2002 blazer: 02 sensor circuit malfunction solenoid it warms
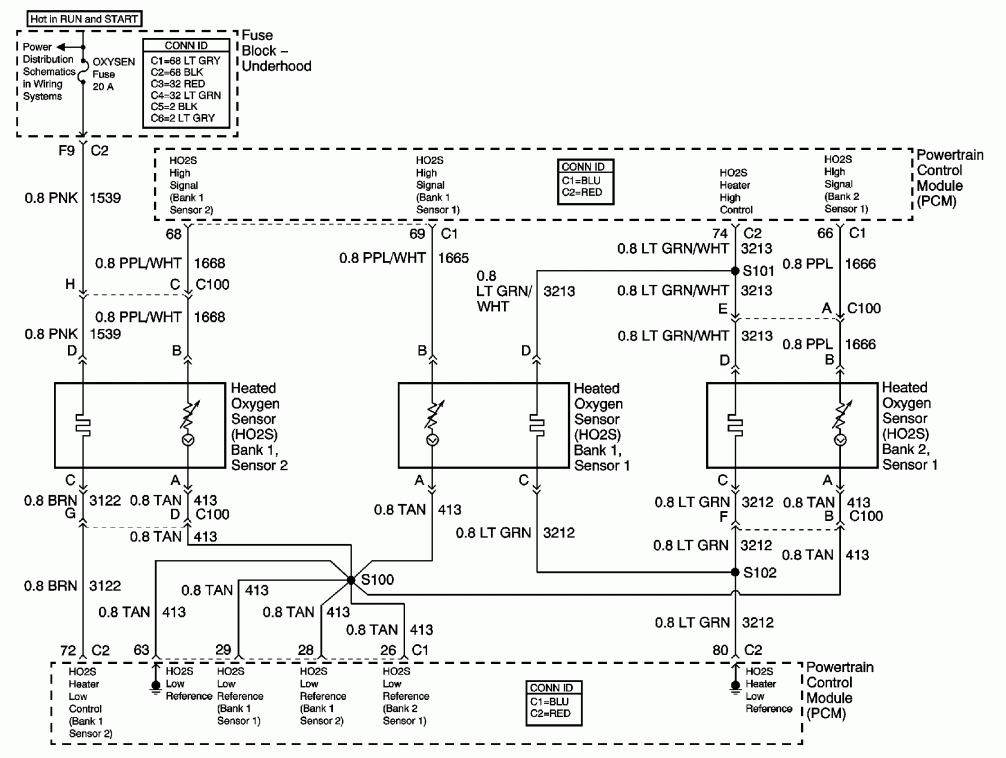
A 2002 Blazer was diagnosed with error codes P0155 and P0756, indicating a malfunction in the O2 sensor heater circuit and a performance issue with the shift solenoid B circuit. The vehicle initially has power, but it loses power when it warms up. The P0155 code points to the Heated Oxygen Sensor circuit for Bank 2, Sensor 1, suggesting that the heater in the sensor may have failed or there could be a wiring issue. Testing is recommended to confirm the problem, or the sensor could be replaced as a precaution, as the heater can degrade over time. To test the heater circuit, the ignition should be turned on to check for power and ground at pins D and C of the connector. With the connector removed, a resistance of about 5 ohms should be measured across the heater. The P0756 code relates to the transmission shift solenoid. Additional PDF resources are available regarding this issue, which can be viewed and printed. It is advisable to seek professional assistance for this problem unless there is sufficient experience and appropriate tools for repair.
The described issues with the 2002 Blazer involve two primary components: the Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) and the transmission shift solenoid. The P0155 code indicates a fault in the heating circuit of the HO2S located in Bank 2, Sensor 1. This sensor plays a crucial role in monitoring the oxygen levels in the exhaust, thereby aiding in the engine's air-fuel mixture regulation. A malfunction in this circuit can lead to poor engine performance, increased emissions, and reduced fuel efficiency.
To diagnose the HO2S issue, a multimeter should be used to measure the voltage and resistance at the sensor's connector. When the ignition is turned on (without starting the engine), voltage should be present at the heater circuit pins (D and C). A resistance check across the heater terminals should yield approximately 5 ohms; significant deviations may indicate a faulty sensor or wiring problems.
The P0756 code pertains to the transmission shift solenoid B circuit, which is responsible for controlling the transmission's shifting behavior. A failure in this circuit can lead to transmission slippage, erratic shifting, or the vehicle remaining in a single gear, resulting in a noticeable loss of power and performance.
The schematic for the sensors and solenoids should include the pin configurations, expected voltage levels, and resistance values for proper troubleshooting. If the problem persists after testing and potential component replacement, it is recommended to consult with a professional technician who can provide a more thorough diagnosis and repair.A 2002 blazer and I ran the codes on it and it came up po 155 and po 756 which a 02 sensor heater circuit malfunction and ashift solenoid b ckt performance of stuck off. What is that and what will it cause. The blazer has power when it first starts then when it warms up it has no power. The P0155 points to the Heated Oxygen Sensor circuit - Bank 2, Sensor 1. It could be that the heater in the sensor has failed, or there is a problem in the wiring to the sensor. It should be tested to find out, or you could just replace the sensor as a guess (they do burn out the heater over time). Here is the schematic for the sensors. To test the circuit for the heater, turn on the ignition and check for power and ground at pins D & C of the connector.
With the connector removed, you should read about 5 ohms across the heater. The P0756 has to do with the transmission shift solenoid. I have a few PDF files for you regarding that issue. You should be able to view these on your computer and print them out. I, personally, would take the vehicle to a shop for this particular problem, unless you have some experience and tools for working on this type of issue. 🔗 External reference
The described issues with the 2002 Blazer involve two primary components: the Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) and the transmission shift solenoid. The P0155 code indicates a fault in the heating circuit of the HO2S located in Bank 2, Sensor 1. This sensor plays a crucial role in monitoring the oxygen levels in the exhaust, thereby aiding in the engine's air-fuel mixture regulation. A malfunction in this circuit can lead to poor engine performance, increased emissions, and reduced fuel efficiency.
To diagnose the HO2S issue, a multimeter should be used to measure the voltage and resistance at the sensor's connector. When the ignition is turned on (without starting the engine), voltage should be present at the heater circuit pins (D and C). A resistance check across the heater terminals should yield approximately 5 ohms; significant deviations may indicate a faulty sensor or wiring problems.
The P0756 code pertains to the transmission shift solenoid B circuit, which is responsible for controlling the transmission's shifting behavior. A failure in this circuit can lead to transmission slippage, erratic shifting, or the vehicle remaining in a single gear, resulting in a noticeable loss of power and performance.
The schematic for the sensors and solenoids should include the pin configurations, expected voltage levels, and resistance values for proper troubleshooting. If the problem persists after testing and potential component replacement, it is recommended to consult with a professional technician who can provide a more thorough diagnosis and repair.A 2002 blazer and I ran the codes on it and it came up po 155 and po 756 which a 02 sensor heater circuit malfunction and ashift solenoid b ckt performance of stuck off. What is that and what will it cause. The blazer has power when it first starts then when it warms up it has no power. The P0155 points to the Heated Oxygen Sensor circuit - Bank 2, Sensor 1. It could be that the heater in the sensor has failed, or there is a problem in the wiring to the sensor. It should be tested to find out, or you could just replace the sensor as a guess (they do burn out the heater over time). Here is the schematic for the sensors. To test the circuit for the heater, turn on the ignition and check for power and ground at pins D & C of the connector.
With the connector removed, you should read about 5 ohms across the heater. The P0756 has to do with the transmission shift solenoid. I have a few PDF files for you regarding that issue. You should be able to view these on your computer and print them out. I, personally, would take the vehicle to a shop for this particular problem, unless you have some experience and tools for working on this type of issue. 🔗 External reference