20MHz High Speed Function Generator
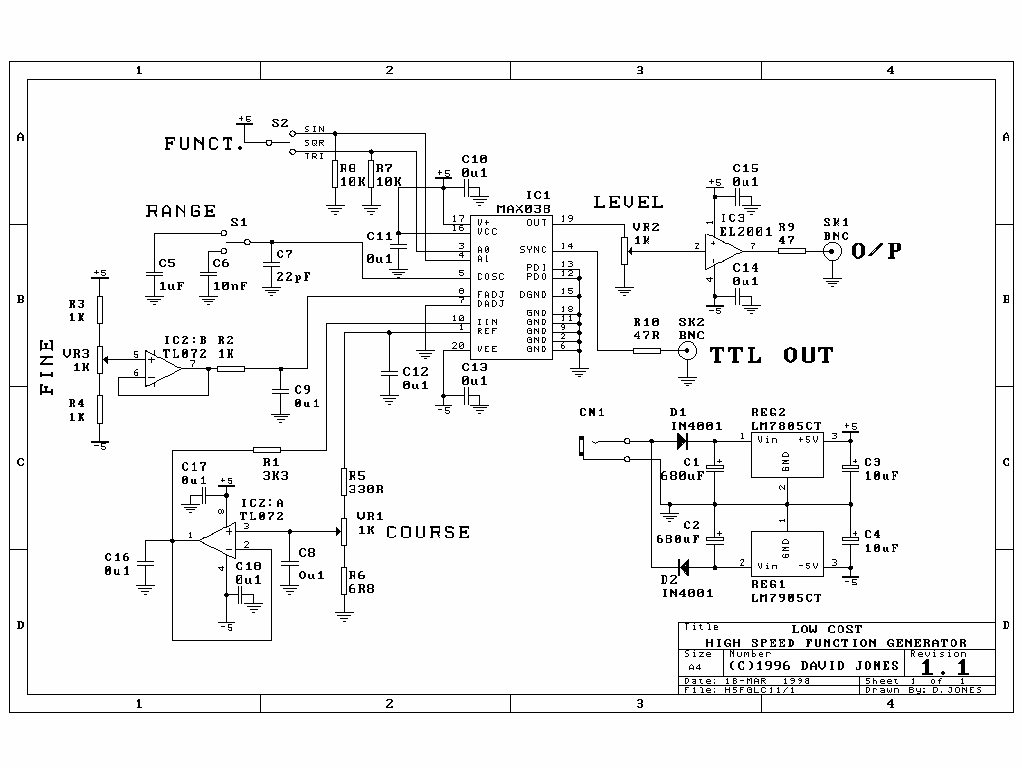
The High Speed Function Generator was published in the professional electronics section of the Aug 1996 issue of Electronics Australia, and has proven to be extremely popular. The kit is no longer available from any of the kit suppliers.
The High Speed Function Generator is designed to produce a variety of waveforms, including sine, square, triangle, and sawtooth, with a high degree of accuracy and stability. The circuit typically employs operational amplifiers (op-amps) for waveform generation, utilizing feedback and RC timing networks to define the frequency and shape of the output signals.
The core of the function generator may include a phase-locked loop (PLL) for frequency stabilization, ensuring that the output waveform maintains a consistent frequency over varying load conditions. Additionally, a microcontroller or a dedicated frequency synthesizer IC might be used to allow for precise frequency adjustments and digital control over waveform parameters.
Output stages are usually designed to drive loads directly, with considerations for output impedance to match typical test equipment or circuits. Protection features may be included to prevent damage from overvoltage or excessive current draw.
In terms of power supply, the function generator often operates from a dual supply voltage, such as ±12V or ±15V, to accommodate the op-amps and other active components, ensuring sufficient headroom for signal swing.
Overall, the High Speed Function Generator serves as a versatile tool in both laboratory and field applications, providing engineers and technicians with reliable waveform generation capabilities for testing and development purposes.The High Speed Function Generator was published in the professional electronics section of the Aug 1996 issue of Electronics Australia, and has proven to be extremely popular. The kit is no longer available from any of the kit suppliers. 🔗 External reference
The High Speed Function Generator is designed to produce a variety of waveforms, including sine, square, triangle, and sawtooth, with a high degree of accuracy and stability. The circuit typically employs operational amplifiers (op-amps) for waveform generation, utilizing feedback and RC timing networks to define the frequency and shape of the output signals.
The core of the function generator may include a phase-locked loop (PLL) for frequency stabilization, ensuring that the output waveform maintains a consistent frequency over varying load conditions. Additionally, a microcontroller or a dedicated frequency synthesizer IC might be used to allow for precise frequency adjustments and digital control over waveform parameters.
Output stages are usually designed to drive loads directly, with considerations for output impedance to match typical test equipment or circuits. Protection features may be included to prevent damage from overvoltage or excessive current draw.
In terms of power supply, the function generator often operates from a dual supply voltage, such as ±12V or ±15V, to accommodate the op-amps and other active components, ensuring sufficient headroom for signal swing.
Overall, the High Speed Function Generator serves as a versatile tool in both laboratory and field applications, providing engineers and technicians with reliable waveform generation capabilities for testing and development purposes.The High Speed Function Generator was published in the professional electronics section of the Aug 1996 issue of Electronics Australia, and has proven to be extremely popular. The kit is no longer available from any of the kit suppliers. 🔗 External reference