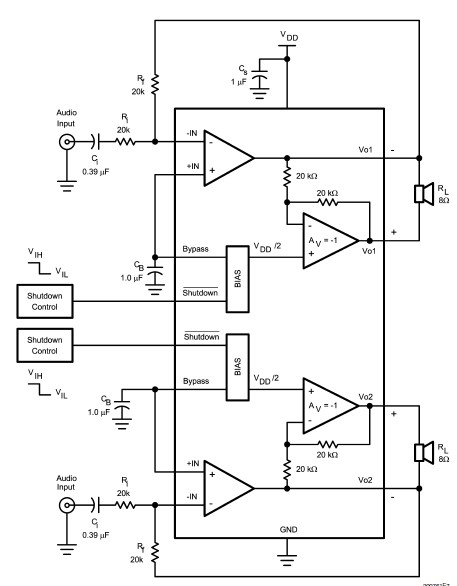
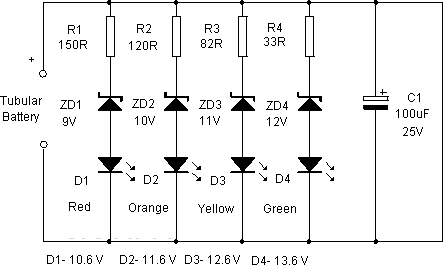
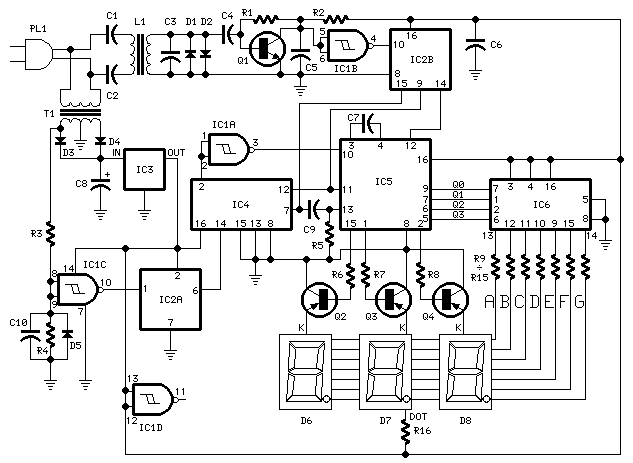
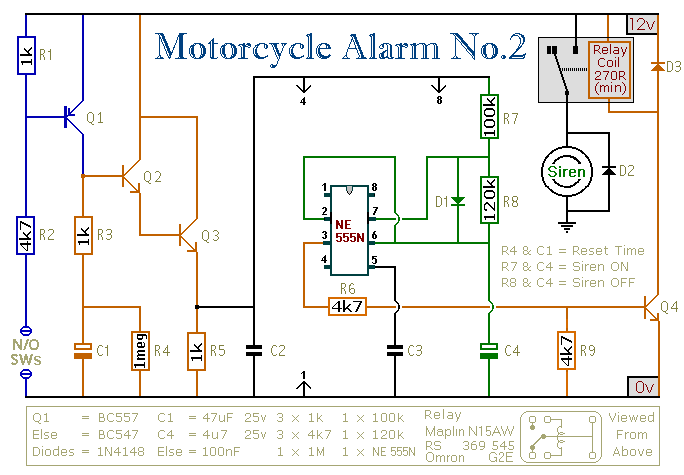
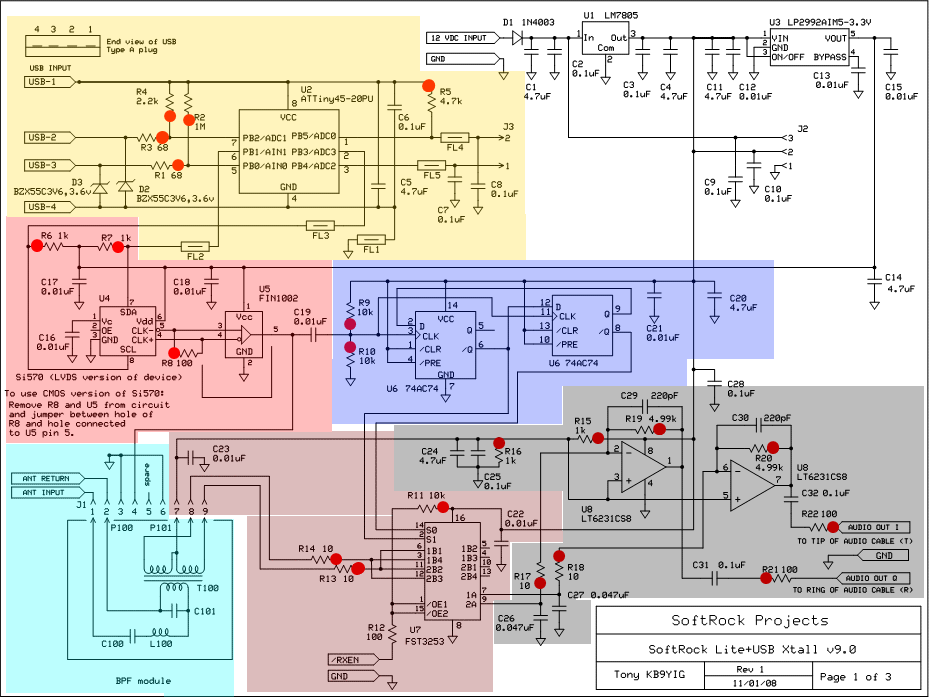
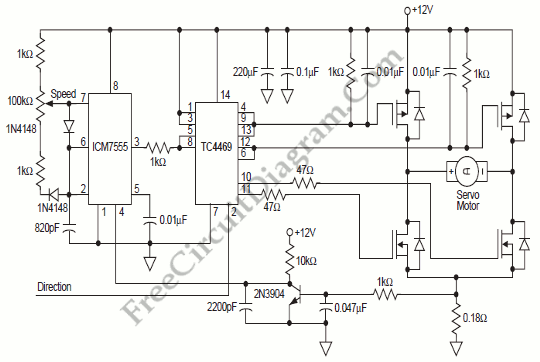
555 meter frequency meter schematic

The circuit consists of a 555 timer along with components R1, C1, and other elements configured as a monostable delay circuit. The input square wave signal is shaped by a Schmitt trigger to meet the triggering requirements.
The 555 timer in monostable mode is designed to produce a single output pulse of a specified duration in response to an external trigger signal. In this configuration, R1 (a resistor) and C1 (a capacitor) determine the timing interval of the output pulse. When the input square wave signal is applied, it is first processed by a Schmitt trigger, which cleans up the signal by providing hysteresis. This ensures that the trigger input is sharply defined, reducing noise susceptibility.
Upon receiving a valid trigger from the Schmitt trigger, the 555 timer activates, causing the output to transition from a low state to a high state. The duration for which the output remains high is determined by the time constant, calculated using the formula T = 1.1 * R1 * C1, where T is the time period in seconds. After this time elapses, the output returns to a low state.
Additional components may include diodes for protection against voltage spikes, and additional resistors or capacitors may be included to further refine the circuit's performance. The monostable delay circuit is widely used in applications such as timers, pulse width modulation, and as a delay mechanism in various electronic systems. The integration of the Schmitt trigger enhances the reliability of the circuit, making it suitable for environments with fluctuating signal levels.FIG. 555 and R1, C1 and other components monostable delay circuit, the input square wave signal or square wave signal by a Schmitt trigger shaping after the trigger requirement s of the circuit 555.
The 555 timer in monostable mode is designed to produce a single output pulse of a specified duration in response to an external trigger signal. In this configuration, R1 (a resistor) and C1 (a capacitor) determine the timing interval of the output pulse. When the input square wave signal is applied, it is first processed by a Schmitt trigger, which cleans up the signal by providing hysteresis. This ensures that the trigger input is sharply defined, reducing noise susceptibility.
Upon receiving a valid trigger from the Schmitt trigger, the 555 timer activates, causing the output to transition from a low state to a high state. The duration for which the output remains high is determined by the time constant, calculated using the formula T = 1.1 * R1 * C1, where T is the time period in seconds. After this time elapses, the output returns to a low state.
Additional components may include diodes for protection against voltage spikes, and additional resistors or capacitors may be included to further refine the circuit's performance. The monostable delay circuit is widely used in applications such as timers, pulse width modulation, and as a delay mechanism in various electronic systems. The integration of the Schmitt trigger enhances the reliability of the circuit, making it suitable for environments with fluctuating signal levels.FIG. 555 and R1, C1 and other components monostable delay circuit, the input square wave signal or square wave signal by a Schmitt trigger shaping after the trigger requirement s of the circuit 555.