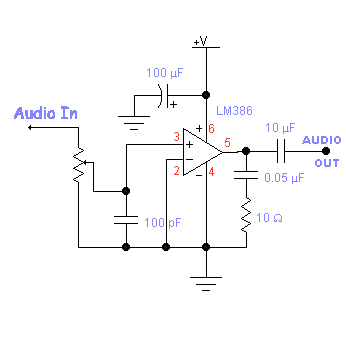
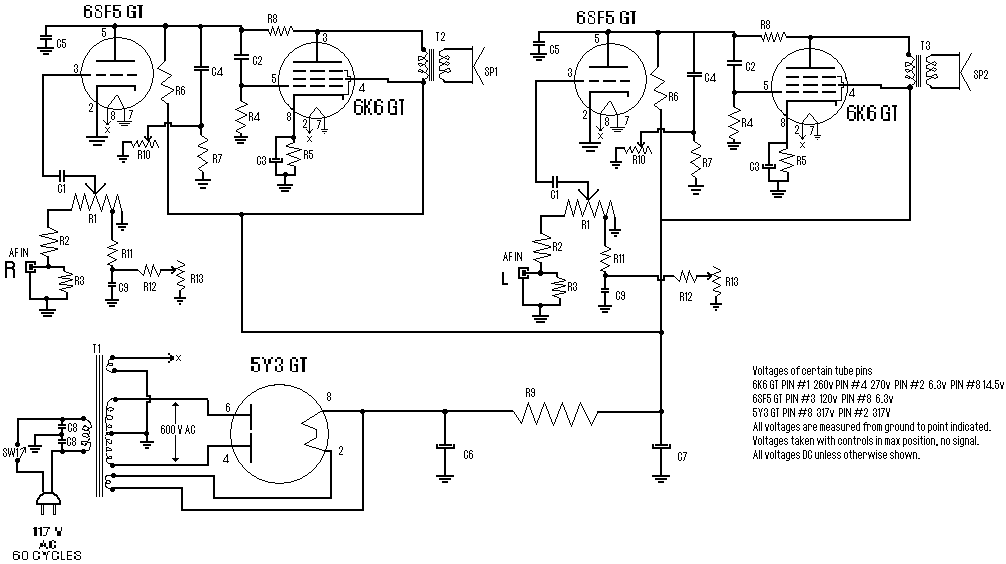
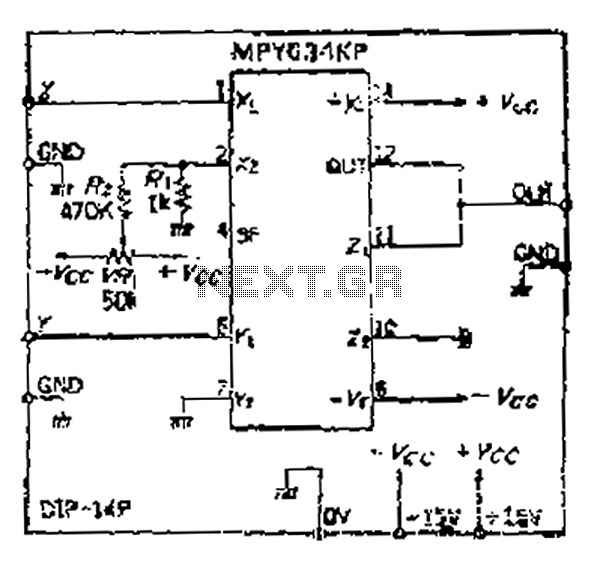
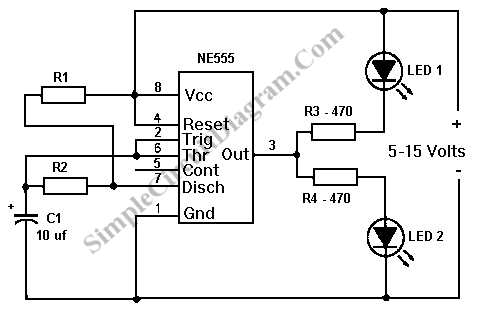
3w 5w audio amplifier circuit schematic
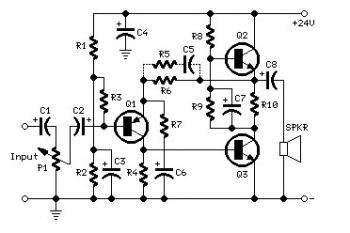
The total electric current drawn by the circuit should be measured by connecting the probes of a multimeter across the positive output of the power supply and the positive rail input of the amplifier. The expected current value is 700 mA. If necessary, adjust resistor R8 to achieve this current level.
To accurately measure the total electric current in the circuit, it is essential to ensure that the multimeter is properly configured for current measurement. This involves connecting the multimeter in series with the circuit component whose current is to be measured. In this case, the measurement should occur between the power supply's positive output and the amplifier's positive rail input.
The multimeter should be set to the appropriate current range, ideally exceeding the expected 700 mA to prevent damage to the device. Once the probes are connected, the circuit can be powered on, and the multimeter will display the current flowing through the circuit.
If the measured current deviates from the target value of 700 mA, adjustments can be made by modifying the resistance of R8. This resistor is likely part of a feedback network or current-limiting circuit, and altering its value will affect the overall current flow. Increasing R8 will reduce the current, while decreasing R8 will increase it. It is important to make small adjustments and re-measure the current to avoid overshooting the desired value.
In summary, the procedure for measuring and adjusting the total electric current in the circuit is straightforward, involving proper multimeter setup, careful measurement, and precise adjustments to R8 as needed to maintain the target current level of 700 mA.Total electric current drawing of the circuit, recommended measured by inserting the probes of an multimeter across the positive output with the power supply and also the positive rail input with the amplifier, should be 700mA. Adjust R8 to obtain this value if needed. 🔗 External reference
To accurately measure the total electric current in the circuit, it is essential to ensure that the multimeter is properly configured for current measurement. This involves connecting the multimeter in series with the circuit component whose current is to be measured. In this case, the measurement should occur between the power supply's positive output and the amplifier's positive rail input.
The multimeter should be set to the appropriate current range, ideally exceeding the expected 700 mA to prevent damage to the device. Once the probes are connected, the circuit can be powered on, and the multimeter will display the current flowing through the circuit.
If the measured current deviates from the target value of 700 mA, adjustments can be made by modifying the resistance of R8. This resistor is likely part of a feedback network or current-limiting circuit, and altering its value will affect the overall current flow. Increasing R8 will reduce the current, while decreasing R8 will increase it. It is important to make small adjustments and re-measure the current to avoid overshooting the desired value.
In summary, the procedure for measuring and adjusting the total electric current in the circuit is straightforward, involving proper multimeter setup, careful measurement, and precise adjustments to R8 as needed to maintain the target current level of 700 mA.Total electric current drawing of the circuit, recommended measured by inserting the probes of an multimeter across the positive output with the power supply and also the positive rail input with the amplifier, should be 700mA. Adjust R8 to obtain this value if needed. 🔗 External reference