A bean sprouts automatic watering controller consisting of 555 circuit
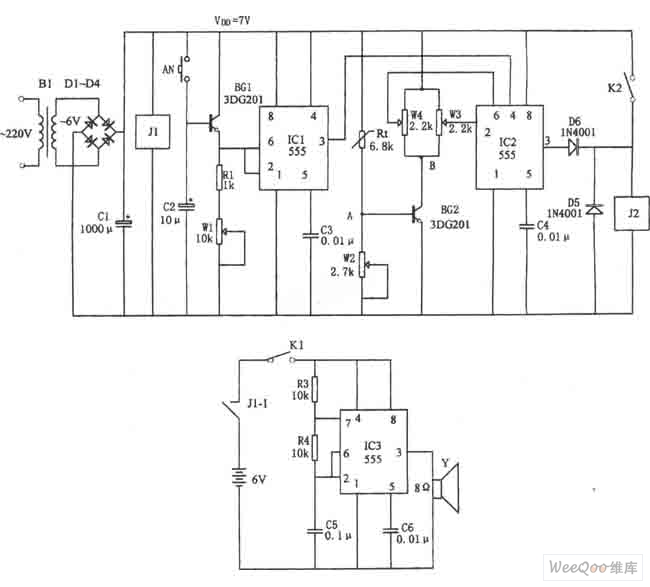
The figure illustrates the automatic watering control circuit for bean sprouts. The controller includes a step-down rectifier circuit, a power outage detection component (IC3), a timing control circuit (IC1), and a temperature control circuit (IC2). The step-down rectifier circuit supplies a DC voltage of VDD = +7 V, which powers the entire controller.
The automatic watering control circuit for bean sprouts is designed to maintain optimal growing conditions by regulating water supply based on environmental parameters. The step-down rectifier circuit converts the input AC voltage to a stable +7 V DC output, which is essential for powering the various integrated circuits within the system. This ensures that the controller operates reliably under varying input conditions.
The power outage detection circuit (IC3) plays a crucial role in monitoring the availability of power. In the event of a power failure, this component triggers an alert or initiates a backup system to ensure that the watering process is not interrupted, thereby safeguarding the bean sprouts from drought conditions.
The timing control circuit (IC1) is responsible for determining the intervals at which the watering system activates. This circuit can be programmed to water the bean sprouts at specific times or intervals, ensuring that they receive adequate moisture without overwatering, which can lead to root rot.
The temperature control circuit (IC2) monitors the ambient temperature and adjusts the watering frequency accordingly. If the temperature rises above a certain threshold, the circuit can increase the watering frequency to prevent the soil from drying out. Conversely, if the temperature drops, it may reduce the watering frequency to conserve water and prevent over-saturation.
Overall, this automatic watering control circuit is a sophisticated system that integrates multiple functionalities to create an efficient growing environment for bean sprouts. Its design emphasizes reliability, adaptability, and ease of use, making it an invaluable tool for both amateur and professional growers.Figure shows the bean sprouts automatic watering control circuit. The controller consists of step-down rectifier circuit, power outage told implement (IC3), timing control circuit (IC1), temperature control circuit(IC2) and so on. The step-down rectifier circuit is VDD = +7 V DC voltage provided by the whole controller. The power outage told implement is con.. 🔗 External reference
The automatic watering control circuit for bean sprouts is designed to maintain optimal growing conditions by regulating water supply based on environmental parameters. The step-down rectifier circuit converts the input AC voltage to a stable +7 V DC output, which is essential for powering the various integrated circuits within the system. This ensures that the controller operates reliably under varying input conditions.
The power outage detection circuit (IC3) plays a crucial role in monitoring the availability of power. In the event of a power failure, this component triggers an alert or initiates a backup system to ensure that the watering process is not interrupted, thereby safeguarding the bean sprouts from drought conditions.
The timing control circuit (IC1) is responsible for determining the intervals at which the watering system activates. This circuit can be programmed to water the bean sprouts at specific times or intervals, ensuring that they receive adequate moisture without overwatering, which can lead to root rot.
The temperature control circuit (IC2) monitors the ambient temperature and adjusts the watering frequency accordingly. If the temperature rises above a certain threshold, the circuit can increase the watering frequency to prevent the soil from drying out. Conversely, if the temperature drops, it may reduce the watering frequency to conserve water and prevent over-saturation.
Overall, this automatic watering control circuit is a sophisticated system that integrates multiple functionalities to create an efficient growing environment for bean sprouts. Its design emphasizes reliability, adaptability, and ease of use, making it an invaluable tool for both amateur and professional growers.Figure shows the bean sprouts automatic watering control circuit. The controller consists of step-down rectifier circuit, power outage told implement (IC3), timing control circuit (IC1), temperature control circuit(IC2) and so on. The step-down rectifier circuit is VDD = +7 V DC voltage provided by the whole controller. The power outage told implement is con.. 🔗 External reference