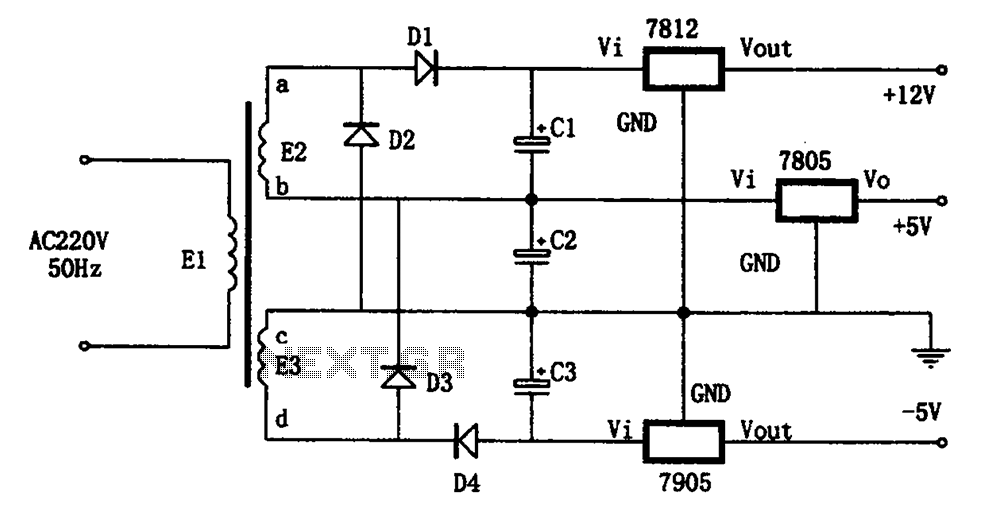
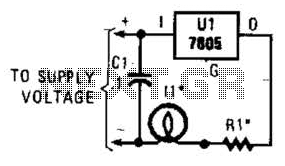
6 digits dynamic display circuit
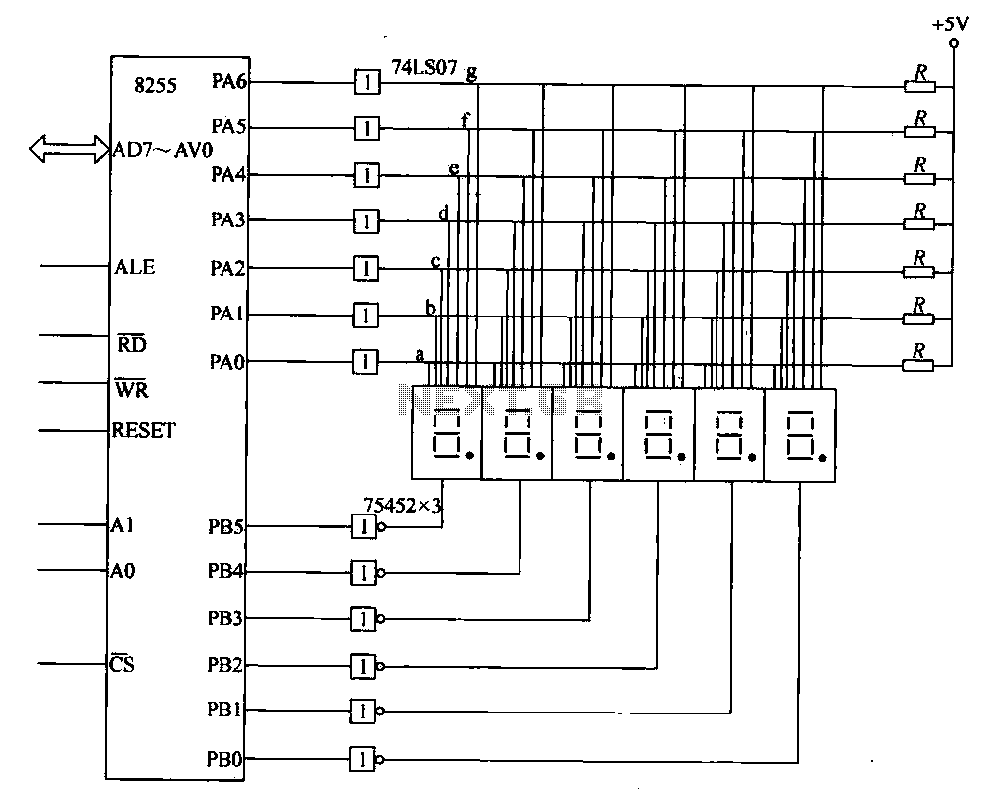
This circuit demonstrates a typical six-digit dynamic display configuration. It utilizes the PA 8255 for display output code and the PB port for bit selection code. The display buffer is designated as DISBUF, which processes the hexadecimal number obtained from the 8255 to initialize the display. The software decoding method is used to control the 7-segment display corresponding to the displayed number. The output code is sent to the display via a 74LS07 driver, which amplifies the display data across each bus. The digital display output depends on the selected bit line signal from the PB port; when the drive signal goes low, the corresponding bit will not emit a display. The display is arranged from left to right, with each digit displayed for a specific period (e.g., 1 ms). After the last digit is shown, the process repeats, creating the illusion of a simultaneous six-digit display for the human eye. The 74LS07 serves to drive the LEDs, ensuring adequate current for operation. The 8255, along with the 74LS07, provides six drives, while the 7-segment display requires two 74LS07 drivers. The PB port interfaces with a 75452 buffer/inverting driver, which acts as a bit selection signal. Each 75452 contains two internal buffers/drivers, with each buffer having two inputs. A total of three 75452 drivers are required to drive six LED displays.
The circuit employs a PA 8255, which is a programmable peripheral interface that facilitates communication between microprocessors and peripheral devices. In this configuration, it manages the output for the display while the PB port is utilized for selecting specific bits that determine which segments of the display are activated. The hexadecimal numbers processed by the PA 8255 are essential for initializing the display, allowing for dynamic control of the visual output.
The 74LS07, a high-speed buffer/driver, amplifies the signals sent to the display, ensuring that the current supplied is sufficient to illuminate the LED segments effectively. This is crucial for maintaining visibility and performance, particularly in applications where the display may be subjected to varying ambient light conditions.
The use of a 75452 buffer/inverting driver enhances the circuit's capability to manage multiple display outputs. Each 75452 can handle two inputs, and since three are required to drive the six displays, this configuration allows for efficient signal management and distribution. The bit selection process is vital for ensuring that only the intended segments of the display are activated at any given time, thereby creating a clear and coherent visual output.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a robust design for dynamic LED displays, utilizing well-established components to achieve effective results in digital representation. The method of cycling through the digits rapidly is a standard technique in multiplexing, allowing for the perception of simultaneous illumination of all six digits by the human eye.Shows - typical of six dynamic display circuit. In the figure, the PA 8255 end date display output code. PB port output bit election code. Let the display buffer is DISBUF, then complete the number (hexadecimal) to be taken after 8255 to initialize a display, using software decoding method determined to be 7-segment display control corresponding to the number displayed by the team and then port the code j output, and after 74LS07 drive to enlarge the display of data on each bus. In the end what a digital display, depending on the location of the election code. Only bit line select signal corresponding PB port after the drive goes low, the corresponding bit will not be emitting display.
If you are displayed in order from left to right, each successive digital display period of time (such as Ims), after the last digit is displayed, then repeat the process, so that the human eye can see is the 6-digit "simultaneously" display. Wherein 74LS07 to six drives, which raise the LED drive current for certain. 8255: As a 74LS07 only six drives, so the 7-segment requires two 74LS07 driving after PB port 75452 via buffer / inverting drive, 'as a bit selection signal.
A 75452 includes two internal buffers / drivers, each buffer red / driver has two inputs. Drive six LED display requires 3 75452.
The circuit employs a PA 8255, which is a programmable peripheral interface that facilitates communication between microprocessors and peripheral devices. In this configuration, it manages the output for the display while the PB port is utilized for selecting specific bits that determine which segments of the display are activated. The hexadecimal numbers processed by the PA 8255 are essential for initializing the display, allowing for dynamic control of the visual output.
The 74LS07, a high-speed buffer/driver, amplifies the signals sent to the display, ensuring that the current supplied is sufficient to illuminate the LED segments effectively. This is crucial for maintaining visibility and performance, particularly in applications where the display may be subjected to varying ambient light conditions.
The use of a 75452 buffer/inverting driver enhances the circuit's capability to manage multiple display outputs. Each 75452 can handle two inputs, and since three are required to drive the six displays, this configuration allows for efficient signal management and distribution. The bit selection process is vital for ensuring that only the intended segments of the display are activated at any given time, thereby creating a clear and coherent visual output.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a robust design for dynamic LED displays, utilizing well-established components to achieve effective results in digital representation. The method of cycling through the digits rapidly is a standard technique in multiplexing, allowing for the perception of simultaneous illumination of all six digits by the human eye.Shows - typical of six dynamic display circuit. In the figure, the PA 8255 end date display output code. PB port output bit election code. Let the display buffer is DISBUF, then complete the number (hexadecimal) to be taken after 8255 to initialize a display, using software decoding method determined to be 7-segment display control corresponding to the number displayed by the team and then port the code j output, and after 74LS07 drive to enlarge the display of data on each bus. In the end what a digital display, depending on the location of the election code. Only bit line select signal corresponding PB port after the drive goes low, the corresponding bit will not be emitting display.
If you are displayed in order from left to right, each successive digital display period of time (such as Ims), after the last digit is displayed, then repeat the process, so that the human eye can see is the 6-digit "simultaneously" display. Wherein 74LS07 to six drives, which raise the LED drive current for certain. 8255: As a 74LS07 only six drives, so the 7-segment requires two 74LS07 driving after PB port 75452 via buffer / inverting drive, 'as a bit selection signal.
A 75452 includes two internal buffers / drivers, each buffer red / driver has two inputs. Drive six LED display requires 3 75452.