transistors Q1 and Q2 before being fed into transformer T1, which is a reverse-connected filament transformer with the appropriate step-up turns ratio. Capacitor C4 and inductor L1 filter the input to T1, ensuring that the output is effectively a sine wave. The value of transformer T1 can be adjusted to achieve the desired output voltage. The output power in watts can be modified by selecting different components. The input voltage can range from +5V to +15V DC, and the working voltage of the 2700µF capacitor should be adjusted accordingly. Suitable replacement types for Q1 include TIP41B, TIP41C, NTE196, ECG196, and for Q2, suitable replacements are TIP42B, TIP42C, NTE197, ECG197, etc.
This inverter circuit operates by converting a low voltage DC input into a high voltage AC output suitable for various applications. The 555 timer IC is pivotal in generating a square wave signal that controls the switching of the transistors, which act as amplifiers to drive the transformer. The frequency potentiometer R4 allows for fine-tuning of the output frequency, accommodating variations in application requirements, particularly for devices that may be sensitive to frequency fluctuations.
Transformer T1 plays a crucial role in stepping up the voltage from the low DC level to the desired AC output level. The choice of transformer is essential, as it must be rated for the appropriate voltage and current to handle the load. The filtering components, capacitor C4 and inductor L1, are designed to smooth the output waveform, minimizing harmonic distortion and ensuring that the output closely resembles a sine wave, which is critical for the operation of many AC devices.
The selection of transistors Q1 and Q2 is also significant as they need to handle the power levels involved without overheating or failing. The recommended replacement parts provide alternatives that can be used if the original components are unavailable, ensuring the circuit can be maintained or repaired easily.
When designing or modifying this inverter circuit, careful consideration must be given to the input voltage range, as this will affect the performance and efficiency of the inverter. The 2700µF capacitor serves as a reservoir for the DC input, and its voltage rating must be selected based on the expected maximum input voltage to prevent failure. Overall, this inverter circuit represents a versatile solution for converting low voltage DC power into usable high voltage AC power, suitable for a wide range of applications.This is a simple 12VDC to 220AC inverter circuit that can be used produces an AC output at line frequency and 220AC or different voltage by selecting transformer T1. The 555 IC is configured as a low-frequency oscillator, tunable over the frequency range of 50 to 60 Hz by Frequency potentiometer R4.
The 555 feeds its output (amplified by Q1 and Q2 ) to the input of transformer T1, a reverse-connected filament transformer with the necessary step-up turns ratio. Capacitor C4 and coil L1 filter the input to T1, assuring that it is effectively a sine wave. Adjust the value of T1 to your voltage. The output ( in watts) is up to you by selecting different components. Input voltage is anywhere from +5V to +15Volt DC, adjust the 2700uF cap`s working voltage accordingly.
Replacement types for Q1 are: TIP41B, TIP41C, NTE196, ECG196, etc. Replacement types for Q2 are: TIP42B, TIP42C, NTE197, ECG197, etc. 🔗 External reference
This inverter circuit operates by converting a low voltage DC input into a high voltage AC output suitable for various applications. The 555 timer IC is pivotal in generating a square wave signal that controls the switching of the transistors, which act as amplifiers to drive the transformer. The frequency potentiometer R4 allows for fine-tuning of the output frequency, accommodating variations in application requirements, particularly for devices that may be sensitive to frequency fluctuations.
Transformer T1 plays a crucial role in stepping up the voltage from the low DC level to the desired AC output level. The choice of transformer is essential, as it must be rated for the appropriate voltage and current to handle the load. The filtering components, capacitor C4 and inductor L1, are designed to smooth the output waveform, minimizing harmonic distortion and ensuring that the output closely resembles a sine wave, which is critical for the operation of many AC devices.
The selection of transistors Q1 and Q2 is also significant as they need to handle the power levels involved without overheating or failing. The recommended replacement parts provide alternatives that can be used if the original components are unavailable, ensuring the circuit can be maintained or repaired easily.
When designing or modifying this inverter circuit, careful consideration must be given to the input voltage range, as this will affect the performance and efficiency of the inverter. The 2700µF capacitor serves as a reservoir for the DC input, and its voltage rating must be selected based on the expected maximum input voltage to prevent failure. Overall, this inverter circuit represents a versatile solution for converting low voltage DC power into usable high voltage AC power, suitable for a wide range of applications.This is a simple 12VDC to 220AC inverter circuit that can be used produces an AC output at line frequency and 220AC or different voltage by selecting transformer T1. The 555 IC is configured as a low-frequency oscillator, tunable over the frequency range of 50 to 60 Hz by Frequency potentiometer R4.
The 555 feeds its output (amplified by Q1 and Q2 ) to the input of transformer T1, a reverse-connected filament transformer with the necessary step-up turns ratio. Capacitor C4 and coil L1 filter the input to T1, assuring that it is effectively a sine wave. Adjust the value of T1 to your voltage. The output ( in watts) is up to you by selecting different components. Input voltage is anywhere from +5V to +15Volt DC, adjust the 2700uF cap`s working voltage accordingly.
Replacement types for Q1 are: TIP41B, TIP41C, NTE196, ECG196, etc. Replacement types for Q2 are: TIP42B, TIP42C, NTE197, ECG197, etc. 🔗 External reference