24hr clock using logic ics
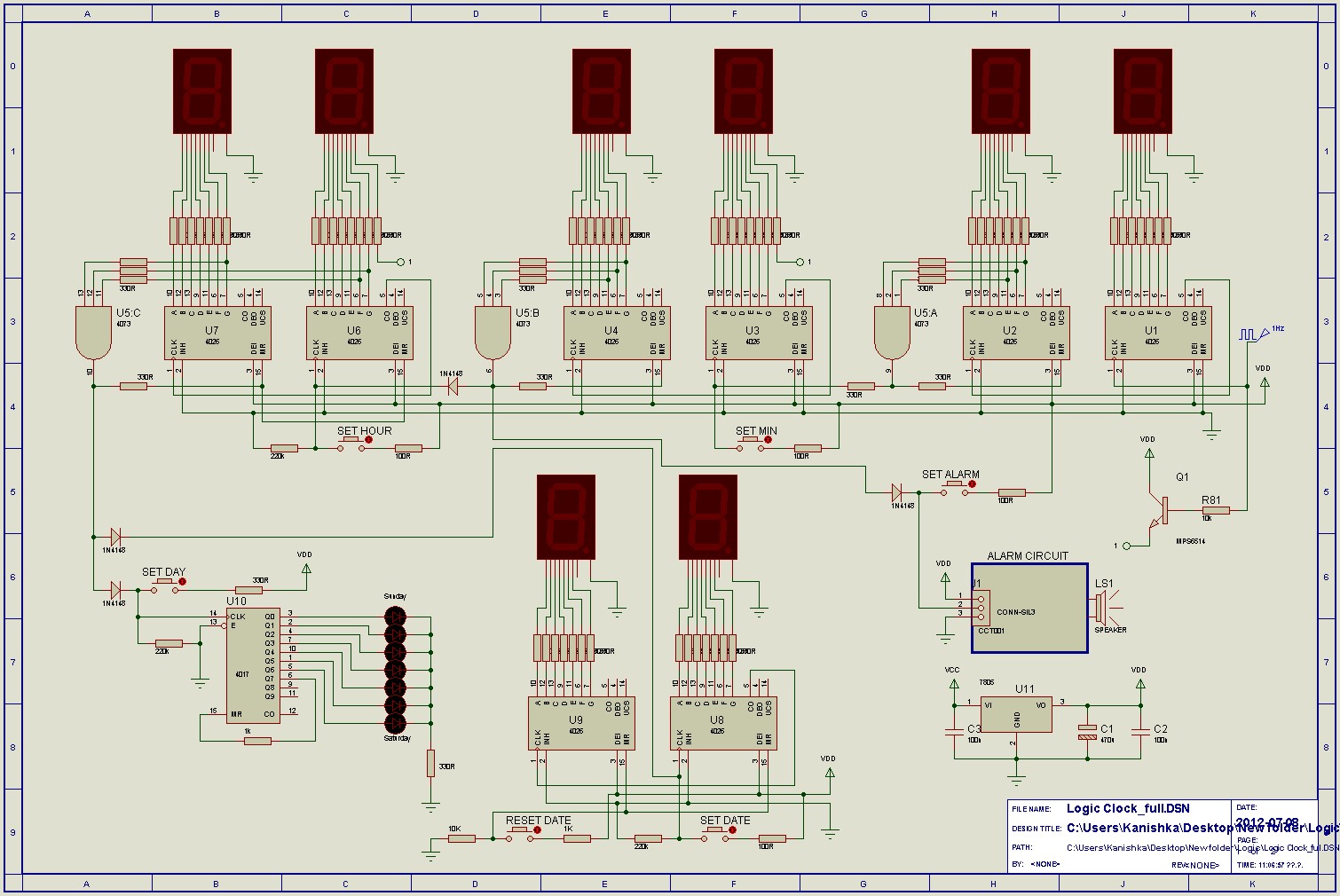
The count advances as the clock input transitions to high (on the rising edge). Each output from Q0 to Q9 activates sequentially as the counting progresses. For specific functions, such as flash sequences, outputs may be combined using diodes. The reset input must be low (0V) for normal operation, allowing counting from 0 to 9. When the reset input is high, it resets the count to zero (with Q0 high). This can be manually controlled with a switch connected between reset and +Vs, along with a 10k resistor linking reset to 0V. To count to fewer than 9, the relevant output (Q0-Q9) can be connected to reset; for instance, to count to 0, 1, 2, or 3, connect Q4 to reset. The disable input should also be low (0V) for normal operation, and when high, it disables counting, causing clock pulses to be ignored and maintaining a constant count. The G·10 output is high for counts 0-4 and low for counts 5-9, providing an output at one-tenth of the clock frequency. This output can be used to drive the clock input of another 4017 IC to count the tens. The outputs a-g will go high to illuminate the corresponding segments of a common-cathode 7-segment display as the count increases. The maximum output current is approximately 1mA with a 4.5V supply and 4mA with a 9V supply, which is adequate for directly driving many 7-segment LED displays. The disable clock input should be low (0V) for normal operation; when it is high, counting is disabled and clock pulses are ignored, maintaining a constant count. The enable display input must be high (+Vs) for normal operation; when low, it sets outputs a-g to low, resulting in a blank display. The enable output tracks this input but with a short delay. The G·10 output (noted as h in the table) is high for counts 0-4 and low for counts 5-9, providing an output at one-tenth of the clock frequency, suitable for driving the clock input of another 4026 IC for multi-digit counting.
The circuit described is based on a decade counter, typically implemented with a 4017 decade counter IC, which counts from 0 to 9 in response to clock pulses. The clock input is essential for advancing the count, and the rising edge of the clock signal triggers the counting action. Outputs Q0 through Q9 are used to indicate the current count, activating sequentially with each clock pulse. The use of diodes to combine outputs for specific sequences allows for flexible applications, such as creating visual effects with LED displays.
The reset function is critical for initializing the counter or for setting specific counting ranges. By connecting an output to the reset pin, the counting can be limited, allowing for applications that do not require a full decade count. The disable input serves as a control mechanism to pause counting, which can be useful in scenarios where the count needs to be held constant temporarily.
The G·10 output is particularly useful for cascading multiple counters, enabling the design of more complex counting systems. This output effectively divides the clock frequency by ten, making it suitable for driving additional decade counters.
The display control inputs—enable display and disable clock—provide user control over the visibility of the count and the counting process itself. These features enhance the versatility of the circuit, allowing it to be adapted for various applications, including digital clocks, scoreboards, and other counting devices.
In summary, this circuit provides a robust solution for counting applications, featuring multiple control inputs for flexible operation, and is capable of driving displays directly, making it suitable for a wide range of electronic projects.The count advances as the clock input becomes high (on the rising-edge). Each output Q0-Q9 goes high in turn as counting advances. For some functions (such as flash sequences) outputs may be combined using diodes. The reset input should be low (0V) for normal operation (counting 0-9). When high it resets the count to zero (Q0 high). This can be do ne manually with a switch between reset and +Vs and a 10k resistor between reset and 0V. Counting to less than 9 is achieved by connecting the relevant output (Q0-Q9) to reset, for example to count 0, 1, 2, 3 connect Q4 to reset. The disable input should be low (0V) for normal operation. When high it disables counting so that clock pulses are ignored and the count is kept constant. The G·10 output is high for counts 0-4 and low for 5-9, so it provides an output at 1/10 of the clock frequency.
It can be used to drive the clock input of another 4017 (to count the tens). The count advances as the clock input becomes high (on the rising-edge). The outputs a-g go high to light the appropriate segments of a common-cathode 7-segment display as the count advances. The maximum output current is about 1mA with a 4. 5V supply and 4mA with a 9V supply. This is sufficient to directly drive many 7-segment LED displays. The table below shows the segment sequence in detail. The disable clock input should be low (0V) for normal operation. When high it disables counting so that clock pulses are ignored and the count is kept constant. The enable display input should be high (+Vs) for normal operation. When low it makes outputs a-g low, giving a blank display. The enable out follows this input but with a brief delay. The G·10 output (h in table) is high for counts 0-4 and low for 5-9, so it provides an output at 1/10 of the clock frequency.
It can be used to drive the clock input of another 4026 to provide multi-digit counting. 🔗 External reference
The circuit described is based on a decade counter, typically implemented with a 4017 decade counter IC, which counts from 0 to 9 in response to clock pulses. The clock input is essential for advancing the count, and the rising edge of the clock signal triggers the counting action. Outputs Q0 through Q9 are used to indicate the current count, activating sequentially with each clock pulse. The use of diodes to combine outputs for specific sequences allows for flexible applications, such as creating visual effects with LED displays.
The reset function is critical for initializing the counter or for setting specific counting ranges. By connecting an output to the reset pin, the counting can be limited, allowing for applications that do not require a full decade count. The disable input serves as a control mechanism to pause counting, which can be useful in scenarios where the count needs to be held constant temporarily.
The G·10 output is particularly useful for cascading multiple counters, enabling the design of more complex counting systems. This output effectively divides the clock frequency by ten, making it suitable for driving additional decade counters.
The display control inputs—enable display and disable clock—provide user control over the visibility of the count and the counting process itself. These features enhance the versatility of the circuit, allowing it to be adapted for various applications, including digital clocks, scoreboards, and other counting devices.
In summary, this circuit provides a robust solution for counting applications, featuring multiple control inputs for flexible operation, and is capable of driving displays directly, making it suitable for a wide range of electronic projects.The count advances as the clock input becomes high (on the rising-edge). Each output Q0-Q9 goes high in turn as counting advances. For some functions (such as flash sequences) outputs may be combined using diodes. The reset input should be low (0V) for normal operation (counting 0-9). When high it resets the count to zero (Q0 high). This can be do ne manually with a switch between reset and +Vs and a 10k resistor between reset and 0V. Counting to less than 9 is achieved by connecting the relevant output (Q0-Q9) to reset, for example to count 0, 1, 2, 3 connect Q4 to reset. The disable input should be low (0V) for normal operation. When high it disables counting so that clock pulses are ignored and the count is kept constant. The G·10 output is high for counts 0-4 and low for 5-9, so it provides an output at 1/10 of the clock frequency.
It can be used to drive the clock input of another 4017 (to count the tens). The count advances as the clock input becomes high (on the rising-edge). The outputs a-g go high to light the appropriate segments of a common-cathode 7-segment display as the count advances. The maximum output current is about 1mA with a 4. 5V supply and 4mA with a 9V supply. This is sufficient to directly drive many 7-segment LED displays. The table below shows the segment sequence in detail. The disable clock input should be low (0V) for normal operation. When high it disables counting so that clock pulses are ignored and the count is kept constant. The enable display input should be high (+Vs) for normal operation. When low it makes outputs a-g low, giving a blank display. The enable out follows this input but with a brief delay. The G·10 output (h in table) is high for counts 0-4 and low for 5-9, so it provides an output at 1/10 of the clock frequency.
It can be used to drive the clock input of another 4026 to provide multi-digit counting. 🔗 External reference