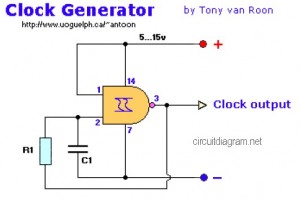
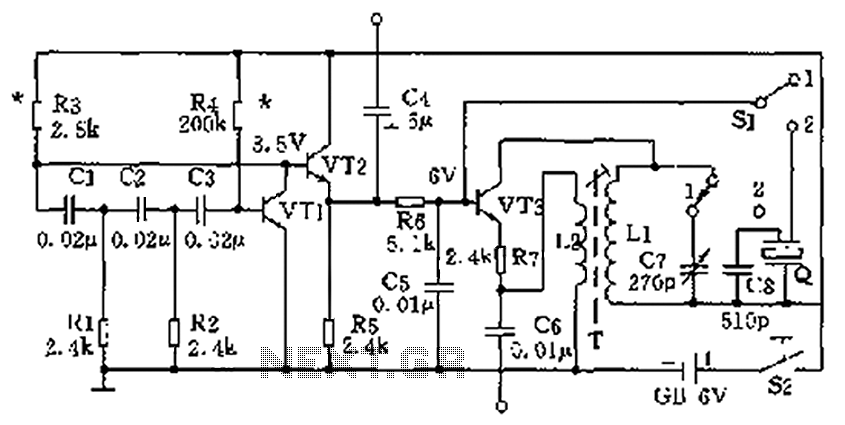
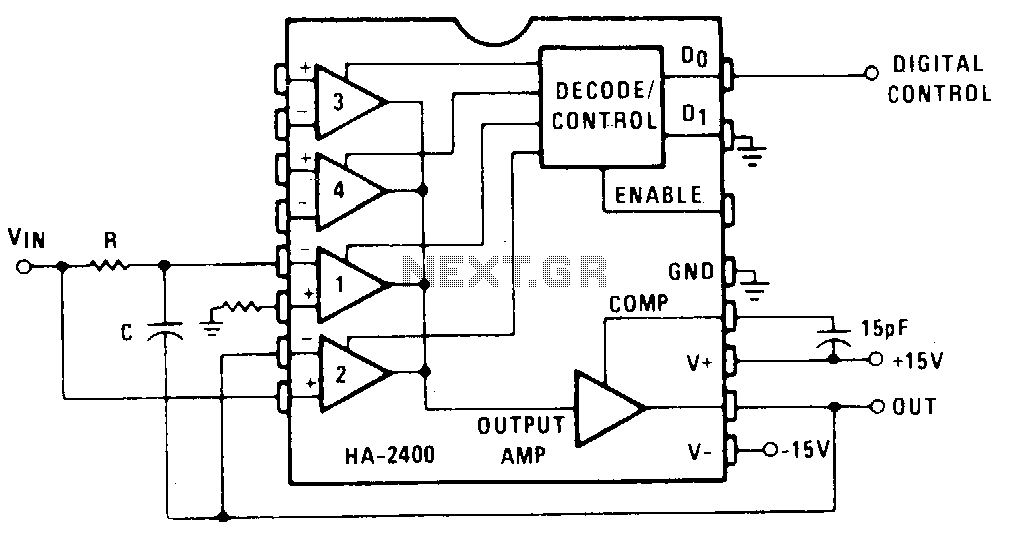
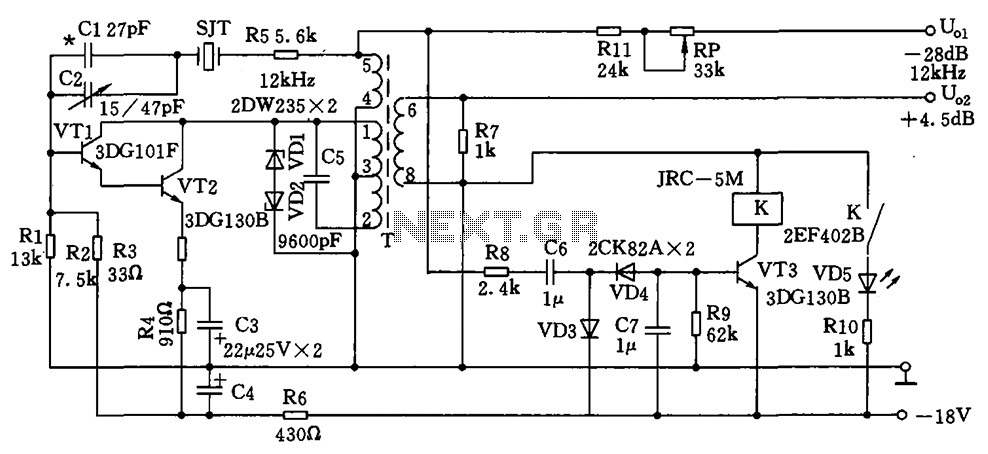
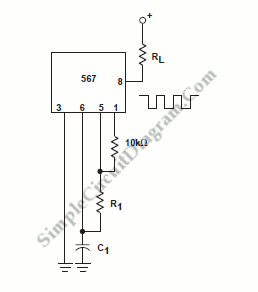
1khz sinewave generator
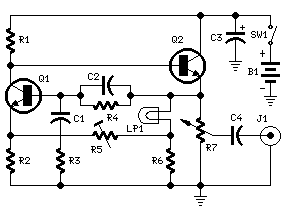
This circuit generates a stable 1 kHz sine wave using the inverted Wien bridge configuration.
The inverted Wien bridge oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that produces sine waves with high stability and low distortion. It operates on the principle of positive and negative feedback, utilizing an RC network to determine the frequency of oscillation. The circuit typically consists of operational amplifiers, resistors, and capacitors arranged to create a feedback loop that sustains oscillation.
In the inverted Wien bridge configuration, two resistors and two capacitors form the frequency-determining network. The resistors are connected in series, while the capacitors are in parallel, which allows for precise tuning of the frequency. The output frequency can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi R_1 R_2 C_1 C_2} \]
where \( R_1 \) and \( R_2 \) are the resistances, and \( C_1 \) and \( C_2 \) are the capacitances in the circuit. For a frequency of 1 kHz, appropriate values for the resistors and capacitors must be selected to meet this requirement.
The operational amplifier serves as the active element in the circuit, providing the necessary gain to sustain oscillation. The gain of the op-amp must be carefully set to ensure that it compensates for losses in the circuit while maintaining stability. A common approach to achieve this is by using a variable resistor in the feedback loop, which allows for automatic gain adjustment as the amplitude of the oscillation changes.
In practical applications, the output of the circuit can be connected to various loads, such as audio devices or signal processing equipment. The sine wave generated by the circuit is typically clean and free from harmonics, making it suitable for testing and calibration purposes in electronic systems. Proper power supply decoupling and layout considerations should be taken into account to minimize noise and interference in the output signal.This circuit generates a good 1KHz sinewave using the inverted Wien bridge configuration.. 🔗 External reference
The inverted Wien bridge oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that produces sine waves with high stability and low distortion. It operates on the principle of positive and negative feedback, utilizing an RC network to determine the frequency of oscillation. The circuit typically consists of operational amplifiers, resistors, and capacitors arranged to create a feedback loop that sustains oscillation.
In the inverted Wien bridge configuration, two resistors and two capacitors form the frequency-determining network. The resistors are connected in series, while the capacitors are in parallel, which allows for precise tuning of the frequency. The output frequency can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi R_1 R_2 C_1 C_2} \]
where \( R_1 \) and \( R_2 \) are the resistances, and \( C_1 \) and \( C_2 \) are the capacitances in the circuit. For a frequency of 1 kHz, appropriate values for the resistors and capacitors must be selected to meet this requirement.
The operational amplifier serves as the active element in the circuit, providing the necessary gain to sustain oscillation. The gain of the op-amp must be carefully set to ensure that it compensates for losses in the circuit while maintaining stability. A common approach to achieve this is by using a variable resistor in the feedback loop, which allows for automatic gain adjustment as the amplitude of the oscillation changes.
In practical applications, the output of the circuit can be connected to various loads, such as audio devices or signal processing equipment. The sine wave generated by the circuit is typically clean and free from harmonics, making it suitable for testing and calibration purposes in electronic systems. Proper power supply decoupling and layout considerations should be taken into account to minimize noise and interference in the output signal.This circuit generates a good 1KHz sinewave using the inverted Wien bridge configuration.. 🔗 External reference