5w 150mhz rf amplifier circuit
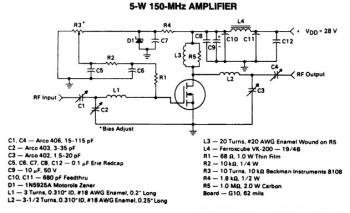
This is a 5W -150MHz RF amplifier circuit that utilizes the MRF123 TMOSFET. The MRF123 is a high-gain FET which may exhibit instability at both VHF and UHF frequencies; therefore, a 68 Ohm input loading resistor is employed to improve stability. This RF amplifier achieves a gain of 14 dB and a drain efficiency of 55%.
The RF amplifier circuit operates within a frequency range of 150 MHz and is designed to deliver an output power of 5 watts. The core component, the MRF123 TMOSFET, is known for its high gain characteristics, making it suitable for amplification tasks in RF applications. However, the high gain can lead to instability, particularly at VHF and UHF frequencies. To mitigate this issue, a 68 Ohm resistor is placed at the input. This resistor serves to dampen potential oscillations and improve the overall stability of the amplifier circuit.
The amplifier's gain of 14 dB indicates that the output signal is significantly amplified relative to the input signal, providing a robust amplification solution for RF signals. The drain efficiency of 55% reflects the ratio of output power to the total power consumed by the amplifier, suggesting that the circuit is relatively efficient in converting DC power into RF output power.
In terms of circuit design, it is essential to ensure proper biasing of the MRF123 to achieve the desired operating point. Additionally, careful attention should be paid to the layout of the circuit to minimize parasitic inductances and capacitances, which can adversely affect performance. The use of decoupling capacitors at the power supply lines is recommended to filter out noise and stabilize the voltage supply, further enhancing the amplifier's performance.
Overall, this RF amplifier circuit is a practical solution for applications requiring reliable amplification of RF signals within the specified frequency range, balancing gain, stability, and efficiency.This is a 5W -150MHz RF amplifier circuit. It applies the MRF123 TMOSFET. The MRF123 is a very high gain FET which potentially unstable at both VHF and UHF frequencies, so the 68 Ohm input loading resistor has been used to enhance the stability. This RF amplifier has a gain of 14 dB and a drain effeciency of 55%. 🔗 External reference
The RF amplifier circuit operates within a frequency range of 150 MHz and is designed to deliver an output power of 5 watts. The core component, the MRF123 TMOSFET, is known for its high gain characteristics, making it suitable for amplification tasks in RF applications. However, the high gain can lead to instability, particularly at VHF and UHF frequencies. To mitigate this issue, a 68 Ohm resistor is placed at the input. This resistor serves to dampen potential oscillations and improve the overall stability of the amplifier circuit.
The amplifier's gain of 14 dB indicates that the output signal is significantly amplified relative to the input signal, providing a robust amplification solution for RF signals. The drain efficiency of 55% reflects the ratio of output power to the total power consumed by the amplifier, suggesting that the circuit is relatively efficient in converting DC power into RF output power.
In terms of circuit design, it is essential to ensure proper biasing of the MRF123 to achieve the desired operating point. Additionally, careful attention should be paid to the layout of the circuit to minimize parasitic inductances and capacitances, which can adversely affect performance. The use of decoupling capacitors at the power supply lines is recommended to filter out noise and stabilize the voltage supply, further enhancing the amplifier's performance.
Overall, this RF amplifier circuit is a practical solution for applications requiring reliable amplification of RF signals within the specified frequency range, balancing gain, stability, and efficiency.This is a 5W -150MHz RF amplifier circuit. It applies the MRF123 TMOSFET. The MRF123 is a very high gain FET which potentially unstable at both VHF and UHF frequencies, so the 68 Ohm input loading resistor has been used to enhance the stability. This RF amplifier has a gain of 14 dB and a drain effeciency of 55%. 🔗 External reference