2 watt amplifier schematic diagram
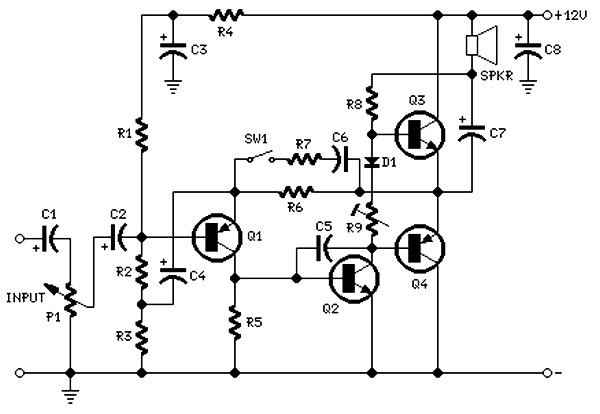
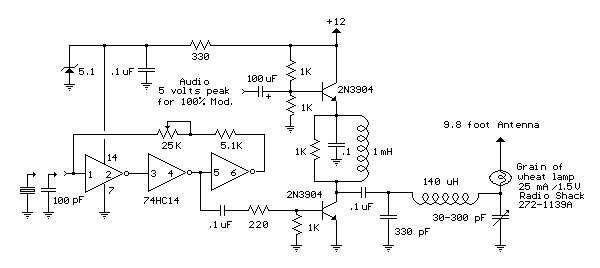
The circuit is intentionally designed using older type transistors to achieve harmonic distortion and to mitigate the challenges of sourcing high-quality components. The amplifiers can be easily powered by a plug-in wall transformer rated at 12V. When SW1 is closed, a bass boost feature is activated; however, the volume control must be adjusted upward to compensate for the power loss at higher frequencies.
The circuit employs vintage transistors, which are known for their unique characteristics that can introduce desirable harmonic distortion, often sought after in audio applications for a warmer sound. The use of older components also simplifies the design and assembly process, as these parts are typically more readily available and cost-effective.
The power supply is a standard 12V wall transformer, which provides a convenient and reliable source of energy for the circuit. This voltage level is suitable for most audio amplifier configurations, ensuring that the transistors operate within their optimal range.
The inclusion of a bass boost feature, activated by the closure of switch SW1, enhances low-frequency response. This feature is particularly useful in audio applications where bass frequencies are crucial for overall sound quality. However, activating this feature can lead to a reduction in power at higher frequencies, necessitating an increase in the volume control to maintain a balanced audio output. This adjustment is critical to ensure that the overall sound remains clear and undistorted across the frequency spectrum.
Overall, the circuit design emphasizes simplicity and functionality, making it an effective solution for audio amplification while accommodating the nuances of sound quality through the use of harmonic distortion and bass enhancement techniques.The circuit is intentionally designed using old type transistor, it is to get the harmonic distortion and to avoid the difficulty of finding good components. Amplifier (s) can be easily supplied by plug-in wall transformer 12V. Closing SW1 bass boost is provided but, at the same time, volume control must be increased to compensate for the loss of
power at higher frequencies. 🔗 External reference
The circuit employs vintage transistors, which are known for their unique characteristics that can introduce desirable harmonic distortion, often sought after in audio applications for a warmer sound. The use of older components also simplifies the design and assembly process, as these parts are typically more readily available and cost-effective.
The power supply is a standard 12V wall transformer, which provides a convenient and reliable source of energy for the circuit. This voltage level is suitable for most audio amplifier configurations, ensuring that the transistors operate within their optimal range.
The inclusion of a bass boost feature, activated by the closure of switch SW1, enhances low-frequency response. This feature is particularly useful in audio applications where bass frequencies are crucial for overall sound quality. However, activating this feature can lead to a reduction in power at higher frequencies, necessitating an increase in the volume control to maintain a balanced audio output. This adjustment is critical to ensure that the overall sound remains clear and undistorted across the frequency spectrum.
Overall, the circuit design emphasizes simplicity and functionality, making it an effective solution for audio amplification while accommodating the nuances of sound quality through the use of harmonic distortion and bass enhancement techniques.The circuit is intentionally designed using old type transistor, it is to get the harmonic distortion and to avoid the difficulty of finding good components. Amplifier (s) can be easily supplied by plug-in wall transformer 12V. Closing SW1 bass boost is provided but, at the same time, volume control must be increased to compensate for the loss of
power at higher frequencies. 🔗 External reference