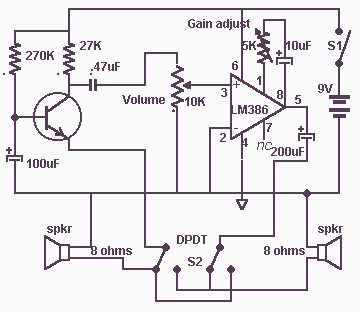
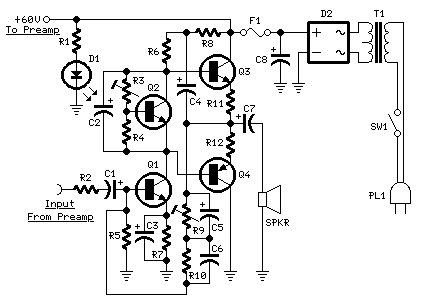
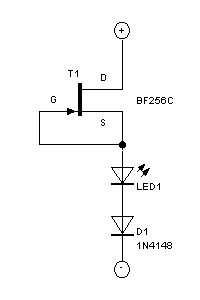
69 SFPR Schematic Telecaster Guitar
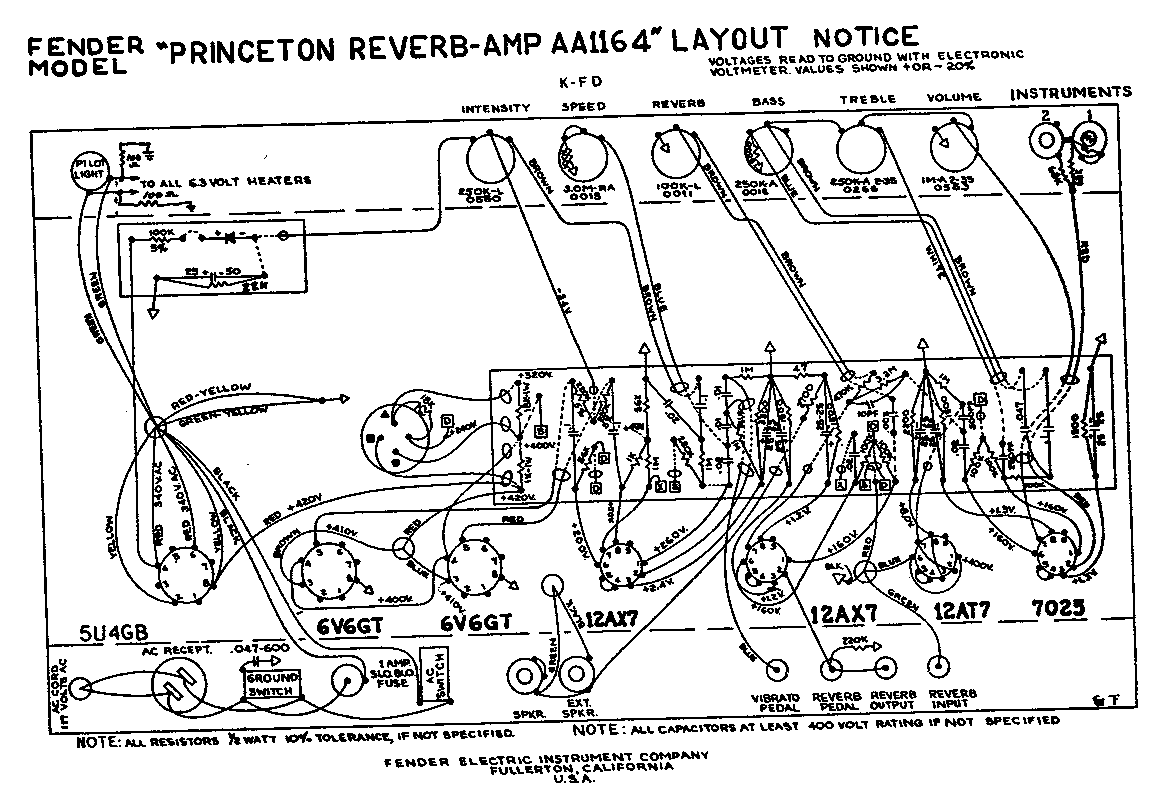
A 1969 Princeton Reverb amplifier is identified as utilizing the AA764 circuit design. Various online resources provide schematics for Fender amplifiers.
The Princeton Reverb amplifier, particularly the model from 1969, is renowned for its warm tone and versatile sound characteristics, making it a favorite among musicians. The AA764 circuit is notable for its design simplicity and effectiveness, providing a rich, clean sound with ample reverb and vibrato effects.
In the AA764 circuit, the preamp section typically consists of two 12AX7 tubes, which amplify the input signal before it reaches the tone control stage. The tone control circuit allows for adjustment of bass and treble frequencies, shaping the amplifier's overall sound profile. Following the tone control, the signal passes to the phase inverter, which prepares the signal for the power stage.
The power section of the AA764 circuit employs a pair of 6V6 power tubes, delivering a warm and dynamic output. The output transformer is designed to match the impedance of the speaker, ensuring optimal power transfer and sound quality. The reverb circuit is integrated into the design, utilizing a spring reverb tank that adds depth and ambiance to the sound.
Additionally, the amplifier features a tremolo circuit, which modulates the amplitude of the signal, creating a pulsating effect that enhances the playing experience. The overall layout of the AA764 circuit is designed for reliability and ease of maintenance, with clearly defined pathways for signal flow and power distribution.
This combination of features makes the 1969 Princeton Reverb with the AA764 circuit an enduring choice for both studio and live performances, offering a blend of classic Fender tone and modern functionality.I have a 69 Princeton Reverb which is labled as having an AA764 circuit. When perusing various web resources for Fender Amplifier Schematics.. 🔗 External reference
The Princeton Reverb amplifier, particularly the model from 1969, is renowned for its warm tone and versatile sound characteristics, making it a favorite among musicians. The AA764 circuit is notable for its design simplicity and effectiveness, providing a rich, clean sound with ample reverb and vibrato effects.
In the AA764 circuit, the preamp section typically consists of two 12AX7 tubes, which amplify the input signal before it reaches the tone control stage. The tone control circuit allows for adjustment of bass and treble frequencies, shaping the amplifier's overall sound profile. Following the tone control, the signal passes to the phase inverter, which prepares the signal for the power stage.
The power section of the AA764 circuit employs a pair of 6V6 power tubes, delivering a warm and dynamic output. The output transformer is designed to match the impedance of the speaker, ensuring optimal power transfer and sound quality. The reverb circuit is integrated into the design, utilizing a spring reverb tank that adds depth and ambiance to the sound.
Additionally, the amplifier features a tremolo circuit, which modulates the amplitude of the signal, creating a pulsating effect that enhances the playing experience. The overall layout of the AA764 circuit is designed for reliability and ease of maintenance, with clearly defined pathways for signal flow and power distribution.
This combination of features makes the 1969 Princeton Reverb with the AA764 circuit an enduring choice for both studio and live performances, offering a blend of classic Fender tone and modern functionality.I have a 69 Princeton Reverb which is labled as having an AA764 circuit. When perusing various web resources for Fender Amplifier Schematics.. 🔗 External reference