300 Watt MOSFET Broadband Amplifier Using MRF141G
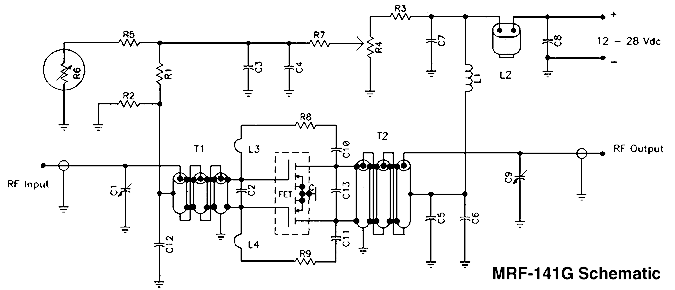
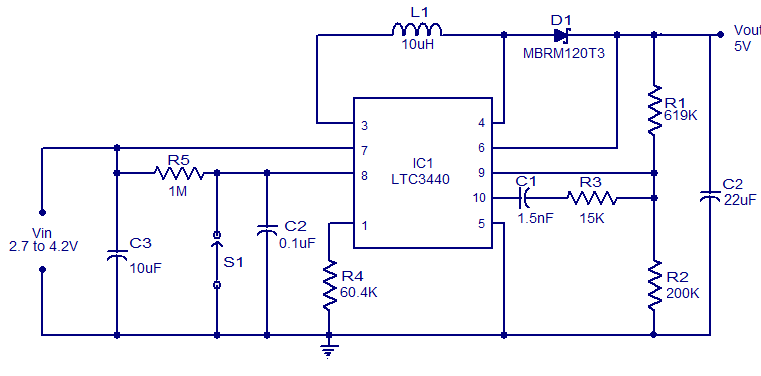
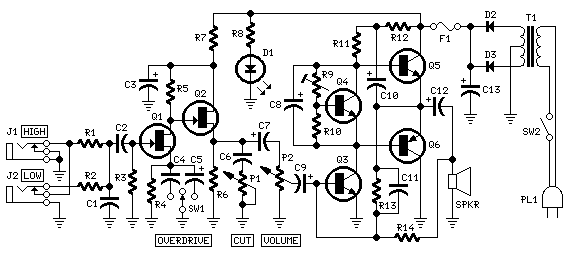
The following segment provides the enhanced Motorola schematic for a typical application of the MRF141G, which includes parasitic stabilization features. The MRF141G is a broadband power RF MOSFET capable of delivering a conservatively rated 300 watts across the FM broadcast band. The flange of the MRF141G should be mounted to a heat spreader, a copper plate that is 5/16" thick and measures 6" x 8". This plate should then be mounted to the heatsink using 6-32 machine screws, assuming the heatsink is drilled and tapped. It is recommended to purchase the two transformer assemblies instead of attempting to create them, as 15-ohm hardline is not readily available. The amplifier features variable gain control through a bias adjustment trim pot. It can be used in conjunction with an SWR bridge circuit to limit power output in the event of high SWR caused by damage to the antenna during a storm or accidental disconnection of the coax transmission line. For those wishing to implement a failsafe shutdown system triggered by loss of PLL lock, a power supply cutoff relay is recommended for complete safety. Caution is advised as this amplifier operates at very high power levels, which can cause severe RF burns if contact is made with open coax feeder from this amplifier. Additionally, if the broadcast antenna is roof-mounted and it falls during a windstorm while fed at full power, it may ignite certain types of roofing insulation. Extreme caution should be exercised during the installation and operation of this unit.
The MRF141G RF MOSFET operates within the FM broadcast band and requires careful thermal management due to its high power output capabilities. The specified heat spreader, made from a 5/16" thick copper plate measuring 6" x 8", is essential for dissipating heat generated during operation. Proper mounting to the heatsink with 6-32 machine screws ensures stable thermal performance.
The variable gain control via a bias adjustment trim pot allows for fine-tuning of the amplifier's output, which is critical for optimizing performance based on specific application needs. The integration of an SWR bridge circuit is a prudent design choice, as it provides real-time monitoring of the standing wave ratio, allowing for proactive management of the amplifier's output power. This feature is particularly important in scenarios where the antenna may be compromised, preventing potential damage to the amplifier and associated components.
For added safety, the implementation of a power supply cutoff relay is recommended, particularly in systems where a loss of PLL lock could lead to uncontrolled output. This relay acts as a failsafe, ensuring that the amplifier is powered down in critical situations, thereby protecting both the equipment and the operator.
The operational safety warnings highlight the importance of handling high-power RF equipment with care. The risk of RF burns from exposed coaxial connections necessitates protective measures, such as insulated tools and proper safety gear during installation and maintenance. Furthermore, the potential fire hazard from a roof-mounted antenna during adverse weather conditions underscores the need for robust installation practices and regular inspections to mitigate risks associated with environmental factors.
Overall, the MRF141G amplifier requires meticulous attention to detail in its design, installation, and operation to ensure optimal performance and safety.The following segment will provide the enhanced Motorola schematic for any typical application for the MRF141G (which includes parasitic stabilization features), a broadband power RF MOSFET which will place out a conservatively-rated 300 watts across the FM broadcast band. The flange about the MRF141G ought to be mounted to a heat spreader, a copp er plate 5/16" thick and 6" x 8", which is then mounted to the heatsink with 6-32 machine screws, if your heatsink is drilled and tapped. I recommend getting the two transformer assemblies, instead of trying to create them, due to the fact 15-ohm hardline is not straightforward to come across.
I`ve had great results ordering them from: This amplifier has the notable attribute of variable acquire manage via the bias adjustment trim pot. It may possibly be used in conjunction with an SWR bridge circuit to limit energy output inside the event of large SWR triggered by harm towards the antenna in the course of a storm, or a person inadvertently disconnecting the coax transmission line.
For those who wish to apply a failsafe shutdown system that is triggered by reduction of PLL lock, I nevertheless suggest a power provide cutoff relay for total basic safety having said that. CAUTION: This amplifier operates at very high power ranges. You are able to obtain severe RF uses up if coming in contact with open coax feeder from this amp. Moreover, if your broadcast antenna is roof-mounted, and it need to blow down inside a windstorm although fed at full power from this amp, it may possibly commence a fire in certain sorts of roofing insulation!
Be extremely cautious with all the utilization, set up and operation in the unit. 🔗 External reference
The MRF141G RF MOSFET operates within the FM broadcast band and requires careful thermal management due to its high power output capabilities. The specified heat spreader, made from a 5/16" thick copper plate measuring 6" x 8", is essential for dissipating heat generated during operation. Proper mounting to the heatsink with 6-32 machine screws ensures stable thermal performance.
The variable gain control via a bias adjustment trim pot allows for fine-tuning of the amplifier's output, which is critical for optimizing performance based on specific application needs. The integration of an SWR bridge circuit is a prudent design choice, as it provides real-time monitoring of the standing wave ratio, allowing for proactive management of the amplifier's output power. This feature is particularly important in scenarios where the antenna may be compromised, preventing potential damage to the amplifier and associated components.
For added safety, the implementation of a power supply cutoff relay is recommended, particularly in systems where a loss of PLL lock could lead to uncontrolled output. This relay acts as a failsafe, ensuring that the amplifier is powered down in critical situations, thereby protecting both the equipment and the operator.
The operational safety warnings highlight the importance of handling high-power RF equipment with care. The risk of RF burns from exposed coaxial connections necessitates protective measures, such as insulated tools and proper safety gear during installation and maintenance. Furthermore, the potential fire hazard from a roof-mounted antenna during adverse weather conditions underscores the need for robust installation practices and regular inspections to mitigate risks associated with environmental factors.
Overall, the MRF141G amplifier requires meticulous attention to detail in its design, installation, and operation to ensure optimal performance and safety.The following segment will provide the enhanced Motorola schematic for any typical application for the MRF141G (which includes parasitic stabilization features), a broadband power RF MOSFET which will place out a conservatively-rated 300 watts across the FM broadcast band. The flange about the MRF141G ought to be mounted to a heat spreader, a copp er plate 5/16" thick and 6" x 8", which is then mounted to the heatsink with 6-32 machine screws, if your heatsink is drilled and tapped. I recommend getting the two transformer assemblies, instead of trying to create them, due to the fact 15-ohm hardline is not straightforward to come across.
I`ve had great results ordering them from: This amplifier has the notable attribute of variable acquire manage via the bias adjustment trim pot. It may possibly be used in conjunction with an SWR bridge circuit to limit energy output inside the event of large SWR triggered by harm towards the antenna in the course of a storm, or a person inadvertently disconnecting the coax transmission line.
For those who wish to apply a failsafe shutdown system that is triggered by reduction of PLL lock, I nevertheless suggest a power provide cutoff relay for total basic safety having said that. CAUTION: This amplifier operates at very high power ranges. You are able to obtain severe RF uses up if coming in contact with open coax feeder from this amp. Moreover, if your broadcast antenna is roof-mounted, and it need to blow down inside a windstorm although fed at full power from this amp, it may possibly commence a fire in certain sorts of roofing insulation!
Be extremely cautious with all the utilization, set up and operation in the unit. 🔗 External reference