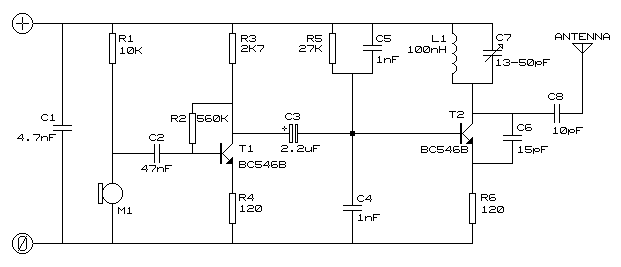
3w fm transmitter

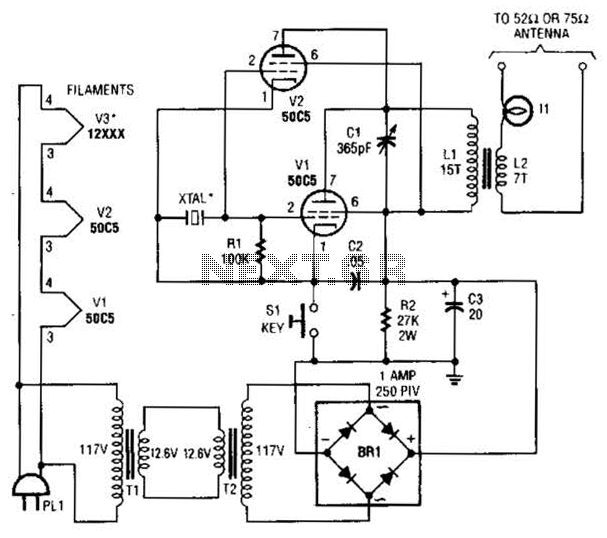
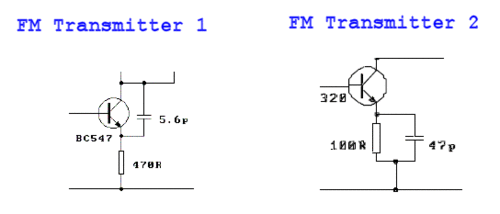
This schematic represents an FM transmitter that delivers an output power of 3 to 3.5 watts, operational within the frequency range of 90 to 110 MHz. While the stability of the circuit is acceptable, incorporating a Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) can enhance its performance.
The FM transmitter circuit is designed to modulate audio signals onto a carrier frequency within the VHF band, specifically between 90 and 110 MHz, which is suitable for FM broadcasting. The output power of 3 to 3.5 watts is adequate for short-range transmission, making it ideal for personal or experimental use.
The main components of the circuit typically include an oscillator, modulator, and amplifier stages. The oscillator generates the carrier frequency, while the modulator superimposes the audio signal onto this carrier wave, creating frequency modulation. The amplifier then boosts the modulated signal to the desired output power level.
In terms of circuit stability, while the basic design may function adequately, the implementation of a Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) can significantly improve frequency stability and reduce drift. A PLL can lock the oscillator frequency to a stable reference, ensuring consistent performance over time and varying environmental conditions. This addition can be particularly beneficial in applications where frequency precision is crucial.
The schematic may also include additional components such as filters to suppress unwanted harmonics, ensuring compliance with broadcasting regulations. Antenna matching networks may be integrated to optimize the transmission efficiency, allowing for effective radiation of the modulated signal.
Overall, this FM transmitter circuit serves as a foundational design for those looking to explore frequency modulation transmission, with the potential for enhancements through advanced techniques such as PLL implementation.This is the schematic for an FM transmitter with 3 to 3.5 W output power that can be used between 90 and 110 MHz. Although the stability isn`t so bad, a PLL can be used on this circuit.. 🔗 External reference
The FM transmitter circuit is designed to modulate audio signals onto a carrier frequency within the VHF band, specifically between 90 and 110 MHz, which is suitable for FM broadcasting. The output power of 3 to 3.5 watts is adequate for short-range transmission, making it ideal for personal or experimental use.
The main components of the circuit typically include an oscillator, modulator, and amplifier stages. The oscillator generates the carrier frequency, while the modulator superimposes the audio signal onto this carrier wave, creating frequency modulation. The amplifier then boosts the modulated signal to the desired output power level.
In terms of circuit stability, while the basic design may function adequately, the implementation of a Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) can significantly improve frequency stability and reduce drift. A PLL can lock the oscillator frequency to a stable reference, ensuring consistent performance over time and varying environmental conditions. This addition can be particularly beneficial in applications where frequency precision is crucial.
The schematic may also include additional components such as filters to suppress unwanted harmonics, ensuring compliance with broadcasting regulations. Antenna matching networks may be integrated to optimize the transmission efficiency, allowing for effective radiation of the modulated signal.
Overall, this FM transmitter circuit serves as a foundational design for those looking to explore frequency modulation transmission, with the potential for enhancements through advanced techniques such as PLL implementation.This is the schematic for an FM transmitter with 3 to 3.5 W output power that can be used between 90 and 110 MHz. Although the stability isn`t so bad, a PLL can be used on this circuit.. 🔗 External reference