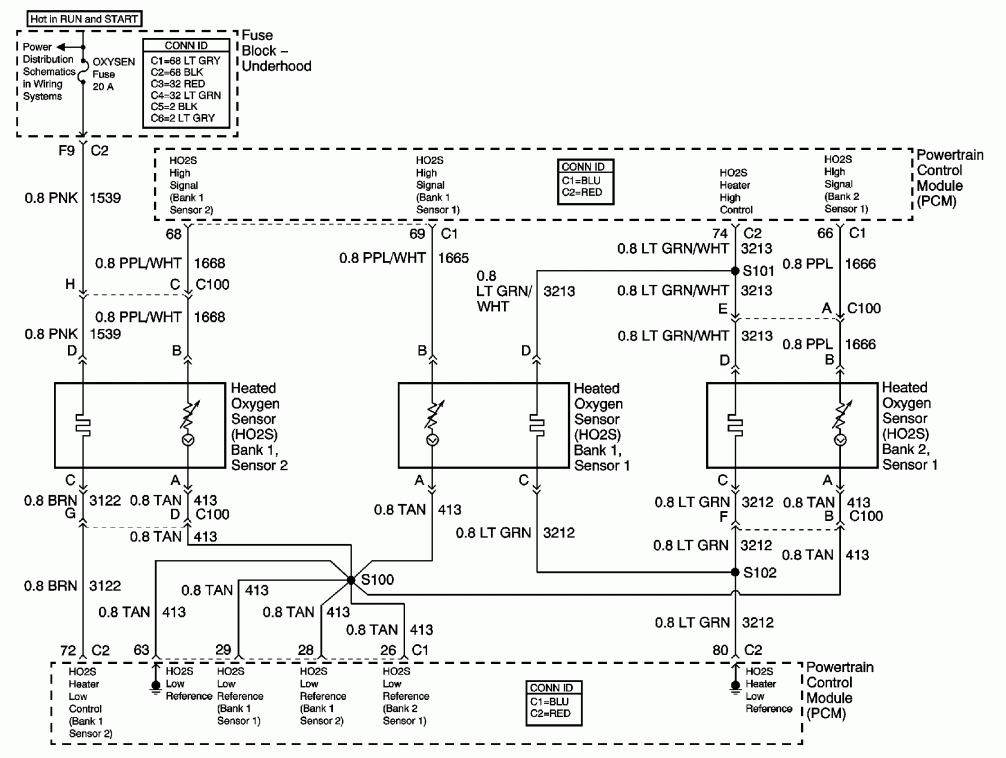
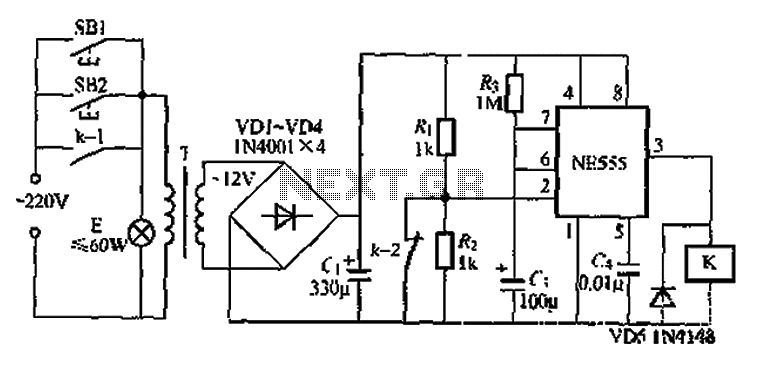
A discrete transistors from the current control circuit diagram of the way
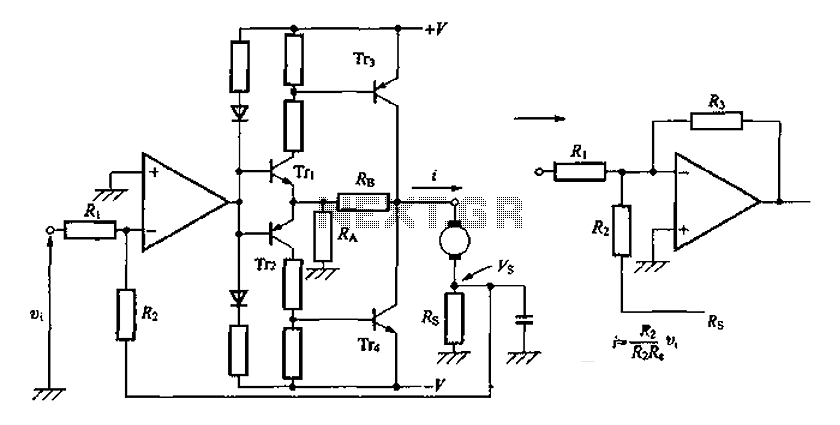
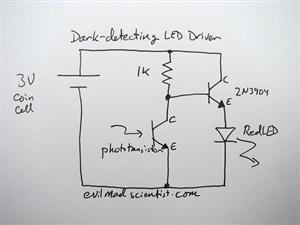
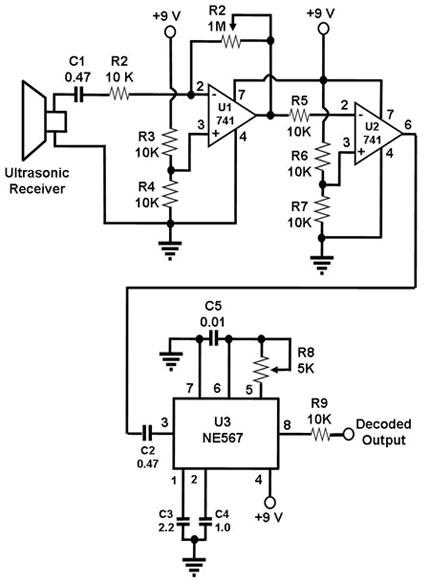
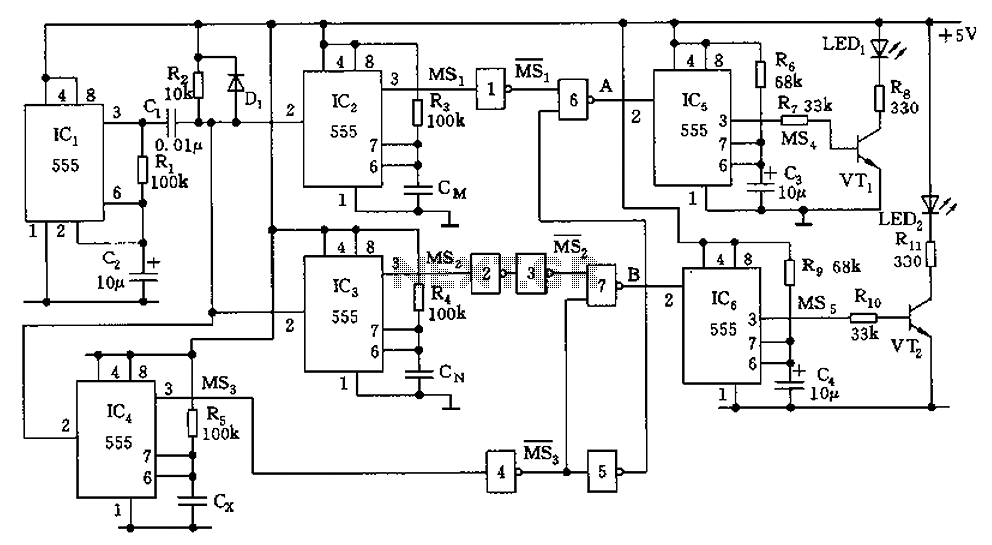
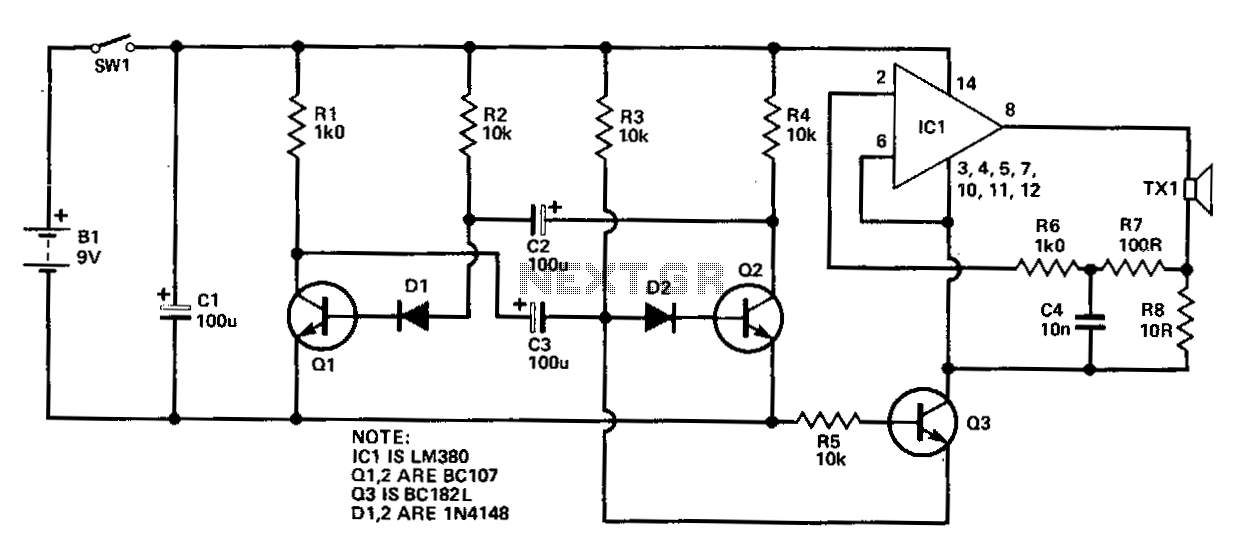
A discrete transistor current control circuit diagram.
The discrete transistor current control circuit is designed to regulate the flow of current through a load by utilizing a transistor as the primary control element. This circuit typically consists of a few key components: a power supply, a load (which could be a resistor, motor, or LED), a transistor (often a bipolar junction transistor or MOSFET), and a control mechanism, which may include a potentiometer or a fixed resistor for setting the desired current level.
In operation, the circuit begins with the power supply providing voltage to the load. The transistor acts as a switch or amplifier, allowing current to flow through the load when the base (or gate, in the case of a MOSFET) is activated by a control signal. The amount of current flowing through the load is determined by the voltage applied to the base/gate of the transistor, which adjusts the transistor's conductivity.
A feedback mechanism may also be incorporated into the circuit to enhance stability and accuracy. This can be achieved by using a resistor in series with the load to sense the current, feeding a portion of the current back to the base/gate of the transistor. This feedback loop helps maintain the desired current level despite variations in load resistance or supply voltage.
The schematic representation of this circuit typically includes the power supply voltage source, the load, the control resistor or potentiometer, the transistor symbol indicating its type, and any additional components such as capacitors for filtering or diodes for protection against reverse polarity.
Overall, this discrete transistor current control circuit is a fundamental building block in electronic design, enabling precise control of current in various applications, from simple LED drivers to complex motor control systems.A discrete transistors by the current control circuit diagram of the way
The discrete transistor current control circuit is designed to regulate the flow of current through a load by utilizing a transistor as the primary control element. This circuit typically consists of a few key components: a power supply, a load (which could be a resistor, motor, or LED), a transistor (often a bipolar junction transistor or MOSFET), and a control mechanism, which may include a potentiometer or a fixed resistor for setting the desired current level.
In operation, the circuit begins with the power supply providing voltage to the load. The transistor acts as a switch or amplifier, allowing current to flow through the load when the base (or gate, in the case of a MOSFET) is activated by a control signal. The amount of current flowing through the load is determined by the voltage applied to the base/gate of the transistor, which adjusts the transistor's conductivity.
A feedback mechanism may also be incorporated into the circuit to enhance stability and accuracy. This can be achieved by using a resistor in series with the load to sense the current, feeding a portion of the current back to the base/gate of the transistor. This feedback loop helps maintain the desired current level despite variations in load resistance or supply voltage.
The schematic representation of this circuit typically includes the power supply voltage source, the load, the control resistor or potentiometer, the transistor symbol indicating its type, and any additional components such as capacitors for filtering or diodes for protection against reverse polarity.
Overall, this discrete transistor current control circuit is a fundamental building block in electronic design, enabling precise control of current in various applications, from simple LED drivers to complex motor control systems.A discrete transistors by the current control circuit diagram of the way