60W Power Amplifier with 2N3055
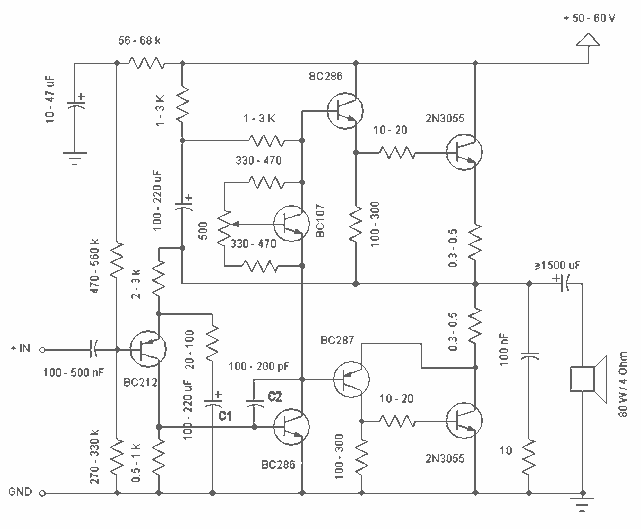
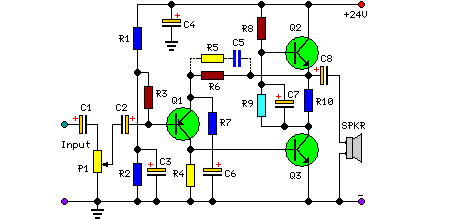
Simple and low cost. The optimal supply voltage is around 50V, but this amp works from 30 to 60V. The maximal input voltage is around 0.8 - 1V. As you can see, in this design the components have a big tolerance, so you can build it almost of the components, which you find at home. The transistors can be any NPN type power transistor, but do not use Darlington types. The output power is around 60W. More: - capacitor C1 regulates the low frequencies (bass), as the capacitance grows, the low frequencies are getting louder. - capacitor C2 regulates the higher frequencies (treble), as the capacitance grows, the higher frequencies are getting quieter.
The described circuit is a simple audio amplifier designed to deliver approximately 60 watts of output power, suitable for driving speakers in various audio applications. The amplifier operates optimally at a supply voltage of 50V, but it is versatile enough to function within a range of 30V to 60V. This flexibility allows for the use of readily available components, which can be sourced from common electronic parts.
The input stage of the amplifier accepts a maximum input voltage of around 0.8V to 1V, making it compatible with standard audio signal levels. The use of NPN power transistors is essential for the output stage, as these components provide the necessary current amplification. It is important to avoid using Darlington pairs in this design due to their higher voltage drop and slower switching times, which could adversely affect performance.
Capacitor C1 plays a critical role in shaping the low-frequency response of the amplifier. By increasing the capacitance of C1, the amplifier can enhance the bass response, allowing for a richer sound at lower frequencies. Conversely, capacitor C2 is responsible for regulating the higher frequencies. Increasing the capacitance of C2 results in a reduction of treble output, which can be useful for tuning the amplifier to suit specific audio preferences or speaker characteristics.
Overall, this design emphasizes simplicity and cost-effectiveness while maintaining sufficient performance for general audio amplification tasks. The tolerance for component selection allows hobbyists and engineers to utilize a wide variety of parts, making it an accessible project for those looking to build their own audio amplifier.Simple and low cost. The optimal supply voltage is around 50V, but this amp work from 30 to 60V. The maximal input voltage is around 0.8 - 1V. As you can see, in this design the components have a big tolerance, so you can build it almost of the components, which you find at home. The and transistors can be any NPN type power transistor, but do not use Darlington types... The output power is around 60W. - capacitor C1 regulates the low frequencies (bass), as the capacitance grows, the low frequncies are getting louder. - capacitor C2 regulates the higher frequencies (treble), as the capacitance grows, the higher frequencies are getting quiter.
- this i 🔗 External reference
The described circuit is a simple audio amplifier designed to deliver approximately 60 watts of output power, suitable for driving speakers in various audio applications. The amplifier operates optimally at a supply voltage of 50V, but it is versatile enough to function within a range of 30V to 60V. This flexibility allows for the use of readily available components, which can be sourced from common electronic parts.
The input stage of the amplifier accepts a maximum input voltage of around 0.8V to 1V, making it compatible with standard audio signal levels. The use of NPN power transistors is essential for the output stage, as these components provide the necessary current amplification. It is important to avoid using Darlington pairs in this design due to their higher voltage drop and slower switching times, which could adversely affect performance.
Capacitor C1 plays a critical role in shaping the low-frequency response of the amplifier. By increasing the capacitance of C1, the amplifier can enhance the bass response, allowing for a richer sound at lower frequencies. Conversely, capacitor C2 is responsible for regulating the higher frequencies. Increasing the capacitance of C2 results in a reduction of treble output, which can be useful for tuning the amplifier to suit specific audio preferences or speaker characteristics.
Overall, this design emphasizes simplicity and cost-effectiveness while maintaining sufficient performance for general audio amplification tasks. The tolerance for component selection allows hobbyists and engineers to utilize a wide variety of parts, making it an accessible project for those looking to build their own audio amplifier.Simple and low cost. The optimal supply voltage is around 50V, but this amp work from 30 to 60V. The maximal input voltage is around 0.8 - 1V. As you can see, in this design the components have a big tolerance, so you can build it almost of the components, which you find at home. The and transistors can be any NPN type power transistor, but do not use Darlington types... The output power is around 60W. - capacitor C1 regulates the low frequencies (bass), as the capacitance grows, the low frequncies are getting louder. - capacitor C2 regulates the higher frequencies (treble), as the capacitance grows, the higher frequencies are getting quiter.
- this i 🔗 External reference