220V LED Flasher Circuit

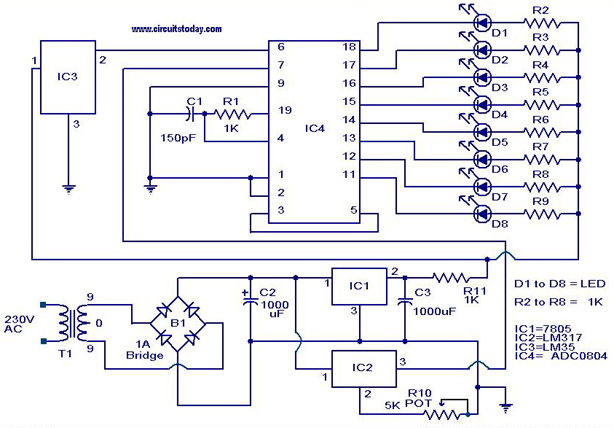
This is an AC-powered LED flasher that can drive two high-bright LEDs directly from the power obtained from the AC lines. The high-bright LED flasher can be...
The AC-powered LED flasher circuit is designed to illuminate two high-bright LEDs using the alternating current (AC) directly from the mains supply. The circuit typically consists of a transformer, rectifier, voltage regulator, and control circuitry to modulate the LED flashing.
The transformer steps down the AC voltage to a lower, manageable level suitable for the circuit. Following the transformer, a rectifier (often a bridge rectifier configuration) converts the AC voltage to direct current (DC). This conversion is crucial as LEDs require a DC supply for proper operation.
After rectification, the voltage may still be too high or unstable for direct LED usage. Therefore, a voltage regulator is employed to ensure that the output voltage remains at a safe and constant level, typically around 3 to 3.5 volts per LED, depending on the specifications of the high-bright LEDs used.
To create the flashing effect, a control circuit, which may include a timer IC or a microcontroller, is integrated into the design. This control circuit modulates the power delivered to the LEDs, turning them on and off at a predetermined frequency, which can be adjusted based on the desired flashing rate.
Additional components such as resistors may be included to limit the current flowing through the LEDs, ensuring they operate within their specified current ratings to prevent damage. Capacitors may also be utilized for smoothing the DC output from the rectifier, reducing flicker and enhancing LED performance.
The overall design of the AC-powered LED flasher circuit is efficient and effective for applications requiring visual signaling, decorative lighting, or attention-grabbing displays. Proper thermal management considerations should also be taken into account to prevent overheating of the components during prolonged operation.This is an AC powered LED flasher that can drive two High bright LEDs directly from the power obtained from the AC lines. The high bright LED flasher can b.. 🔗 External reference
The AC-powered LED flasher circuit is designed to illuminate two high-bright LEDs using the alternating current (AC) directly from the mains supply. The circuit typically consists of a transformer, rectifier, voltage regulator, and control circuitry to modulate the LED flashing.
The transformer steps down the AC voltage to a lower, manageable level suitable for the circuit. Following the transformer, a rectifier (often a bridge rectifier configuration) converts the AC voltage to direct current (DC). This conversion is crucial as LEDs require a DC supply for proper operation.
After rectification, the voltage may still be too high or unstable for direct LED usage. Therefore, a voltage regulator is employed to ensure that the output voltage remains at a safe and constant level, typically around 3 to 3.5 volts per LED, depending on the specifications of the high-bright LEDs used.
To create the flashing effect, a control circuit, which may include a timer IC or a microcontroller, is integrated into the design. This control circuit modulates the power delivered to the LEDs, turning them on and off at a predetermined frequency, which can be adjusted based on the desired flashing rate.
Additional components such as resistors may be included to limit the current flowing through the LEDs, ensuring they operate within their specified current ratings to prevent damage. Capacitors may also be utilized for smoothing the DC output from the rectifier, reducing flicker and enhancing LED performance.
The overall design of the AC-powered LED flasher circuit is efficient and effective for applications requiring visual signaling, decorative lighting, or attention-grabbing displays. Proper thermal management considerations should also be taken into account to prevent overheating of the components during prolonged operation.This is an AC powered LED flasher that can drive two High bright LEDs directly from the power obtained from the AC lines. The high bright LED flasher can b.. 🔗 External reference