NAND Gate Clock Generator circuit diagram
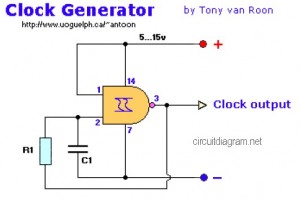
The following diagram represents a Clock Generator circuit that is constructed using NAND Gate logic integrated circuits (ICs). The circuit can utilize either IC 7400 or IC 4011. The 7400 is a TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic) type, whereas the 4011 is a CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) type. While the 4011 is more cost-effective than the 7400, the 7400 offers faster performance compared to the 4011.
The Clock Generator circuit designed with NAND gates serves as a fundamental building block in digital electronics, providing a square wave output that can be used to synchronize operations in various digital systems. In this configuration, the NAND gates are arranged in such a way that they create oscillations, generating a clock signal with a specific frequency determined by the external components connected to the circuit.
For implementing this circuit, a basic understanding of the timing characteristics of the chosen IC is essential. The frequency of oscillation can be adjusted by varying the resistor and capacitor values connected to the NAND gates. Typically, a resistor-capacitor (RC) network is employed to set the time period of the clock signal, where the resistor (R) and capacitor (C) values dictate the charge and discharge times, ultimately influencing the output frequency.
In practical applications, the output clock signal can be utilized in microcontrollers, digital counters, and frequency dividers, among other applications. The choice between the 7400 and 4011 ICs should be made based on the specific requirements of speed and cost for the intended application. The TTL 7400 is preferable for high-speed applications, while the CMOS 4011 may be selected for battery-operated devices where power consumption is a critical factor.
Overall, the Clock Generator circuit is an essential component in digital design, facilitating the timing necessary for synchronous operation in various electronic systems.The following diagram is the Clock Generator circuit diagram which build based on NAND Gate logic IC. You may use IC 7400 or 4011 for this circuit. The 7400 is a TTL type, while 4011 is CMOS type. IC 4011 is cheaper than 7400 but the 7400 is faster than 4011. 🔗 External reference
The Clock Generator circuit designed with NAND gates serves as a fundamental building block in digital electronics, providing a square wave output that can be used to synchronize operations in various digital systems. In this configuration, the NAND gates are arranged in such a way that they create oscillations, generating a clock signal with a specific frequency determined by the external components connected to the circuit.
For implementing this circuit, a basic understanding of the timing characteristics of the chosen IC is essential. The frequency of oscillation can be adjusted by varying the resistor and capacitor values connected to the NAND gates. Typically, a resistor-capacitor (RC) network is employed to set the time period of the clock signal, where the resistor (R) and capacitor (C) values dictate the charge and discharge times, ultimately influencing the output frequency.
In practical applications, the output clock signal can be utilized in microcontrollers, digital counters, and frequency dividers, among other applications. The choice between the 7400 and 4011 ICs should be made based on the specific requirements of speed and cost for the intended application. The TTL 7400 is preferable for high-speed applications, while the CMOS 4011 may be selected for battery-operated devices where power consumption is a critical factor.
Overall, the Clock Generator circuit is an essential component in digital design, facilitating the timing necessary for synchronous operation in various electronic systems.The following diagram is the Clock Generator circuit diagram which build based on NAND Gate logic IC. You may use IC 7400 or 4011 for this circuit. The 7400 is a TTL type, while 4011 is CMOS type. IC 4011 is cheaper than 7400 but the 7400 is faster than 4011. 🔗 External reference