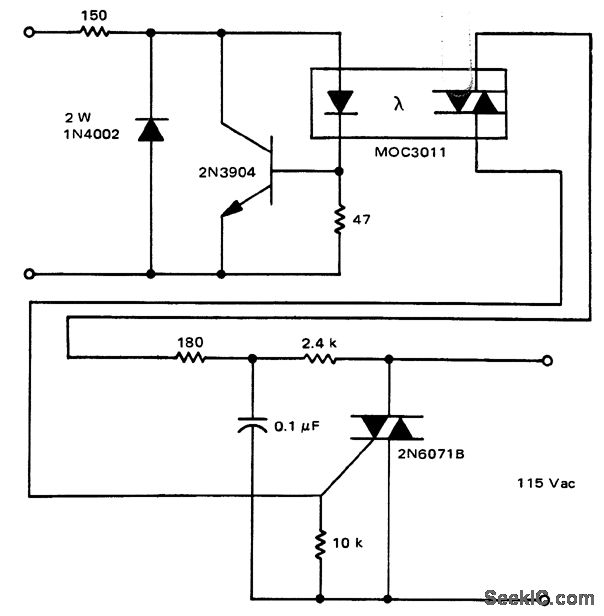
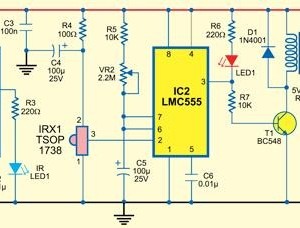
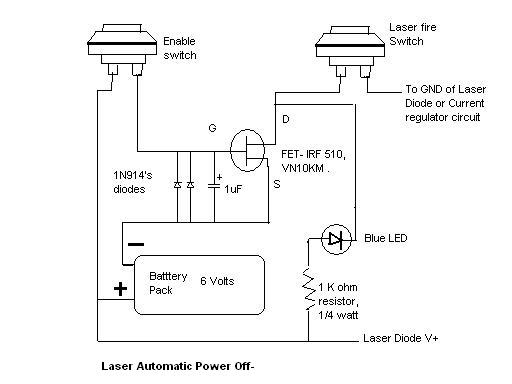
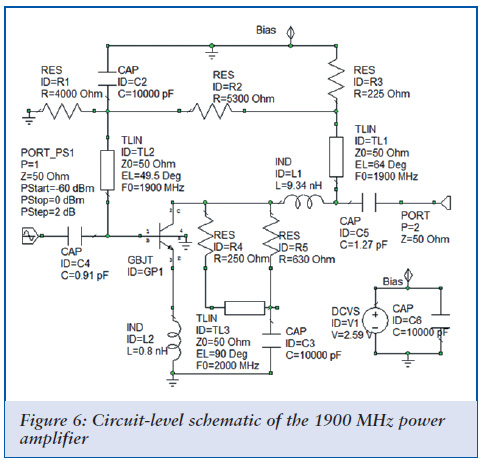
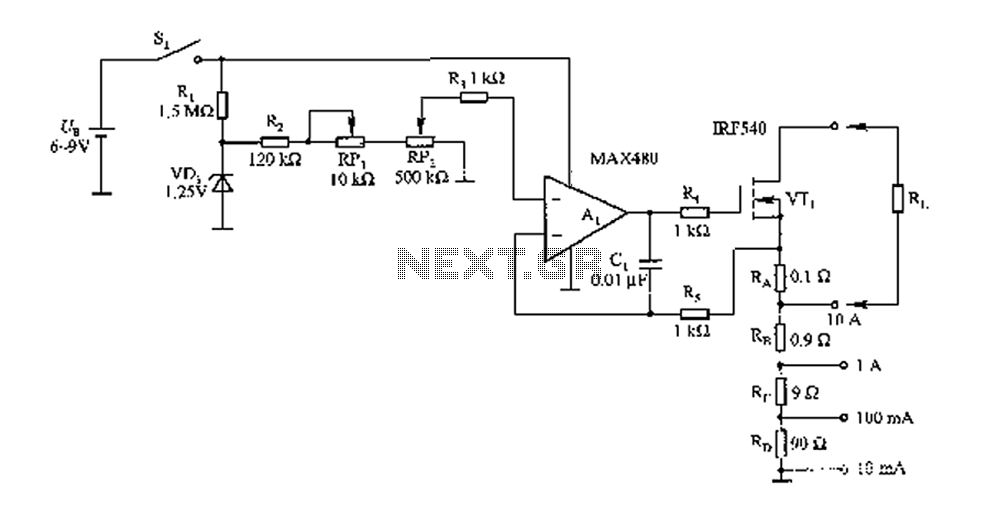
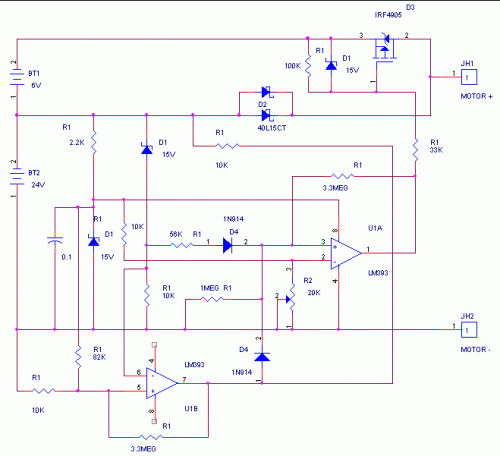
Bridge circuit
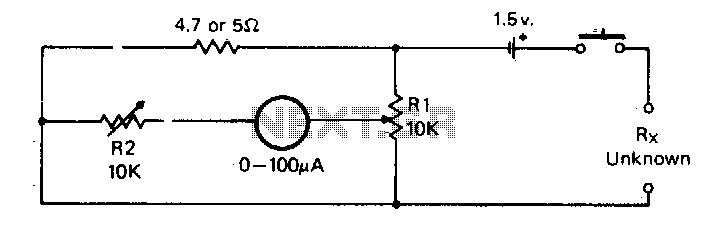
For the measurement of resistances ranging from approximately 5 ohms down to about 0.1 ohm. This circuit is highly practical.
The described circuit is designed to measure low resistances with high precision, specifically in the range from 5 ohms down to 0.1 ohm. Such measurements are crucial in various applications, including material testing, component characterization, and quality control in manufacturing processes.
The circuit typically employs a four-wire (Kelvin) measurement technique to eliminate the effects of lead and contact resistances, which can significantly influence the accuracy of low-resistance measurements. The configuration consists of two pairs of wires: one pair carries the current through the resistor under test, while the other pair measures the voltage across the resistor. This method ensures that the voltage measurement is taken directly across the resistor, thereby providing an accurate reading of its resistance.
Key components of the circuit may include a precision current source, a high-resolution voltmeter or an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for digital readings, and a microcontroller for processing the measurements and displaying results. The current source is often adjustable to allow for different measurement ranges and to ensure that the current level does not exceed the power rating of the resistor being tested.
In addition, the circuit can incorporate filtering and amplification stages to enhance measurement stability and reduce noise, which is particularly important when dealing with very low resistance values. The output can be presented in various formats, such as a digital display or transmitted to a computer for further analysis.
Overall, the design of this low-resistance measurement circuit emphasizes accuracy, stability, and ease of use, making it a valuable tool in both laboratory and industrial environments.For measurement of resistances from about 5 ohms down to about 1/10 ohm A very practical circuit.
The described circuit is designed to measure low resistances with high precision, specifically in the range from 5 ohms down to 0.1 ohm. Such measurements are crucial in various applications, including material testing, component characterization, and quality control in manufacturing processes.
The circuit typically employs a four-wire (Kelvin) measurement technique to eliminate the effects of lead and contact resistances, which can significantly influence the accuracy of low-resistance measurements. The configuration consists of two pairs of wires: one pair carries the current through the resistor under test, while the other pair measures the voltage across the resistor. This method ensures that the voltage measurement is taken directly across the resistor, thereby providing an accurate reading of its resistance.
Key components of the circuit may include a precision current source, a high-resolution voltmeter or an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for digital readings, and a microcontroller for processing the measurements and displaying results. The current source is often adjustable to allow for different measurement ranges and to ensure that the current level does not exceed the power rating of the resistor being tested.
In addition, the circuit can incorporate filtering and amplification stages to enhance measurement stability and reduce noise, which is particularly important when dealing with very low resistance values. The output can be presented in various formats, such as a digital display or transmitted to a computer for further analysis.
Overall, the design of this low-resistance measurement circuit emphasizes accuracy, stability, and ease of use, making it a valuable tool in both laboratory and industrial environments.For measurement of resistances from about 5 ohms down to about 1/10 ohm A very practical circuit.