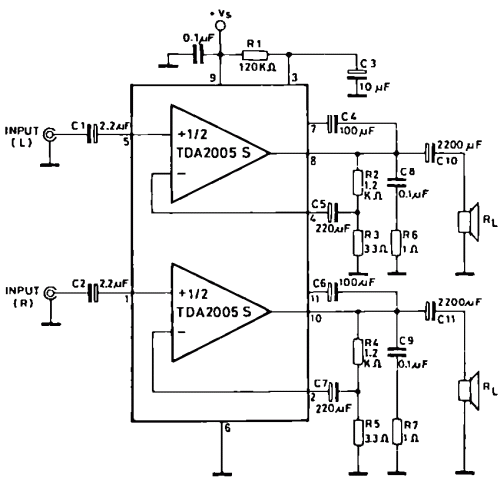
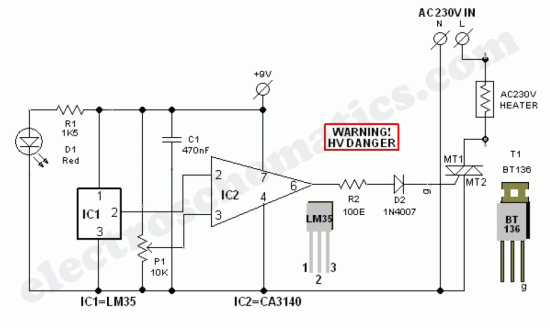
Doorphone Intercom schematic
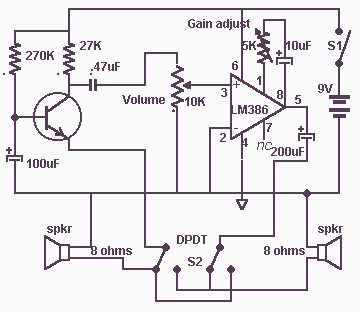
In this doorphone circuit, an 8 ohm speaker is used both as a microphone and also an output device. The BC109C stage amplifies in common base mode, giving good voltage gain, whilst providing a low impedance input to match the speaker. Self DC bias is used allowing for variations in transistor current gain. More: An LM386 is used in non-inverting mode as a power amplifier to boost voltage gain and drive the 8 ohm speaker. The 10k potentiometer acts as the volume control, and overall gain may be adjusted using the 5k preset. The double pole double throw switch, rev
The doorphone circuit operates by utilizing an 8-ohm speaker for dual functionality, serving as both a microphone and an audio output device. The circuit begins with the BC109C transistor, configured in a common base mode, which is advantageous for providing a high voltage gain while ensuring a low impedance input. This configuration is essential as it effectively matches the impedance of the 8-ohm speaker, facilitating efficient signal transfer.
The self DC biasing technique employed in the BC109C stage is designed to accommodate variations in the transistor's current gain, ensuring stable operation across different conditions. This feature is critical for maintaining consistent performance in various environmental scenarios, which may affect the transistor's characteristics.
Following the initial amplification stage, an LM386 power amplifier is integrated into the circuit in a non-inverting configuration. This component is pivotal for further boosting the voltage gain, enabling the circuit to drive the 8-ohm speaker effectively. The LM386 is known for its low power consumption and ability to deliver sufficient output power, making it suitable for battery-operated devices like doorphones.
Volume control is achieved through a 10k potentiometer, allowing users to adjust the audio output level according to their preferences. Additionally, a 5k preset resistor is included in the design to provide further adjustments to the overall gain of the circuit, facilitating fine-tuning of the audio performance.
The circuit also incorporates a double pole double throw (DPDT) switch, which serves to select between different operational modes or to engage/disengage specific components of the circuit as needed. This flexibility enhances the functionality of the doorphone, allowing it to adapt to various usage scenarios.
Overall, the design of this doorphone circuit emphasizes efficient audio processing and user control, ensuring a reliable communication solution.In this doorphone circuit,an 8 ohm speaker is used both as a microphone and also an output device. The BC109C stage amplifies in common base mode, giving good voltage gain , whilst providing a low impedance input to match the speaker. Self DC bias is used allowing for variations in transistor current gain. An LM386 is used in non-inverting mode as a power amplifier to boost voltage gain and drive the 8 ohm speaker. The 10k potentiometer acts as the volume control, and overall gain may be adjusted using the 5k preset.
The double pole double throw switch, rev 🔗 External reference
The doorphone circuit operates by utilizing an 8-ohm speaker for dual functionality, serving as both a microphone and an audio output device. The circuit begins with the BC109C transistor, configured in a common base mode, which is advantageous for providing a high voltage gain while ensuring a low impedance input. This configuration is essential as it effectively matches the impedance of the 8-ohm speaker, facilitating efficient signal transfer.
The self DC biasing technique employed in the BC109C stage is designed to accommodate variations in the transistor's current gain, ensuring stable operation across different conditions. This feature is critical for maintaining consistent performance in various environmental scenarios, which may affect the transistor's characteristics.
Following the initial amplification stage, an LM386 power amplifier is integrated into the circuit in a non-inverting configuration. This component is pivotal for further boosting the voltage gain, enabling the circuit to drive the 8-ohm speaker effectively. The LM386 is known for its low power consumption and ability to deliver sufficient output power, making it suitable for battery-operated devices like doorphones.
Volume control is achieved through a 10k potentiometer, allowing users to adjust the audio output level according to their preferences. Additionally, a 5k preset resistor is included in the design to provide further adjustments to the overall gain of the circuit, facilitating fine-tuning of the audio performance.
The circuit also incorporates a double pole double throw (DPDT) switch, which serves to select between different operational modes or to engage/disengage specific components of the circuit as needed. This flexibility enhances the functionality of the doorphone, allowing it to adapt to various usage scenarios.
Overall, the design of this doorphone circuit emphasizes efficient audio processing and user control, ensuring a reliable communication solution.In this doorphone circuit,an 8 ohm speaker is used both as a microphone and also an output device. The BC109C stage amplifies in common base mode, giving good voltage gain , whilst providing a low impedance input to match the speaker. Self DC bias is used allowing for variations in transistor current gain. An LM386 is used in non-inverting mode as a power amplifier to boost voltage gain and drive the 8 ohm speaker. The 10k potentiometer acts as the volume control, and overall gain may be adjusted using the 5k preset.
The double pole double throw switch, rev 🔗 External reference