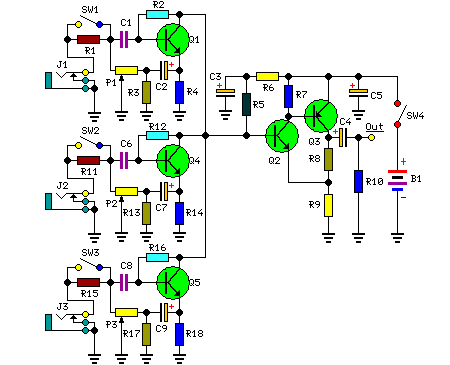
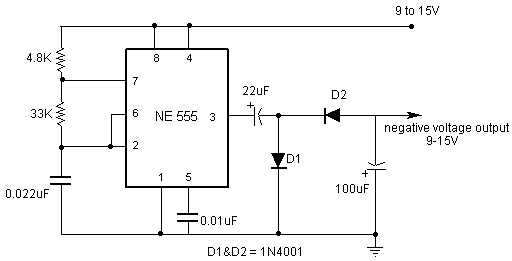
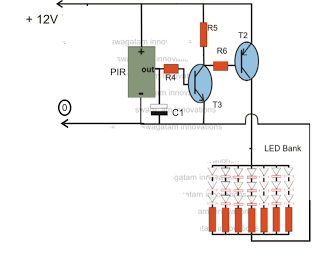
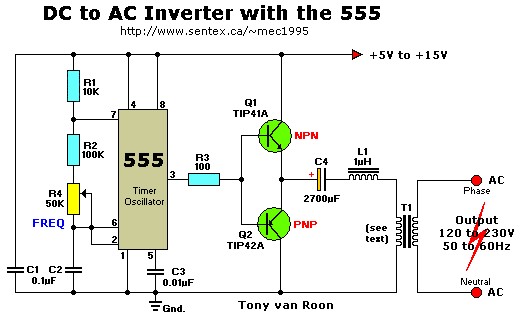
2M Fet Power Amplifier Circuit
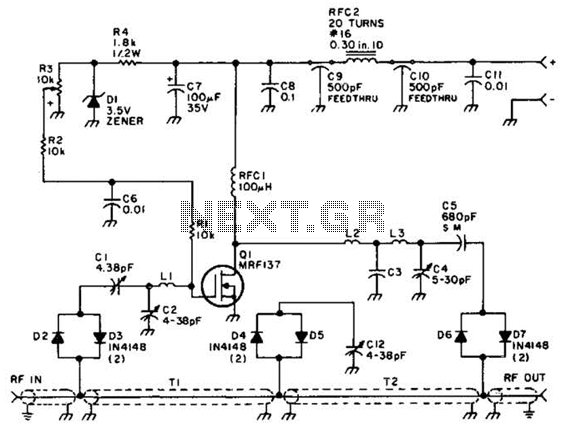
Using a power MOSFET, this amplifier can achieve a 2-W handheld radio power level, increasing it to approximately 10 W on the 2-meter band. A transmission-line RF switch is employed for transmit/receive (T/R) switching.
The described amplifier utilizes a power MOSFET as its primary amplification component, which is capable of handling significant power levels while maintaining efficiency. The 2-W output power is suitable for handheld transceivers, allowing for effective communication over short distances. The amplifier's design is optimized for operation on the 2-meter band, commonly used in amateur radio, which enhances its usability for hobbyists and professionals alike.
To facilitate the transition between transmitting and receiving modes, a transmission-line RF switch is integrated into the circuit. This type of switch is advantageous due to its low insertion loss and high isolation characteristics, which are crucial for maintaining signal integrity during operation. The RF switch effectively routes the signal from the amplifier to the antenna during transmission and connects the receiver to the antenna during reception.
The overall design of the amplifier circuit includes necessary biasing components for the MOSFET, ensuring that it operates within its optimal range. The layout should minimize parasitic inductances and capacitances to enhance performance and reliability. Proper heat dissipation measures, such as heat sinks or thermal pads, are also essential, given the power levels involved.
In summary, this amplifier design combines the efficiency of a power MOSFET with the reliability of a transmission-line RF switch, making it suitable for applications requiring moderate power output on the 2-meter band. The circuit's design considerations play a critical role in achieving the desired performance characteristics while ensuring robust operation in various conditions. Using a power MOSFET, this amplifier can boast a 2-W handie-talkie power level to around 10 W on 2 meters. A transmission-line RF switch is used for T/R switching.
The described amplifier utilizes a power MOSFET as its primary amplification component, which is capable of handling significant power levels while maintaining efficiency. The 2-W output power is suitable for handheld transceivers, allowing for effective communication over short distances. The amplifier's design is optimized for operation on the 2-meter band, commonly used in amateur radio, which enhances its usability for hobbyists and professionals alike.
To facilitate the transition between transmitting and receiving modes, a transmission-line RF switch is integrated into the circuit. This type of switch is advantageous due to its low insertion loss and high isolation characteristics, which are crucial for maintaining signal integrity during operation. The RF switch effectively routes the signal from the amplifier to the antenna during transmission and connects the receiver to the antenna during reception.
The overall design of the amplifier circuit includes necessary biasing components for the MOSFET, ensuring that it operates within its optimal range. The layout should minimize parasitic inductances and capacitances to enhance performance and reliability. Proper heat dissipation measures, such as heat sinks or thermal pads, are also essential, given the power levels involved.
In summary, this amplifier design combines the efficiency of a power MOSFET with the reliability of a transmission-line RF switch, making it suitable for applications requiring moderate power output on the 2-meter band. The circuit's design considerations play a critical role in achieving the desired performance characteristics while ensuring robust operation in various conditions. Using a power MOSFET, this amplifier can boast a 2-W handie-talkie power level to around 10 W on 2 meters. A transmission-line RF switch is used for T/R switching.