3-30 V/2.5 A Stabilized variable power supply
This is a very useful project for anyone working in electronics. It is a versatile power supply that will solve most of the supply problems arising in the everyday work of any electronics workshop. It covers a wide range of voltages being continuously variable from 30 V down to 3 V. The output current is 2.5 A maximum, more than enough for most applications. The circuit is completely stabilized even at the extremes of its output range and is fully protected against short-circuits and overloading. More: Technical Specifications - Characteristics Input voltage: 24V DC Output current: 2.5 A Output voltage: 3-30V DC
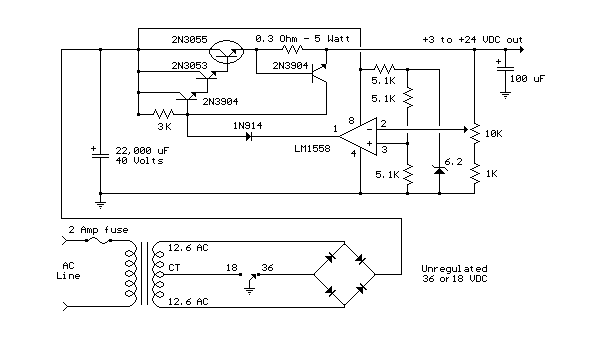
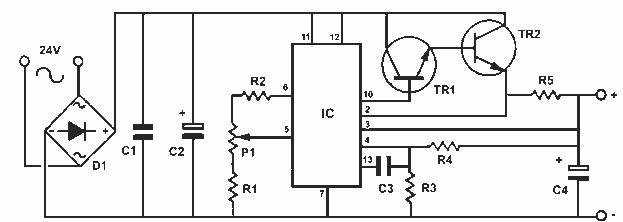
How it Works The power supply is using a well-known and quite popular VOLTAGE STABILIZER IC the LM 723. The IC can be adjusted for output voltages that vary continuously between 2 and 37 VDC and has a current rating of 150 mA which is of course too low for any serious use. In order to increase the current handling capacity of the circuit, the output of the IC is used to drive a Darlington pair formed by two power transistors the BD 135 and the 2N 3055. The use of the transistors to increase the maximum current output limits the range of output voltages somewhat and this is why the circuit has been designed to operate from 3 to 30 VDC. The resistor R5 that you see connected in series with the output of the supply is used for the protection of the circuit from overloading. If an excessively large current flows through R5, the voltage across it increases and any voltage greater than 0.3 V across it has as a result to cut the supply off, thus effectively protecting it from overloads. This protection feature is built into the LM 723 and the voltage drop across R5 is sensed by the IC itself between pins 2 and 3. At the same time the IC is continuously comparing the output voltage to its internal reference and if the difference exceeds the designer's standards it corrects it automatically. This ensures great stability under different loads. The potentiometer P1 is used to adjust the output voltage at the desired level. If the full range from 3 to 30 V is desired then you should use a mains transformer with a secondary winding having a rating of at least 24 V/3 A. If the maximum voltage output is not desired, you can of course use a transformer with a lower secondary voltage output. (However, once rectified the voltage across the capacitor C2 should exceed by 4-5 volts the maximum output expected from the circuit.
The power supply circuit described utilizes the LM 723 voltage regulator IC, which serves as the core component for voltage regulation. This IC is known for its reliability and versatility, allowing for adjustable output voltages between 2 V and 37 V. Given its limited current output capacity of 150 mA, the circuit employs a Darlington pair configuration using BD 135 and 2N 3055 transistors to enhance the output current capability to a maximum of 2.5 A. This arrangement not only boosts the current handling but also defines the operational voltage range from 3 V to 30 V.
The design includes an important safety feature through the inclusion of a series resistor, R5, which acts as a current sensing element. When excessive current is detected, the voltage across R5 rises above 0.3 V, triggering the LM 723 to cut off the output, thus preventing damage to the circuit. The IC continuously monitors the output voltage against its internal reference, ensuring that voltage fluctuations are corrected automatically, maintaining stability under varying load conditions.
For adjusting the output voltage, a potentiometer (P1) is integrated into the circuit, allowing users to set the desired voltage level easily. Additionally, the transformer used in the circuit must be capable of providing a secondary voltage of at least 24 V at 3 A to ensure adequate performance across the entire output range. The design also notes that the rectified voltage across the smoothing capacitor (C2) must exceed the maximum output voltage by a margin of 4-5 volts to ensure proper operation. This comprehensive approach to design and safety makes this power supply a valuable tool for electronics professionals and hobbyists alike.This is a very useful project for anyone working in electronics. It is a versatile power supply that will solve most of the supply problems arising in the everyday work of any electronics work shop. It covers a wide range of voltages being continuously variable from 30 V down to 3 V. The output current is 2.5 A maximum, more than enough for most applications. The circuit is completely stabilised even at the extremes of its output range and is fully protected against short-circuits and overloading.
Technical Specifications - Characteristics Input voltage: 24V DC Output current: 2.5 A Output volytage: 3-30V DC -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- How it Works The power supply is using a well known and quite popular VOLTAGE STABILIZER IC the LM 723. The IC can be adjusted for out put voltages that vary continuously between 2 and 37 VDC and has a current rating of 150 mA which is of course too low for any serious use.
In order to increase the current handling capacity of the circuit the output of the IC is used to drive a darlington pair formed by two power transistors the BD 135 and the 2N 3055. The use of the transistors to increase the maximum current output limits the range of output voltages somewhat and this is why the circuit has been designed to operate from 3 to 30 VDC.
The resistor R5 that you see connected in series with the output of the supply is used for the protection of the circuit from overloading. If an excessively large current flows through R5, the voltage across it increases and any voltage greater than 0.3 V across it has as a result to cut the supply off, thus effectively protecting it from overloads.
This protection feature is built in the LM 723 and the voltage drop across R5 is sensed by the IC itself between pins 2 and 3. At the same time the IC is continuously comparing the output voltage to its internal reference and if the difference exceeds the designer?s standards it corrects it automatically.
This ensures great stability under different loads. The potentiometer P1 is used to adjust the out put voltage at the desired level. If the full range from 3 to 30 V is desired then you should use a mains transformer with a secondary winding having a rating of at least 24 V/3 A. If the maxi mum voltage output is not desired you can of course use a transformer with a lower secondary voltage output.
(However, once rectified the voltage across the capacitor C2 should exceed by 4-5 volts the maximum output expected from the circuit. 🔗 External reference
How it Works The power supply is using a well-known and quite popular VOLTAGE STABILIZER IC the LM 723. The IC can be adjusted for output voltages that vary continuously between 2 and 37 VDC and has a current rating of 150 mA which is of course too low for any serious use. In order to increase the current handling capacity of the circuit, the output of the IC is used to drive a Darlington pair formed by two power transistors the BD 135 and the 2N 3055. The use of the transistors to increase the maximum current output limits the range of output voltages somewhat and this is why the circuit has been designed to operate from 3 to 30 VDC. The resistor R5 that you see connected in series with the output of the supply is used for the protection of the circuit from overloading. If an excessively large current flows through R5, the voltage across it increases and any voltage greater than 0.3 V across it has as a result to cut the supply off, thus effectively protecting it from overloads. This protection feature is built into the LM 723 and the voltage drop across R5 is sensed by the IC itself between pins 2 and 3. At the same time the IC is continuously comparing the output voltage to its internal reference and if the difference exceeds the designer's standards it corrects it automatically. This ensures great stability under different loads. The potentiometer P1 is used to adjust the output voltage at the desired level. If the full range from 3 to 30 V is desired then you should use a mains transformer with a secondary winding having a rating of at least 24 V/3 A. If the maximum voltage output is not desired, you can of course use a transformer with a lower secondary voltage output. (However, once rectified the voltage across the capacitor C2 should exceed by 4-5 volts the maximum output expected from the circuit.
The power supply circuit described utilizes the LM 723 voltage regulator IC, which serves as the core component for voltage regulation. This IC is known for its reliability and versatility, allowing for adjustable output voltages between 2 V and 37 V. Given its limited current output capacity of 150 mA, the circuit employs a Darlington pair configuration using BD 135 and 2N 3055 transistors to enhance the output current capability to a maximum of 2.5 A. This arrangement not only boosts the current handling but also defines the operational voltage range from 3 V to 30 V.
The design includes an important safety feature through the inclusion of a series resistor, R5, which acts as a current sensing element. When excessive current is detected, the voltage across R5 rises above 0.3 V, triggering the LM 723 to cut off the output, thus preventing damage to the circuit. The IC continuously monitors the output voltage against its internal reference, ensuring that voltage fluctuations are corrected automatically, maintaining stability under varying load conditions.
For adjusting the output voltage, a potentiometer (P1) is integrated into the circuit, allowing users to set the desired voltage level easily. Additionally, the transformer used in the circuit must be capable of providing a secondary voltage of at least 24 V at 3 A to ensure adequate performance across the entire output range. The design also notes that the rectified voltage across the smoothing capacitor (C2) must exceed the maximum output voltage by a margin of 4-5 volts to ensure proper operation. This comprehensive approach to design and safety makes this power supply a valuable tool for electronics professionals and hobbyists alike.This is a very useful project for anyone working in electronics. It is a versatile power supply that will solve most of the supply problems arising in the everyday work of any electronics work shop. It covers a wide range of voltages being continuously variable from 30 V down to 3 V. The output current is 2.5 A maximum, more than enough for most applications. The circuit is completely stabilised even at the extremes of its output range and is fully protected against short-circuits and overloading.
Technical Specifications - Characteristics Input voltage: 24V DC Output current: 2.5 A Output volytage: 3-30V DC -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- How it Works The power supply is using a well known and quite popular VOLTAGE STABILIZER IC the LM 723. The IC can be adjusted for out put voltages that vary continuously between 2 and 37 VDC and has a current rating of 150 mA which is of course too low for any serious use.
In order to increase the current handling capacity of the circuit the output of the IC is used to drive a darlington pair formed by two power transistors the BD 135 and the 2N 3055. The use of the transistors to increase the maximum current output limits the range of output voltages somewhat and this is why the circuit has been designed to operate from 3 to 30 VDC.
The resistor R5 that you see connected in series with the output of the supply is used for the protection of the circuit from overloading. If an excessively large current flows through R5, the voltage across it increases and any voltage greater than 0.3 V across it has as a result to cut the supply off, thus effectively protecting it from overloads.
This protection feature is built in the LM 723 and the voltage drop across R5 is sensed by the IC itself between pins 2 and 3. At the same time the IC is continuously comparing the output voltage to its internal reference and if the difference exceeds the designer?s standards it corrects it automatically.
This ensures great stability under different loads. The potentiometer P1 is used to adjust the out put voltage at the desired level. If the full range from 3 to 30 V is desired then you should use a mains transformer with a secondary winding having a rating of at least 24 V/3 A. If the maxi mum voltage output is not desired you can of course use a transformer with a lower secondary voltage output.
(However, once rectified the voltage across the capacitor C2 should exceed by 4-5 volts the maximum output expected from the circuit. 🔗 External reference